Colesevelam Hydrochloride
Colesevelam Hydrochloride Prescribing Information
Tablets: 625 mg tablets are off-white to light yellow, capsule shaped coated tablets imprinted with “083” in black ink on one side and plain on other side and free from physical defects.
Colesevelam hydrochloride is contraindicated in patients with:
• Serum TG concentrations >500 mg/dL
Colesevelam hydrochloride, like other bile acid sequestrants, can increase serum TG concentrations.
Hypertriglyceridemia can cause acute pancreatitis.
Colesevelam hydrochloride had effects on serum TG (median increase 5% compared to placebo) in trials of patients with primary hyperlipidemia.
In trials in patients with type 2 diabetes, greater increases in TG levels occurred when colesevelam hydrochloride was used as monotherapy (median increase 9.7% compared to placebo) and when colesevelam hydrochloride was used in combination with pioglitazone (median increase 11% compared to placebo in combination with pioglitazone), sulfonylureas (median increase 18% compared to placebo in combination with sulfonylureas), and insulin (median increase 22% compared to placebo in combination with insulin)
Obtain lipid parameters, including TG levels, before starting colesevelam hydrochloride and periodically thereafter. Colesevelam hydrochloride is contraindicated in patients with TG levels >500 mg/dL or patients with a history of hypertriglyceridemia-induced pancreatitis [see Contraindications (4)]. Patients with TG levels greater than 300 mg/dL could have greater increases in serum TG levels with colesevelam hydrochloride and may require additional TG monitoring. Instruct patients to discontinue colesevelam hydrochloride and seek prompt medical attention if the symptoms of acute pancreatitis occur (e.g., severe abdominal pain with or without nausea and vomiting). Discontinue colesevelam hydrochloride if TG levels exceed 500 mg/dL
• History of hypertriglyceridemia-induced pancreatitis
Colesevelam hydrochloride, like other bile acid sequestrants, can increase serum TG concentrations.
Hypertriglyceridemia can cause acute pancreatitis.
Colesevelam hydrochloride had effects on serum TG (median increase 5% compared to placebo) in trials of patients with primary hyperlipidemia.
In trials in patients with type 2 diabetes, greater increases in TG levels occurred when colesevelam hydrochloride was used as monotherapy (median increase 9.7% compared to placebo) and when colesevelam hydrochloride was used in combination with pioglitazone (median increase 11% compared to placebo in combination with pioglitazone), sulfonylureas (median increase 18% compared to placebo in combination with sulfonylureas), and insulin (median increase 22% compared to placebo in combination with insulin)
Obtain lipid parameters, including TG levels, before starting colesevelam hydrochloride and periodically thereafter. Colesevelam hydrochloride is contraindicated in patients with TG levels >500 mg/dL or patients with a history of hypertriglyceridemia-induced pancreatitis [see Contraindications (4)]. Patients with TG levels greater than 300 mg/dL could have greater increases in serum TG levels with colesevelam hydrochloride and may require additional TG monitoring. Instruct patients to discontinue colesevelam hydrochloride and seek prompt medical attention if the symptoms of acute pancreatitis occur (e.g., severe abdominal pain with or without nausea and vomiting). Discontinue colesevelam hydrochloride if TG levels exceed 500 mg/dL
• A history of bowel obstruction
Postmarketing cases of bowel obstruction have occurred with colesevelam hydrochloride
Because of the tablet size, colesevelam hydrochloride tablets can cause dysphagia or esophageal obstruction. For patients with difficulty swallowing tablets, use colesevelam hydrochloride for oral suspention.
The following important adverse reactions are described below and elsewhere in the labeling:
• Hypertriglyceridemia and Pancreatitis
Colesevelam hydrochloride, like other bile acid sequestrants, can increase serum TG concentrations.
Hypertriglyceridemia can cause acute pancreatitis.
Colesevelam hydrochloride had effects on serum TG (median increase 5% compared to placebo) in trials of patients with primary hyperlipidemia.
In trials in patients with type 2 diabetes, greater increases in TG levels occurred when colesevelam hydrochloride was used as monotherapy (median increase 9.7% compared to placebo) and when colesevelam hydrochloride was used in combination with pioglitazone (median increase 11% compared to placebo in combination with pioglitazone), sulfonylureas (median increase 18% compared to placebo in combination with sulfonylureas), and insulin (median increase 22% compared to placebo in combination with insulin)
Obtain lipid parameters, including TG levels, before starting colesevelam hydrochloride and periodically thereafter. Colesevelam hydrochloride is contraindicated in patients with TG levels >500 mg/dL or patients with a history of hypertriglyceridemia-induced pancreatitis [see Contraindications (4)]. Patients with TG levels greater than 300 mg/dL could have greater increases in serum TG levels with colesevelam hydrochloride and may require additional TG monitoring. Instruct patients to discontinue colesevelam hydrochloride and seek prompt medical attention if the symptoms of acute pancreatitis occur (e.g., severe abdominal pain with or without nausea and vomiting). Discontinue colesevelam hydrochloride if TG levels exceed 500 mg/dL
• Gastrointestinal Obstruction
Postmarketing cases of bowel obstruction have occurred with colesevelam hydrochloride
Because of the tablet size, colesevelam hydrochloride tablets can cause dysphagia or esophageal obstruction. For patients with difficulty swallowing tablets, use colesevelam hydrochloride for oral suspention.
• Vitamin K or Fat-Soluble Vitamin Deficiencies
Colesevelam hydrochloride may decrease the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K. Patients with a susceptibility to deficiencies of vitamin K (e.g., patients on warfarin, patients with malabsorption syndromes) or other fat-soluble vitamins may be at increased risk when taking colesevelam hydrochloride.
Patients on oral vitamin supplementation should take their vitamins at least 4 hours prior to colesevelam hydrochloride
Colesevelam hydrochloride is a non-absorbed, polymeric, lipid-lowering and glucose-lowering agent for oral administration. Colesevelam hydrochloride is a high-capacity bile acid-binding molecule.
Colesevelam hydrochloride is poly(allylamine hydrochloride) cross-linked with epichlorohydrin and alkylated with 1-bromodecane and (6-bromohexyl)-trimethylammonium bromide. The chemical name (IUPAC) of colesevelam hydrochloride is allylamine polymer with 1-chloro-2,3-epoxypropane, [6-(allylamino)-hexyl]trimethylammonium chloride and N-allyldecylamine, hydrochloride. The chemical structure of colesevelam hydrochloride is represented by the following formula:
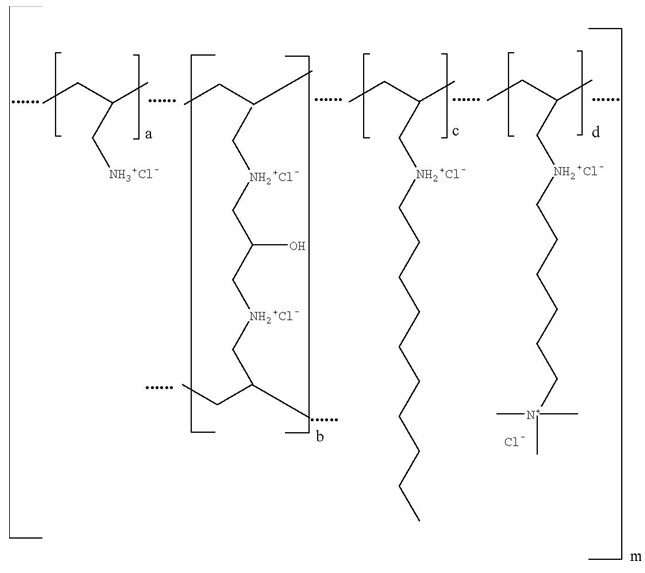
wherein (a) represents allyl amine monomer units that have not been alkylated by either of the 1-bromodecane or (6-bromohexyl)-trimethylammonium bromide alkylating agents or cross-linked by epichlorohydrin; (b) represents allyl amine units that have undergone cross-linking with epichlorohydrin; (c) represents allyl amine units that have been alkylated with a decyl group; (d) represents allyl amine units that have been alkylated with a (6-trimethylammonium) hexyl group, and m represents a number ≥ 100 to indicate an extended polymer network. A small amount of the amines are dialkylated and are not depicted in the formula above. No regular order of the groups is implied by the structure; cross-linking and alkylation are expected to occur randomly along the polymer chains. A large amount of the amines are protonated. The polymer is depicted in the hydrochloride form; a small amount of the halides are bromide. Colesevelam hydrochloride is hydrophilic and insoluble in water.
Colesevelam hydrochloride tablets are off-white to light yellow, capsule shaped, coated, tablets each containing 625 mg colesevelam hydrochloride. In addition, each tablet contains the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, hypromellose 2910, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol 6000. The tablets are imprinted using a black ink of opacode black S-1-17823 containing ferrosoferric oxide, propylene glycol and shellac.
Colesevelam hydrochloride tablets, 625 mg, are supplied as off-white to light yellow, capsule shaped coated tablets imprinted with “083” in black ink on one side and plain on other side and free from physical defects. Colesevelam hydrochloride tablets are available as follows:
• Bottles of 180 - NDC 75834-152-18
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15-30°C (59-86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Protect from moisture. Brief exposure to 40°C (104°F) does not adversely affect colesevelam hydrochloride tablets.