Clindamycin Phosphate
Clindamycin Phosphate Prescribing Information
Clindamycin phosphate gel is indicated in the treatment of acne vulgaris. In view of the potential for diarrhea, bloody diarrhea and pseudomembranous colitis, the physician should consider whether other agents are more appropriate (see
Clindamycin phosphate gel is contraindicated in individuals with a history of hypersensitivity to preparations containing clindamycin or lincomycin, a history of regional enteritis or ulcerative colitis, or a history of antibiotic-associated colitis.
In 18 clinical studies of various formulations of clindamycin phosphate solution, gel and lotion using placebo vehicle and/or active comparator drugs as controls, patients experienced a number of treatment emergent adverse dermatologic events [see table below].
# not recorded | |||
*of 126 subjects | |||
Treatment Emergent Adverse Event | Solution n=553(%) | Gel n=148(%) | Lotion n=160(%) |
| Burning | 62 (11) | 15 (10) | 17 (11) |
| Itching | 36 (7) | 15 (10) | 17 (11) |
| Burning/Itching | 60 (11) | # ( – ) | # ( – ) |
| Dryness | 105 (19) | 34 (23) | 29 (18) |
| Erythema | 86 (16) | 10 (7) | 22 (14) |
| Oiliness/Oily Skin | 8 (1) | 26 (18) | 12* (10) |
| Peeling | 61 (11) | # ( – ) | 11 (7) |
Orally and parenterally administered clindamycin has been associated with severe colitis which may end fatally.
Cases of diarrhea, bloody diarrhea and colitis (including pseudomembranous colitis) have been reported as adverse reactions in patients treated with oral and parenteral formulations of clindamycin and rarely with topical clindamycin (see WARNINGS).
Abdominal pain, gastrointestinal disturbances, gram-negative folliculitis, eye pain and contact dermatitis have also been reported in association with the use of topical formulations of clindamycin.
Apply a thin film of clindamycin phosphate gel twice daily to affected area.
Clindamycin phosphate gel is contraindicated in individuals with a history of hypersensitivity to preparations containing clindamycin or lincomycin, a history of regional enteritis or ulcerative colitis, or a history of antibiotic-associated colitis.
In 18 clinical studies of various formulations of clindamycin phosphate solution, gel and lotion using placebo vehicle and/or active comparator drugs as controls, patients experienced a number of treatment emergent adverse dermatologic events [see table below].
# not recorded | |||
*of 126 subjects | |||
Treatment Emergent Adverse Event | Solution n=553(%) | Gel n=148(%) | Lotion n=160(%) |
| Burning | 62 (11) | 15 (10) | 17 (11) |
| Itching | 36 (7) | 15 (10) | 17 (11) |
| Burning/Itching | 60 (11) | # ( – ) | # ( – ) |
| Dryness | 105 (19) | 34 (23) | 29 (18) |
| Erythema | 86 (16) | 10 (7) | 22 (14) |
| Oiliness/Oily Skin | 8 (1) | 26 (18) | 12* (10) |
| Peeling | 61 (11) | # ( – ) | 11 (7) |
Orally and parenterally administered clindamycin has been associated with severe colitis which may end fatally.
Cases of diarrhea, bloody diarrhea and colitis (including pseudomembranous colitis) have been reported as adverse reactions in patients treated with oral and parenteral formulations of clindamycin and rarely with topical clindamycin (see
Abdominal pain, gastrointestinal disturbances, gram-negative folliculitis, eye pain and contact dermatitis have also been reported in association with the use of topical formulations of clindamycin.
Clindamycin phosphate gel USP contains clindamycin phosphate, USP, at a concentration equivalent to 10 mg clindamycin per gram.
Clindamycin phosphate is a water soluble ester of the semi-synthetic antibiotic produced by a 7(S)-chloro-substitution of the 7(R)-hydroxyl group of the parent antibiotic lincomycin.
The gel contains allantoin, carbopol 974P, methylparaben, polyethylene glycol 400, propylene glycol, sodium hydroxide, and purified water.
The structural formula is represented below:
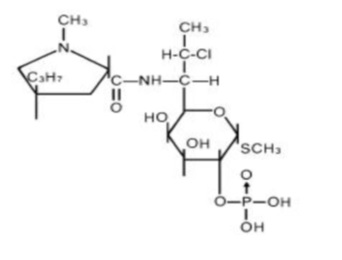
The chemical name for clindamycin phosphate is Methyl 7-chloro-6,7,8-trideoxy-6-(1-methyl-
The mechanism of action of clindamycin in treating acne vulgaris is unknown.
Following multiple topical applications of clindamycin phosphate at a concentration equivalent to 10 mg clindamycin per mL in an isopropyl alcohol and water solution, very low levels of clindamycin are present in the serum (0 to 3 ng/mL) and less than 0.2% of the dose is recovered in urine as clindamycin.
Although clindamycin phosphate is inactive
Clindamycin inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by binding to the 23S RNA of the 50S subunit of the ribosome. Clindamycin is bacteriostatic.
Clindamycin is active
Resistance to clindamycin is most often caused by modification of specific bases of the 23S ribosomal RNA. Cross-resistance between clindamycin and lincomycin is complete. Because the binding sites for these antibacterial drugs overlap, cross resistance is sometimes observed among lincosamides, macrolides and streptogramin B. Macrolide-inducible resistance to clindamycin occurs in some isolates of macrolide-resistant bacteria.