Cyclobenzaprine Hydrochloride
Cyclobenzaprine Hydrochloride Prescribing Information
Cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride tablets, USP are indicated as an adjunct to rest and physical therapy for relief of muscle spasm associated with acute, painful musculoskeletal conditions.
Improvement is manifested by relief of muscle spasm and its associated signs and symptoms, namely, pain, tenderness, limitation of motion, and restriction in activities of daily living.
Cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride tablets, USP have not been found effective in the treatment of spasticity associated with cerebral or spinal cord disease, or in children with cerebral palsy.
For most patients, the recommended dose of cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride tablets is 5 mg three times a day. Based on individual patient response, the dose may be increased to 10 mg three times a day. Use of cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride tablets for periods longer than two or three weeks is not recommended. (see
Cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride tablets, USP are indicated as an adjunct to rest and physical therapy for relief of muscle spasm associated with acute, painful musculoskeletal conditions.
Improvement is manifested by relief of muscle spasm and its associated signs and symptoms, namely, pain, tenderness, limitation of motion, and restriction in activities of daily living.
Cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride tablets, USP have not been found effective in the treatment of spasticity associated with cerebral or spinal cord disease, or in children with cerebral palsy.
Less frequent dosing should be considered for hepatically impaired or elderly patients (see
The plasma concentration of cyclobenzaprine is increased in patients with hepatic impairment (see
The plasma concentration of cyclobenzaprine is increased in the elderly (see
Hypersensitivity to any component of this product.
Concomitant use of monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors or within 14 days after their discontinuation. Hyperpyretic crisis seizures, and deaths have occurred in patients receiving cyclobenzaprine (or structurally similar tricyclic antidepressants) concomitantly with MAO inhibitor drugs.
Acute recovery phase of myocardial infarction, and patients with arrhythmias, heart block or conduction disturbances, or congestive heart failure.
Hyperthyroidism.
Incidence of most common adverse reactions in the 2 double-blind3, placebo-controlled 5 mg studies (incidence of > 3% on cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride 5 mg):
| Cyclobenzaprine Hydrochloride 5 mg | Cyclobenzaprine Hydrochloride 10 mg | Placebo | |
|---|---|---|---|
| N=464 | N=249 | N=469 | |
| Drowsiness | 29% | 38% | 10% |
| Dry Mouth | 21% | 32% | 7% |
| Fatigue | 6% | 6% | 3% |
| Headache | 5% | 5% | 8% |
Adverse reactions which were reported in 1% to 3% of the patients were: abdominal pain, acid regurgitation, constipation, diarrhea, dizziness, nausea, irritability, mental acuity decreased, nervousness, upper respiratory infection, and pharyngitis.
The following list of adverse reactions is based on the experience in 473 patients treated with cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride 10 mg in additional controlled clinical studies, 7607 patients in the postmarketing surveillance program, and reports received since the drug was marketed. The overall incidence of adverse reactions among patients in the surveillance program was less than the incidence in the controlled clinical studies.
The adverse reactions reported most frequently with cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride were drowsiness, dry mouth and dizziness. The incidence of these common adverse reactions was lower in the surveillance program than in the controlled clinical studies:
| Clinical Studies With Cyclobenzaprine Hydrochloride 10 mg | Surveillance Program With Cyclobenzaprine Hydrochloride 10 mg | |
|---|---|---|
| Drowsiness | 39% | 16% |
| Dry Mouth | 27% | 7% |
| Dizziness | 11% | 3% |
Among the less frequent adverse reactions, there was no appreciable difference in incidence in controlled clinical studies or in the surveillance program. Adverse reactions which were reported in 1% to 3% of the patients were: fatigue/tiredness, asthenia, nausea, constipation, dyspepsia, unpleasant taste, blurred vision, headache, nervousness, and confusion.
The following adverse reactions have been reported in post-marketing experience or with an incidence of less than 1% of patients in clinical trials with the 10 mg tablet:
Body as a Whole:
Cardiovascular:
Digestive:
Hypersensitivity:
Musculoskeletal:
Nervous System and Psychiatric:
Skin:
Special Senses:
Urogenital:
Other reactions, reported rarely for cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride under circumstances where a causal relationship could not be established or reported for other tricyclic drugs, are listed to serve as alerting information to physicians:
Body as a whole:
Cardiovascular:
Digestive:
Endocrine:
Hematic and Lymphatic:
Metabolic, Nutritional and Immune:
Musculoskeletal:
Nervous System and Psychiatric:
Respiratory:
Skin:
Urogenital:
Cyclobenzaprine may have life-threatening interactions with MAO inhibitors (see
Hypersensitivity to any component of this product.
Concomitant use of monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors or within 14 days after their discontinuation. Hyperpyretic crisis seizures, and deaths have occurred in patients receiving cyclobenzaprine (or structurally similar tricyclic antidepressants) concomitantly with MAO inhibitor drugs.
Acute recovery phase of myocardial infarction, and patients with arrhythmias, heart block or conduction disturbances, or congestive heart failure.
Hyperthyroidism.
The development of a potentially life-threatening serotonin syndrome has been reported with cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride when used in combination with other drugs, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), tramadol, bupropion, meperidine, verapamil, or MAO inhibitors. The concomitant use of cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride with MAO inhibitors is contraindicated (see
Cyclobenzaprine is closely related to the tricyclic antidepressants, e.g., amitriptyline and imipramine. In short term studies for indications other than muscle spasm associated with acute musculoskeletal conditions, and usually at doses somewhat greater than those recommended for skeletal muscle spasm, some of the more serious central nervous system reactions noted with the tricyclic antidepressants have occurred (see
Tricyclic antidepressants have been reported to produce arrhythmias, sinus tachycardia, prolongation of the conduction time leading to myocardial infarction and stroke.
Cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride may enhance the effects of alcohol, barbiturates, and other CNS depressants.
Cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride may enhance the effects of alcohol, barbiturates, and other CNS depressants.
Tricyclic antidepressants may block the antihypertensive action of guanethidine and similarly acting compounds.
Tricyclic antidepressants may enhance the seizure risk in patients taking tramadol.2
2ULTRAM® (tramadol HCl tablets, PriCara, Division of Ortho-McNeil-Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc.)
ULTRACET® (tramadol HCl and acetaminophen tablets, PriCara, Division of Ortho-McNeil-Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc.)
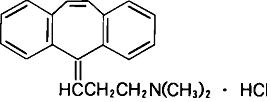
Cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride, USP is a white, crystalline tricyclic amine salt with the molecular formula C20H21N • HCl and a molecular weight of 311.9. It has a melting point of 217ºC, and a pKa of 8.47 at 25ºC. It is freely soluble in water and alcohol, sparingly soluble in isopropanol, and insoluble in hydrocarbon solvents. If aqueous solutions are made alkaline, the free base separates. Cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride is designated chemically as 3-(
Cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride is supplied as 5 mg or 10 mg tablets for oral administration. Each tablet contains the following inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, polyethylene glycol, pregelatinized starch (maize) and titanium dioxide. In addition 5 mg also contains D&C yellow #10 aluminum lake and FD&C yellow #6 aluminum lake and 10 mg also contains yellow iron oxide.
FDA approved dissolution test specifications differ from USP.