Cordran
(Flurandrenolide)Cordran Prescribing Information
For relief of the inflammatory and pruritic manifestations of corticosteroid-responsive dermatoses, particularly dry, scaling localized lesions.
Occlusive dressings may be used for the management of psoriasis or recalcitrant conditions.
If an infection develops, the use of Cordran Tape and other occlusive dressings should be discontinued and appropriate antimicrobial therapy instituted.
Replacement of the tape every 12 hours produces the lowest incidence of adverse reactions, but it may be left in place for 24 hours if it is well tolerated and adheres satisfactorily. When necessary, the tape may be used at night only and removed during the day.
If ends of the tape loosen prematurely, they may be trimmed off and replaced with fresh tape.
The directions given below are included for the patient to follow unless otherwise instructed by the physician.
Topical corticosteroids are contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to any of the components of these preparations.
Use of Cordran Tape is not recommended for lesions exuding serum or in intertriginous areas.
The following local adverse reactions are reported infrequently with topical corticosteroids but may occur more frequently with the use of occlusive dressings. These reactions are listed in an approximate decreasing order of occurrence: burning, itching, irritation, dryness, folliculitis, hypertrichosis, acneiform eruptions, hypopigmentation, perioral dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis.
The following may occur more frequently with occlusive dressings: maceration of the skin, secondary infection, skin atrophy, striae, miliaria.
Cordran Tape (Flurandrenolide Tape, USP) is a transparent, inconspicuous, plastic surgical tape. It contains Cordran (Flurandrenolide, USP), a potent corticosteroid for topical use. Flurandrenolide occurs as white to off-white, fluffy crystalline powder and is odorless. Flurandrenolide is practically insoluble in water and in ether. One gram dissolves in 72 mL of alcohol and in 10 mL of chloroform. The molecular weight of flurandrenolide is 436.52.
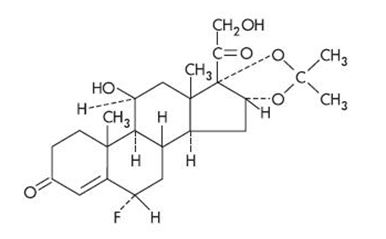
The chemical name of flurandrenolide is Pregn-4-ene-3,20-dione, 6-fluoro-11,21 dihydroxy-16,17-[(1-methylethylidene)bis(oxy)]-, (6α, 11ß, 16α)-; its empirical formula is C24H33FO6. The structural formula is as follows:
Each square centimeter contains 4 mcg (0.00916 μmol) flurandrenolide uniformly distributed in the adhesive layer. The tape is made of a thin, matte-finish polyethylene film that is slightly elastic and highly flexible.
The adhesive is a synthetic copolymer of acrylate ester and acrylic acid that is free from substances of plant origin. The pressure-sensitive adhesive surface is covered with a protective paper liner to permit handling and trimming before application.
Cordran is primarily effective because of its anti-inflammatory, antipruritic, and vasoconstrictive actions.
The mechanism of the anti-inflammatory effect of topical corticosteroids is not completely understood. Various laboratory methods, including vasoconstrictor assays, are used to compare and predict potencies and/or clinical efficacies of the topical corticosteroids. There is some evidence to suggest that a recognizable correlation exists between vasoconstrictor potency and therapeutic efficacy in man. Corticosteroids with anti-inflammatory activity may stabilize cellular and lysosomal membranes. There is also the suggestion that the effect on the membranes of lysosomes prevents the release of proteolytic enzymes and, thus, plays a part in reducing inflammation.
The tape serves as both a vehicle and an occlusive dressing. Retention of insensible perspiration by the tape results in hydration of the stratum corneum and improved diffusion of the medication. The skin is protected from scratching, rubbing, desiccation, and chemical irritation. The tape acts as a mechanical splint to fissured skin. Since it prevents removal of the medication by washing or the rubbing action of clothing, the tape formulation provides a sustained action.
Topical corticosteroids can be absorbed from normal intact skin. Inflammation and/or other disease processes in the skin increase percutaneous absorption. Occlusive dressings substantially increase the percutaneous absorption of topical corticosteroids. Thus, occlusive dressings may be a valuable therapeutic adjunct for treatment of resistant dermatoses (
Occlusive dressings may be used for the management of psoriasis or recalcitrant conditions.
If an infection develops, the use of Cordran Tape and other occlusive dressings should be discontinued and appropriate antimicrobial therapy instituted.
Replacement of the tape every 12 hours produces the lowest incidence of adverse reactions, but it may be left in place for 24 hours if it is well tolerated and adheres satisfactorily. When necessary, the tape may be used at night only and removed during the day.
If ends of the tape loosen prematurely, they may be trimmed off and replaced with fresh tape.
The directions given below are included for the patient to follow unless otherwise instructed by the physician.
Once absorbed through the skin, topical corticosteroids are handled through pharmacokinetic pathways similar to those of systemically administered corticosteroids. Corticosteroids are bound to plasma proteins in varying degrees. They are metabolized primarily in the liver and then excreted in the kidneys. Some of the topical corticosteroids and their metabolites are also excreted into the bile.