Clinimix E
(Leucine, Phenylalanine, Lysine, Methionine, Isoleucine, Valine, Histidine, Threonine, Tryptophan, Alanine, Glycine, Arginine, Proline, Serine, Tyrosine, Dibasic Potassium Phosphate, Magnesium Chloride, Sodium Chloride, Calcium Chloride, Dextrose)Clinimix E Prescribing Information
1.000000000000000e+00 Open by tearing protective overwrap at slit and remove solution container. The two port container includes an oxygen-absorbing sachet. Discard the oxygen-absorbing sachet after removal from the overwrap.2.000000000000000e+00 To proceed with activation, the container should be at room temperature. Lay the room temperature container onto a flat surface. Grasp the container firmly on each side of the top of the container (Figure 1).3.000000000000000e+00 Starting from the top, using some pressure, slowly roll the container to open seal between chambers as shown inFigure 2. Do not pull or rip the seal apart. The seal must be completely opened towards the port side of the container. The upper section of the seal towards the hanger side can remain unbroken.4.000000000000000e+00 Mix the contents thoroughly by inverting the container upside down to ensure a homogenous admixture (Figure 3).5.000000000000000e+00 Once the container is mixed, check for leaks.6.000000000000000e+00 Make additions (if prescribed).Because additives may be incompatible, evaluate all additions to the container for compatibility and stability of the resulting preparation. Consult with pharmacist, if available. Questions about compatibility may be directed to Baxter. If it is deemed advisable to introduce additives, use aseptic technique. For information on adding lipid emulsions see Dosage and Administration (2.4).a. Prepare medication port.b. Using syringe with 19 to 22 gauge needle, puncture resealable medication port and inject.c. Mix solution and medication thoroughly (Figure 3). For high density medication (high specific gravity), such as potassium chloride, squeeze ports while ports are upright and mix thoroughly.
7.000000000000000e+00 Inspect final solution for discoloration and particulate matter. Check for leaks.8.000000000000000e+00 Spike and hang container.a. Suspend container from eyelet support.b. Twist off protector from outlet port at bottom of container (Figure 4).c. Attach administration set. Refer to complete directions accompanying set.
For single dose only. Discard unused portion.
Figures 1 – 4 (Three Port Container):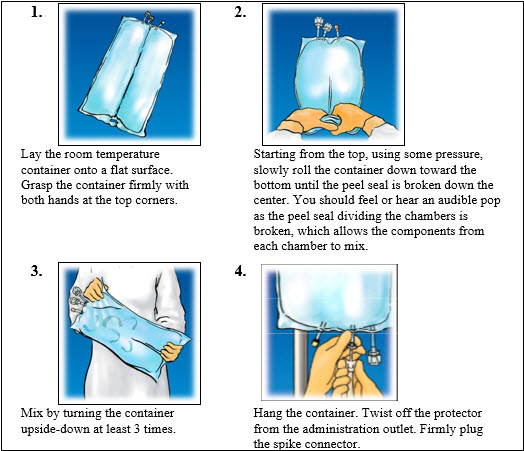 Figures 1 – 4 (Two Port Container):
Figures 1 – 4 (Two Port Container):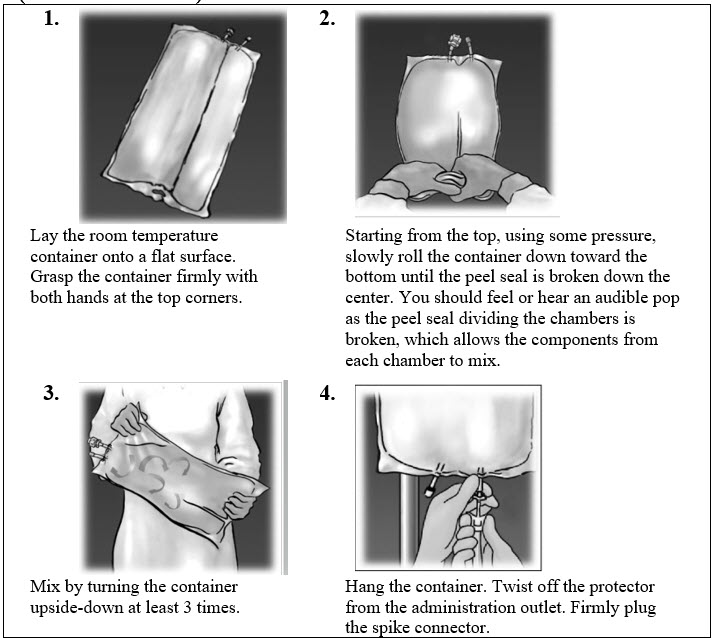 Instructions on StorageStorage After Removal of Overwrap:
Instructions on StorageStorage After Removal of Overwrap:Once removed from the protective overwrap, mixed (peel seal activated) or unmixed (peel seal intact), CLINIMIX E solutions may be stored under refrigeration for up to 9 days.
Storage Once any Additive is Added:Use promptly after mixing. Any storage with additives should be under refrigeration and limited to a brief period of time, less than 24 hours. After removal from refrigeration, use promptly and complete the infusion within 24 hours. Any remaining mixture must be discarded.
Protect the activated parenteral nutrition solution from light.
Figure 1-4 
Clinimix E Figures 1-4 - (Two Port Container) ) 04/20212.7 Dosage Modifications in Patients with Kidney DiseasePrior to administration, correct severe fluid or electrolyte imbalances. Closely monitor serum electrolyte levels and adjust the volume of CLINIMIX E administered as required
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)].Chronic kidney disease patients with less than nephrotic range proteinuria require 0.8 g of protein/kg/day. Chronic kidney disease patients with nephrotic range proteinuria require 0.8 g of protein/kg/day plus 1 g of protein for each gram of proteinuria. Patients needing dialysis should receive from 1.2 g of protein/kg/day up to a maximum of 2.5 g of protein/kg/day depending on the nutritional status and the dialysis modality. Serum electrolyte levels should be closely monitored. The CLINIMIX E dosage can be adjusted based on the severity of kidney disease, supplementing protein as indicated. If required, additional amino acids may be added to the CLINIMIX E container or infused separately. Compatibility of additions should be evaluated by a pharmacist and questions may be directed to Baxter.
Warnings and Precautions04/20215.6 Hyperglycemia or Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic StateWhen using CLINIMIX E in patients with diabetes mellitus, impaired glucose tolerance may worsen hyperglycemia. Administration of dextrose at a rate exceeding the patient’s utilization rate may lead to hyperglycemia, coma, and death. Patients with dehydration, resulting in a transient reduction in glomerular filtration rate and pre-renal azotemia, may be at greater risk of developing hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state. Monitor blood glucose levels and treat hyperglycemia to maintain optimum levels while administering CLINIMIX E. Insulin may be administered or adjusted to maintain optimal blood glucose levels during CLINIMIX E administration.
Dosage and Administration,2.1 Preparation Prior to Administration• CLINIMIX E is available in a three port container configuration and a two port container configuration.• Three Port Container:the ports consist of one medication port, one additive port and one outlet port. Additives can be introduced to the container through the medication port and lipids through the additive port on the three port container.• Two Port Container:the ports consist of one medication port and one outlet port. Additives, including lipids, can be introduced to the container through the medication port on the two port container.
• Tear protective overwrap at slit and remove solution container. Small amounts of moisture may be found on the solution container from water permeating from inside the container. The amount of permeated water is insufficient to affect the solution significantly. If larger amounts of water are found, the container should be checked for tears or leaks.• Inspect the container prior to activation. Some opacity of the plastic due to moisture absorption during the sterilization process may be observed. This is normal and does not affect the solution quality or safety. The opacity will diminish gradually. Evaluate the following:• If the outlet or additive port protectors are damaged, detached, or not present, discard container as solution path sterility may be impaired.• Check to ensure seal between chambers is intact, solutions are contained in separate chambers, and the content of the individual chambers is clear, colorless or slightly yellow. Discard if the seal is broken or if the solution is bright yellow or yellowish brown.• Check for minute leaks by separately squeezing each chamber. If external leaks or leakage between the chambers are found, discard solution as sterility or stability may be impaired.
• Lipids and/or additives can be introduced to the container after opening seal between chambers. Because additives may be incompatible, evaluate all additions to the plastic container for compatibility. Activate chambers of container prior to introduction of additives. Mix thoroughly when additives have been introduced. Supplemental medication may be added with a 19 to 22 gauge needle through the medication port.• Calcium and phosphate ratios must be considered. Excess addition of calcium and phosphate, especially in the form of mineral salts, may result in the formation of calcium phosphate precipitates[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].• Inspect the container to ensure precipitates have not formed during the mixing or addition of additives. A slight yellow color does not alter the quality and efficacy of this product. If lipid has been added, ensure the emulsion has not separated. Separation of the emulsion can be visibly identified by a yellowish streaking or the accumulation of yellowish droplets in the mixed emulsion. Discard the admixture if any of the above are observed.
,2.3 Instructions for Use1.000000000000000e+00 Open by tearing protective overwrap at slit and remove solution container. The two port container includes an oxygen-absorbing sachet. Discard the oxygen-absorbing sachet after removal from the overwrap.2.000000000000000e+00 To proceed with activation, the container should be at room temperature. Lay the room temperature container onto a flat surface. Grasp the container firmly on each side of the top of the container (Figure 1).3.000000000000000e+00 Starting from the top, using some pressure, slowly roll the container to open seal between chambers as shown inFigure 2. Do not pull or rip the seal apart. The seal must be completely opened towards the port side of the container. The upper section of the seal towards the hanger side can remain unbroken.4.000000000000000e+00 Mix the contents thoroughly by inverting the container upside down to ensure a homogenous admixture (Figure 3).5.000000000000000e+00 Once the container is mixed, check for leaks.6.000000000000000e+00 Make additions (if prescribed).Because additives may be incompatible, evaluate all additions to the container for compatibility and stability of the resulting preparation. Consult with pharmacist, if available. Questions about compatibility may be directed to Baxter. If it is deemed advisable to introduce additives, use aseptic technique. For information on adding lipid emulsions see Dosage and Administration (2.4).a. Prepare medication port.b. Using syringe with 19 to 22 gauge needle, puncture resealable medication port and inject.c. Mix solution and medication thoroughly (Figure 3). For high density medication (high specific gravity), such as potassium chloride, squeeze ports while ports are upright and mix thoroughly.
7.000000000000000e+00 Inspect final solution for discoloration and particulate matter. Check for leaks.8.000000000000000e+00 Spike and hang container.a. Suspend container from eyelet support.b. Twist off protector from outlet port at bottom of container (Figure 4).c. Attach administration set. Refer to complete directions accompanying set.
For single dose only. Discard unused portion.
Figures 1 – 4 (Three Port Container): Figures 1 – 4 (Two Port Container):
Figures 1 – 4 (Two Port Container): Instructions on StorageStorage After Removal of Overwrap:
Instructions on StorageStorage After Removal of Overwrap:Once removed from the protective overwrap, mixed (peel seal activated) or unmixed (peel seal intact), CLINIMIX E solutions may be stored under refrigeration for up to 9 days.
Storage Once any Additive is Added:Use promptly after mixing. Any storage with additives should be under refrigeration and limited to a brief period of time, less than 24 hours. After removal from refrigeration, use promptly and complete the infusion within 24 hours. Any remaining mixture must be discarded.
Protect the activated parenteral nutrition solution from light.
Figure 1-4 
Clinimix E Figures 1-4 - (Two Port Container) ,2.4 Preparation and Addition of Lipid EmulsionThree Port Container1.000000000000000e+00 Prior to adding lipid emulsion, mix amino acid and dextrose injection as shown inFigures 1-3.2.000000000000000e+00 Prepare lipid emulsion transfer set following instructions provided.3.000000000000000e+00 Attach transfer set to lipid emulsion container using aseptic technique.4.000000000000000e+00 Twist off protector on the additive port of the container.5.000000000000000e+00 Attach the transfer set to the exposed additive port.6.000000000000000e+00 Open clamp on transfer set.7.000000000000000e+00 After completing transfer, use appropriate plastic clamp or metal ferrule to seal off additive port tube.8.000000000000000e+00 Remove transfer set.9.000000000000000e+00 Mix contents of container thoroughly. Inspect final solution for discoloration and particulate matter. Check for leaks.
Two Port Container1.000000000000000e+00 Prior to adding lipid emulsion, mix amino acid and dextrose injection as shown in Figures 1-3.2.000000000000000e+00 Prepare lipid emulsion transfer set following instructions provided.3.000000000000000e+00 Attach transfer set to lipid emulsion container using aseptic technique.4.000000000000000e+00 Prepare medication port.5.000000000000000e+00 Using a 19 to 22 gauge needle, puncture resealable medication port.6.000000000000000e+00 Open clamp on transfer set and transfer lipid emulsion.7.000000000000000e+00 Remove needle.8.000000000000000e+00 Mix contents of container thoroughly. Inspect final solution for discoloration and particulate matter. Check for leaks.
Storage Once Lipids are Added:Use promptly after mixing. Any storage with additives should be under refrigeration and limited to a brief period of time, no longer than 24 hours. After removal from refrigeration, use promptly and complete the infusion within 24 hours. Any mixture remaining must be discarded.
,2.6 Recommended Dosage in AdultsThe recommended daily nutritional requirements for protein and dextrose compared to the amount of nutrition provided by CLINIMIX E are shown in Table 1. As indicated on an individual basis, maintenance vitamins, additional electrolytes, trace elements and other components (including lipids) should be administered as required to prevent deficiencies and complications from developing. The maximum infusion rates in adult patients are show in Table 2.
In addition to meeting protein needs, the administration rate should be governed, especially during the first few day of therapy, by the patient’s tolerance to dextrose. Daily intake of amino acids and dextrose should be increased gradually to the maximum required dose as indicated by frequent determinations of blood glucose levels.
Table 1: Nutritional Comparison – Adult Patients Recommended CLINIMIX E Adult DosageCLINIMIX E 2.75/5CLINIMIX E 4.25/5CLINIMIX E 4.25/10CLINIMIX E 5/15CLINIMIX E 5/20CLINIMIX E 8/10CLINIMIX E 8/14Fluid(mL/kg/day)29 to 40
19 to 40
19 to 40
16 to 40
16 to 40
10 to 25
10 to 25
ProteinProtein is provided as amino acids. When infused intravenously amino acids are metabolized and utilized as the building blocks of protein.(g/kg/day)
(Nitrogen g/kg/day)0.8 to 1.1
(0.13 to 0.18)0.8 to 1.7
(0.13 to 0.27)0.8 to 1.7
(0.13 to 0.27)0.8 to 2
(0.13 to 0.32)0.8 to 2
(0.13 to 0.32)0.8 to 2
(0.13 to 0.32)0.8 to 2
(0.13 to 0.32)Dextrose(g/kg/day)1.45 to 2
0.95 to 2
1.9 to 4
2.4 to 6
3.2 to 8
1 to 2.5
1.4 to 3.5
Table 2: Maximum Infusion Rate in Adult Patients Maximum Infusion Rates in Adults PatientsCLINIMIX E 2.75/5CLINIMIX E 4.25/5CLINIMIX E 4.25/10CLINIMIX E 5/15CLINIMIX E 5/20CLINIMIX E 8/10CLINIMIX E 8/14Maximum Infusion Rate (mL/kg/hour)3.6
2.4
2.4
1.67
1.25
1.3
1.3
Corresponding infusion rateAmino Acid (g/kg/hour)0.1Rate limiting factor
0.1
0.1
0.08
0.06
0.1
0.1
Dextrose
(g/kg/hour)0.18
0.12
0.24
0.25
0.25
0.13
0.18
09/20202.8 Recommended Dosage in Pediatric PatientsThe dosage and constant infusion rate of intravenous dextrose must be selected with caution in pediatric patients, particularly neonates and low weight infants, because of the increased risk of hyperglycemia/hypoglycemia
[see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)]. Frequent monitoring of serum glucose concentrations is required when dextrose is prescribed to pediatric patients, particularly neonates and low birth weight infants. The infusion rate and volume should be determined by the consulting physician experienced in pediatric intravenous fluid therapy.In pediatric patients, CLINIMIX E is dosed on the basis of protein provided as amino acids. The recommended dosage, by age group is provided in
Tables 3 - 6. Infusion rates are based on protein and do not take carbohydrates, fluid or electrolytes into consideration.This product does not contain the amino acids cysteine and taurine, considered conditionally essential for neonates and infants. If possible, these amino acids should be added to this product if used in this pediatric population.
Table 3: Preterm and Term Infants Less than 1 Month of Age Recommended CLINIMIX E Dosage in Preterm and Term Infants Less than 1 Month of AgeCLINIMIX E 2.75/5CLINIMIX E 4.25/5CLINIMIX E 4.25/10CLINIMIX E 5/15CLINIMIX E 5/20CLINIMIX E 8/10CLINIMIX E 8/14Infusion Rate Range(mL/kg/hr)4.5 to 6
2.9 to 3.9
2.9 to 3.9
2.5 to 3.3
2.5 to 3.3
1.6 to 2.1
1.6 to 2.1
Fluid(mL/kg/day)108 to 144
70 to 94
70 to 94
60 to 79
60 to 79
38.4 to 50
38.4 to 50
ProteinProtein is provided as amino acids. When infused intravenously amino acids are metabolized and utilized as the building blocks of protein.(g/kg/day)
(Nitrogen g/kg/day)3 to 4
(0.48 to 0.64)3 to 4
(0.48 to 0.64)3 to 4
(0.48 to 0.64)3 to 4
(0.48 to 0.64)3 to 4
(0.48 to 0.64)3 to 4
(0.48 to 0.64)3 to 4
(0.48 to 0.64)Dextrose(g/kg/day)5.4 to 7.2
3.5 to 4.7
7 to 9.4
9 to 11.9
12 to 15.8
3.8 to 5
5.4 to 7
Table 4: Pediatric Patients 1 Month to Less than 1 Year of Age Recommended CLINIMIX E Dosage in Pediatric Patients 1 Month to Less than 1 Year of AgeCLINIMIX E 2.75/5CLINIMIX E 4.25/5CLINIMIX E 4.25/10CLINIMIX E 5/15CLINIMIX E 5/20CLINIMIX E 8/10CLINIMIX E 8/14Infusion Rate Range(mL/kg/hr)3 to 4.5
2 to 2.9
2 to 2.9
1.7 to 2.5
1.7 to 2.5
1 to 1.6
1 to 1.6
Fluid(mL/kg/day)72 to 108
48 to 70
48 to 70
41 to 60
41 to 60
24 to 38.4
24 to 38.4
ProteinProtein is provided as amino acids. When infused intravenously amino acids are metabolized and utilized as the building blocks of protein.(g/kg/day)
(Nitrogen g/kg/day)2 to 3
(0.32 to 0.48)2 to 3
(0.32 to 0.48)2 to 3
(0.32 to 0.48)2 to 3
(0.32 to 0.48)2 to 3
(0.32 to 0.48)2 to 3
(0.32 to 0.48)2 to 3
(0.32 to 0.48)Dextrose(g/kg/day)3.6 to 5.4
2.4 to 3.5
4.8 to 7
6.1 to 9
8.2 to 12
2.4 to 3.8
3.4 to 5.4
Table 5: Pediatric Patients 1 Year to Less than 11 Years of Age Recommended CLINIMIX E Dosage in Pediatric Patients 1 Year to Less than 11 Years of AgeCLINIMIX E 2.75/5CLINIMIX E 4.25/5CLINIMIX E 4.25/10CLINIMIX E 5/15CLINIMIX E 5/20CLINIMIX E 8/10CLINIMIX E 8/14Infusion Rate Range(mL/kg/hr)1.5 to 3
1 to 2
1 to 2
0.8 to 1.7
0.8 to 1.7
0.5 to 1
0.5 to 1
Fluid(mL/kg/day)36 to 72
24 to 48
24 to 48
19 to 41
19 to 41
12 to 24
12 to 24
ProteinProtein is provided as amino acids. When infused intravenously amino acids are metabolized and utilized as the building blocks of protein.(g/kg/day)
(Nitrogen g/kg/day)1 to 2
(0.16 to 0.32)1 to 2
(0.16 to 0.32)1 to 2
(0.16 to 0.32)1 to 2
(0.16 to 0.32)1 to 2
(0.16 to 0.32)1 to 2
(0.16 to 0.32)1 to 2
(0.16 to 0.32)Dextrose(g/kg/day)1.8 to 3.6
1.2 to 2.4
2.4 to 4.8
2.9 to 6.1
3.8 to 8.2
1.2 to 2.4
1.7 to 3.4
Table 6: Pediatric Patients 11 Years to 17 Years of Age Recommended CLINIMIX E Dosage in Pediatric Patients 11 Years to 17 Years of AgeCLINIMIX E 2.75/5CLINIMIX E 4.25/5CLINIMIX E 4.25/10CLINIMIX E 5/15CLINIMIX E 5/20CLINIMIX E 8/10CLINIMIX E 8/14Infusion Rate Range(mL/kg/hr)1.2 to 2.3
0.8 to 1.5
0.8 to 1.5
0.7 to 1.3
0.7 to 1.3
0.4 to 0.8
0.4 to 0.8
Fluid(mL/kg/day)29 to 55
19 to 36
19 to 36
17 to 31
17 to 31
9.6 to 19.2
9.6 to 19.2
ProteinProtein is provided as amino acids. When infused intravenously amino acids are metabolized and utilized as the building blocks of protein.(g/kg/day)
(Nitrogen g/kg/day)0.8 to 1.5
(0.13 to 0.24)0.8 to 1.5
(0.13 to 0.24)0.8 to 1.5
(0.13 to 0.24)0.8 to 1.5
(0.13 to 0.24)0.8 to 1.5
(0.13 to 0.24)0.8 to 1.5
(0.13 to 0.24)0.8 to 1.5
(0.13 to 0.24)Dextrose(g/kg/day)1.4 to 2.8
1 to 1.8
1.9 to 3.6
2.5 to 4.7
3.4 to 6.2
1 to 1.9
1.4 to 2.7
CLINIMIX E is indicated as a source of calories, protein, and electrolytes for patients requiring parenteral nutrition when oral or enteral nutrition is not possible, insufficient, or contraindicated. CLINIMIX E may be used to treat negative nitrogen balance in patients.
See full prescribing information for information on preparation, administration, instructions for use, dosing considerations, including the recommended dosage in adults and pediatrics, and dosage modifications in patients with kidney disease. (
• CLINIMIX E is available in a three port container configuration and a two port container configuration.• Three Port Container:the ports consist of one medication port, one additive port and one outlet port. Additives can be introduced to the container through the medication port and lipids through the additive port on the three port container.• Two Port Container:the ports consist of one medication port and one outlet port. Additives, including lipids, can be introduced to the container through the medication port on the two port container.
• Tear protective overwrap at slit and remove solution container. Small amounts of moisture may be found on the solution container from water permeating from inside the container. The amount of permeated water is insufficient to affect the solution significantly. If larger amounts of water are found, the container should be checked for tears or leaks.• Inspect the container prior to activation. Some opacity of the plastic due to moisture absorption during the sterilization process may be observed. This is normal and does not affect the solution quality or safety. The opacity will diminish gradually. Evaluate the following:• If the outlet or additive port protectors are damaged, detached, or not present, discard container as solution path sterility may be impaired.• Check to ensure seal between chambers is intact, solutions are contained in separate chambers, and the content of the individual chambers is clear, colorless or slightly yellow. Discard if the seal is broken or if the solution is bright yellow or yellowish brown.• Check for minute leaks by separately squeezing each chamber. If external leaks or leakage between the chambers are found, discard solution as sterility or stability may be impaired.
• Lipids and/or additives can be introduced to the container after opening seal between chambers. Because additives may be incompatible, evaluate all additions to the plastic container for compatibility. Activate chambers of container prior to introduction of additives. Mix thoroughly when additives have been introduced. Supplemental medication may be added with a 19 to 22 gauge needle through the medication port.• Calcium and phosphate ratios must be considered. Excess addition of calcium and phosphate, especially in the form of mineral salts, may result in the formation of calcium phosphate precipitates[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].• Inspect the container to ensure precipitates have not formed during the mixing or addition of additives. A slight yellow color does not alter the quality and efficacy of this product. If lipid has been added, ensure the emulsion has not separated. Separation of the emulsion can be visibly identified by a yellowish streaking or the accumulation of yellowish droplets in the mixed emulsion. Discard the admixture if any of the above are observed.
• Set the vent to the closed position on a vented intravenous administration set to prevent air embolism.• Use a dedicated line without any connections to avoid air embolism.• CLINIMIX E is for intravenous infusion only into a central or peripheral vein. The choice of a central or peripheral venous route should depend on the osmolarity of the final infusate. Solutions with osmolarity of 900 mOsm/L or greater must be infused through a central catheter[see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].• For central vein infusion only: CLINIMIX E 4.25/10, 5/15, 5/20, 8/10, 8/14• For central or peripheral vein infusion: CLINIMIX E 2.75/5 and 4.25/5
• The solution should be inspected for precipitates before admixing, after admixing, and again before administration.• Use a 0.22 micron filter for administration of CLINIMIX E. If a lipid is also administered, use a 1.2 micron filter.• If lipid emulsion is added, do not use administration sets and lines that contain di-2-ethylhexyl phthalate (DEHP). Administration sets that contain polyvinyl chloride (PVC) components have DEHP as a plasticizer.• Ceftriaxone must not be administered simultaneously with calcium-containing intravenous solutions such as CLINIMIX E via a Y-site. However, in patients other than neonates, ceftriaxone and CLINIMIX E may be administered sequentially if the infusion lines are thoroughly flushed between infusions with a compatible fluid[see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
1.000000000000000e+00 Open by tearing protective overwrap at slit and remove solution container. The two port container includes an oxygen-absorbing sachet. Discard the oxygen-absorbing sachet after removal from the overwrap.2.000000000000000e+00 To proceed with activation, the container should be at room temperature. Lay the room temperature container onto a flat surface. Grasp the container firmly on each side of the top of the container (Figure 1).3.000000000000000e+00 Starting from the top, using some pressure, slowly roll the container to open seal between chambers as shown inFigure 2. Do not pull or rip the seal apart. The seal must be completely opened towards the port side of the container. The upper section of the seal towards the hanger side can remain unbroken.4.000000000000000e+00 Mix the contents thoroughly by inverting the container upside down to ensure a homogenous admixture (Figure 3).5.000000000000000e+00 Once the container is mixed, check for leaks.6.000000000000000e+00 Make additions (if prescribed).Because additives may be incompatible, evaluate all additions to the container for compatibility and stability of the resulting preparation. Consult with pharmacist, if available. Questions about compatibility may be directed to Baxter. If it is deemed advisable to introduce additives, use aseptic technique. For information on adding lipid emulsions see Dosage and Administration (2.4).a. Prepare medication port.b. Using syringe with 19 to 22 gauge needle, puncture resealable medication port and inject.c. Mix solution and medication thoroughly (Figure 3). For high density medication (high specific gravity), such as potassium chloride, squeeze ports while ports are upright and mix thoroughly.
7.000000000000000e+00 Inspect final solution for discoloration and particulate matter. Check for leaks.8.000000000000000e+00 Spike and hang container.a. Suspend container from eyelet support.b. Twist off protector from outlet port at bottom of container (Figure 4).c. Attach administration set. Refer to complete directions accompanying set.
For single dose only. Discard unused portion.


Once removed from the protective overwrap, mixed (peel seal activated) or unmixed (peel seal intact), CLINIMIX E solutions may be stored under refrigeration for up to 9 days.
Use promptly after mixing. Any storage with additives should be under refrigeration and limited to a brief period of time, less than 24 hours. After removal from refrigeration, use promptly and complete the infusion within 24 hours. Any remaining mixture must be discarded.


CLINIMIX E injection is available in 1000 mL and 2000 mL dual chamber containers. The individual chambers contain essential and nonessential amino acids with electrolytes and dextrose with calcium.
Strength of CLINIMIX E | CLINIMIX E | CLINIMIX E | CLINIMIX E | CLINIMIX E | CLINIMIX | CLINIMIX E | CLINIMIX E | |
Dextrose Hydrous, USP (g/100 mL) | 5 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 10 | 14 | |
Amino Acids (g/100 mL) | 2.75 | 4.25 | 4.25 | 5 | 5 | 8 | 8 | |
Total Nitrogen (mg/100 mL) | 454 | 702 | 702 | 826 | 826 | 1320 | 1320 | |
| Leucine | 201 | 311 | 311 | 365 | 365 | 584 | 584 |
Isoleucine | 165 | 255 | 255 | 300 | 300 | 480 | 480 | |
Valine | 160 | 247 | 247 | 290 | 290 | 464 | 464 | |
Lysine (added as the hydrochloride salt) | 159 | 247 | 247 | 290 | 290 | 464 | 464 | |
Phenylalanine | 154 | 238 | 238 | 280 | 280 | 448 | 448 | |
Histidine | 132 | 204 | 204 | 240 | 240 | 384 | 384 | |
Threonine | 116 | 179 | 179 | 210 | 210 | 336 | 336 | |
Methionine | 110 | 170 | 170 | 200 | 200 | 320 | 320 | |
Tryptophan | 50 | 77 | 77 | 90 | 90 | 144 | 144 | |
| Alanine | 570 | 880 | 880 | 1035 | 1035 | 1656 | 1656 |
Arginine | 316 | 489 | 489 | 575 | 575 | 920 | 920 | |
Glycine | 283 | 438 | 438 | 515 | 515 | 824 | 824 | |
Proline | 187 | 289 | 289 | 340 | 340 | 544 | 544 | |
Serine | 138 | 213 | 213 | 250 | 250 | 400 | 400 | |
Tyrosine | 11 | 17 | 17 | 20 | 20 | 32 | 32 | |
| Sodium Acetate Trihydrate, USP | 217 | 297 | 297 | 340 | 340 | 0 | 0 |
Dibasic Potassium Phosphate, USP | 261 | 261 | 261 | 261 | 261 | 261 | 261 | |
Sodium Chloride, USP | 112 | 77 | 77 | 59 | 59 | 205 | 205 | |
Magnesium Chloride, USP | 51 | 51 | 51 | 51 | 51 | 51 | 51 | |
Calcium Chloride Dihydrate, USP | 33 | 33 | 33 | 33 | 33 | 33 | 33 | |
Electrolyte Profile Balanced by ions from amino acids.(mEq/L) | Sodium | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 |
Potassium | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | |
Magnesium | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | |
Calcium | 4.5 | 4.5 | 4.5 | 4.5 | 4.5 | 4.5 | 4.5 | |
AcetateDerived from glacial acetic acid (for pH adjustment) and sodium acetate. | 51 | 70 | 70 | 80 | 80 | 83 | 83 | |
ChlorideContributed by calcium chloride, lysine hydrochloride, magnesium chloride, sodium chloride, and hydrochloric acid. | 39 | 39 | 39 | 39 | 39 | 76 | 76 | |
Phosphate (as HPO4=) | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | |
pHpH of sulfite-free amino acid injection with electrolytes in the outlet port chamber was adjusted with glacial acetic acid and pH of dextrose injection port chamber was adjusted with hydrochloric acid.(Range) | 6.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | |
Osmolarity (mOsmol/L) (calc) | 665 | 815 | 1070 | 1395 | 1650 | 1450 | 1650 | |
Caloric Content (kcal/L) | From Dextrose | 170 | 170 | 340 | 510 | 680 | 343 | 477 |
From Amino Acids | 110 | 170 | 170 | 200 | 200 | 320 | 320 | |
TOTAL (Dextrose and Amino Acids) | 280 | 340 | 510 | 710 | 880 | 663 | 797 | |
Strength of CLINIMIX E | CLINIMIX E | CLINIMIX E | CLINIMIX E | CLINIMIX E | CLINIMIX | CLINIMIX E | CLINIMIX E | |
Dextrose Hydrous, USP (g/100 mL) | 5 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 10 | 14 | |
Amino Acids (g/100 mL) | 2.75 | 4.25 | 4.25 | 5 | 5 | 8 | 8 | |
Total Nitrogen (mg/100 mL) | 454 | 702 | 702 | 826 | 826 | 1320 | 1320 | |
| Leucine | 201 | 311 | 311 | 365 | 365 | 584 | 584 |
Isoleucine | 165 | 255 | 255 | 300 | 300 | 480 | 480 | |
Valine | 160 | 247 | 247 | 290 | 290 | 464 | 464 | |
Lysine (added as the hydrochloride salt) | 159 | 247 | 247 | 290 | 290 | 464 | 464 | |
Phenylalanine | 154 | 238 | 238 | 280 | 280 | 448 | 448 | |
Histidine | 132 | 204 | 204 | 240 | 240 | 384 | 384 | |
Threonine | 116 | 179 | 179 | 210 | 210 | 336 | 336 | |
Methionine | 110 | 170 | 170 | 200 | 200 | 320 | 320 | |
Tryptophan | 50 | 77 | 77 | 90 | 90 | 144 | 144 | |
| Alanine | 570 | 880 | 880 | 1035 | 1035 | 1656 | 1656 |
Arginine | 316 | 489 | 489 | 575 | 575 | 920 | 920 | |
Glycine | 283 | 438 | 438 | 515 | 515 | 824 | 824 | |
Proline | 187 | 289 | 289 | 340 | 340 | 544 | 544 | |
Serine | 138 | 213 | 213 | 250 | 250 | 400 | 400 | |
Tyrosine | 11 | 17 | 17 | 20 | 20 | 32 | 32 | |
| Sodium Acetate Trihydrate, USP | 217 | 297 | 297 | 340 | 340 | 0 | 0 |
Dibasic Potassium Phosphate, USP | 261 | 261 | 261 | 261 | 261 | 261 | 261 | |
Sodium Chloride, USP | 112 | 77 | 77 | 59 | 59 | 205 | 205 | |
Magnesium Chloride, USP | 51 | 51 | 51 | 51 | 51 | 51 | 51 | |
Calcium Chloride Dihydrate, USP | 33 | 33 | 33 | 33 | 33 | 33 | 33 | |
Electrolyte Profile Balanced by ions from amino acids.(mEq/L) | Sodium | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 |
Potassium | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | |
Magnesium | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | |
Calcium | 4.5 | 4.5 | 4.5 | 4.5 | 4.5 | 4.5 | 4.5 | |
AcetateDerived from glacial acetic acid (for pH adjustment) and sodium acetate. | 51 | 70 | 70 | 80 | 80 | 83 | 83 | |
ChlorideContributed by calcium chloride, lysine hydrochloride, magnesium chloride, sodium chloride, and hydrochloric acid. | 39 | 39 | 39 | 39 | 39 | 76 | 76 | |
Phosphate (as HPO4=) | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | |
pHpH of sulfite-free amino acid injection with electrolytes in the outlet port chamber was adjusted with glacial acetic acid and pH of dextrose injection port chamber was adjusted with hydrochloric acid. (Range) | 6.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | |
Osmolarity (mOsmol/L) (calc) | 665 | 815 | 1070 | 1395 | 1650 | 1450 | 1650 | |
Caloric Content (kcal/L) | From Dextrose | 170 | 170 | 340 | 510 | 680 | 343 | 477 |
From Amino Acids | 110 | 170 | 170 | 200 | 200 | 320 | 320 | |
TOTAL (Dextrose and Amino Acids) | 280 | 340 | 510 | 710 | 880 | 663 | 797 | |
- Pediatric Use:increased risk of hypoglycemia/hyperglycemia: monitor serum glucose concentrations. ()
8.4 Pediatric UseSafety and effectiveness of CLINIMIX E in pediatric patients have not been established by adequate and well-controlled studies. Use of dextrose, amino acid infusions and electrolytes in pediatric patients is based on clinical practice
[see Dosage and Administration (2.8)].Deaths have occurred in neonates (28 days of age or younger) who received concomitant intravenous calcium-containing solutions with ceftriaxone resulting from calcium-ceftriaxone precipitates in the lungs and kidneys, even when separate infusion lines were used. CLINIMIX E is contraindicated in neonates receiving ceftriaxone
[see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].Newborns, especially those born premature and with low birth weight, are at increased risk of developing hypo – or hyperglycemia and therefore need close monitoring during treatment with intravenous glucose solutions to ensure adequate glycemic control in order to avoid potential long term adverse effects. Hypoglycemia in the newborn can cause prolonged seizures, coma and brain damage. Hyperglycemia has been associated with intraventricular hemorrhage, late onset bacterial and fungal infection, retinopathy of prematurity, necrotizing enterocolitis, bronchopulmonary dysplasia, prolonged length of hospital stay, and death. Plasma electrolyte concentrations should be closely monitored in the pediatric population as this population may have impaired ability to regulate fluids and electrolytes.
Because of immature renal function, preterm infants receiving prolonged treatment with CLINIMIX E, may be at risk of aluminum toxicity
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].Patients, including pediatric patients, may be at risk for Parenteral Nutrition Associated Liver Disease (PNALD)
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].Hyperammonemia is of special significance in infants (birth to two years). This reaction appears to be related to a deficiency of the urea cycle amino acids of genetic or product origin. It is essential that blood ammonia be measured frequently in infants
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
1. Neonates (28 days of age or younger) receiving concomitant treatment with ceftriaxone, even if separate infusion lines are used, due to the risk of fatal ceftriaxone calcium salt precipitation in the neonate’s bloodstream[see.,5.2 Precipitation with CeftriaxonePrecipitation of ceftriaxone-calcium can occur when ceftriaxone is mixed with calcium-containing parenteral nutrition solutions, such as CLINIMIX E, in the same intravenous administration line. Do not administer ceftriaxone simultaneously with CLINIMIX E via a Y-site.
Deaths have occurred in neonates (less than 28 days of age) who received concomitant intravenous calcium-containing solutions with ceftriaxone resulting from calcium-ceftriaxone precipitates in the lungs and kidneys, even when separate infusion lines were used. CLINIMIX E is contraindicated in neonates receiving ceftriaxone
[see Contraindications (4), Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].In patients older than 28 days (including adults), ceftriaxone and CLINIMIX E may be administered sequentially if the infusion lines are thoroughly flushed between infusions with a compatible fluid
.]8.4 Pediatric UseSafety and effectiveness of CLINIMIX E in pediatric patients have not been established by adequate and well-controlled studies. Use of dextrose, amino acid infusions and electrolytes in pediatric patients is based on clinical practice
[see Dosage and Administration (2.8)].Deaths have occurred in neonates (28 days of age or younger) who received concomitant intravenous calcium-containing solutions with ceftriaxone resulting from calcium-ceftriaxone precipitates in the lungs and kidneys, even when separate infusion lines were used. CLINIMIX E is contraindicated in neonates receiving ceftriaxone
[see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].Newborns, especially those born premature and with low birth weight, are at increased risk of developing hypo – or hyperglycemia and therefore need close monitoring during treatment with intravenous glucose solutions to ensure adequate glycemic control in order to avoid potential long term adverse effects. Hypoglycemia in the newborn can cause prolonged seizures, coma and brain damage. Hyperglycemia has been associated with intraventricular hemorrhage, late onset bacterial and fungal infection, retinopathy of prematurity, necrotizing enterocolitis, bronchopulmonary dysplasia, prolonged length of hospital stay, and death. Plasma electrolyte concentrations should be closely monitored in the pediatric population as this population may have impaired ability to regulate fluids and electrolytes.
Because of immature renal function, preterm infants receiving prolonged treatment with CLINIMIX E, may be at risk of aluminum toxicity
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].Patients, including pediatric patients, may be at risk for Parenteral Nutrition Associated Liver Disease (PNALD)
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].Hyperammonemia is of special significance in infants (birth to two years). This reaction appears to be related to a deficiency of the urea cycle amino acids of genetic or product origin. It is essential that blood ammonia be measured frequently in infants
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].2. Patients with known hypersensitivity to one or more amino acids or dextrose[see.]5.3 Hypersensitivity ReactionsHypersensitivity/infusion reactions including anaphylaxis have been reported with CLINIMIX E. Stop infusion immediately and treat patient accordingly if any signs or symptoms of a hypersensitivity reaction develop. Signs or symptoms may include: hypotension, hypertension, peripheral cyanosis, tachycardia, dyspnea, vomiting, nausea, urticaria, rash, pruritus, erythema, hyperhidrosis, pyrexia, and chills.
3. Patients with inborn errors of amino acid metabolism due to risk of severe metabolic and neurologic complications.4. Patients with pulmonary edema or acidosis due to low cardiac output.