Cyproheptadine Hydrochloride
Cyproheptadine Hydrochloride Prescribing Information
Perennial and seasonal allergic rhinitis
Vasomotor rhinitis
Allergic conjunctivitis due to inhalant allergens and foods
Mild, uncomplicated allergic skin manifestations of urticaria and angioedema.
Amelioration of allergic reactions to blood or plasma
Cold urticaria
Dermatographism
As therapy for anaphylactic reactions adjunctive to epinephrine and other standard measures after the acute manifestations have been controlled.
DOSAGE SHOULD BE INDIVIDUALIZED ACCORDING TO THE NEEDS AND THE RESPONSE OF THE PATIENT.
Each tablet contains 4 mg of cyproheptadine hydrochloride.
The total daily dosage for pediatric patients may be calculated on the basis of body weight or body area using approximately 0.25 mg/kg/day or 8 mg per square meter of body surface (8 mg/m2).
The usual dose is 2 mg (½ tablet) two or three times a day, adjusted as necessary to the size and response of the patient. The dose is not to exceed 12 mg a day.
The usual dose is 4 mg (1 tablet) two or three times a day adjusted as necessary to the size and response of the patient. The dose is not to exceed 16 mg a day.
The total daily dose for adults should not exceed 0.5 mg/kg/day. The therapeutic range is 4 to 20 mg a day, with the majority of patients requiring 12 to 16 mg a day. An occasional patient may require as much as 32 mg a day for adequate relief. It is suggested that dosage be initiated with 4 mg (1 tablet) three times a day and adjusted according to the size and response of the patient.
This drug should not be used in newborn or premature infants.
Because of the higher risk of antihistamines for infants generally and for newborns and prematures in particular, antihistamine therapy is contraindicated in nursing mothers.
Hypersensitivity to cyproheptadine and other drugs of similar chemical structure.
Monoamine oxidase inhibitor therapy (See
Angle-closure glaucoma
Stenosing peptic ulcer
Symptomatic prostatic hypertrophy
Bladder neck obstruction
Pyloroduodenal obstruction
Elderly, debilitated patients
Adverse reactions which have been reported with the use of antihistamines are as follows:
Sedation and sleepiness (often transient), dizziness, disturbed coordination, confusion, restlessness, excitation, nervousness, tremor, irritability, insomnia, paresthesias, neuritis, convulsions, euphoria, hallucinations, hysteria, faintness.
Allergic manifestation of rash and edema, excessive perspiration, urticaria, photosensitivity.
Acute labyrinthitis, blurred vision, diplopia, vertigo, tinnitus.
Hypotension, palpitation, tachycardia, extrasystoles, anaphylactic shock.
Hemolytic anemia, leukopenia, agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia.
Cholestasis, hepatic failure, hepatitis, hepatic function abnormality, dryness of mouth, epigastric distress, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, jaundice.
Urinary frequency, difficult urination, urinary retention, early menses.
Dryness of nose and throat, thickening of bronchial secretions, tightness of chest and wheezing, nasal stuffiness.
Fatigue, chills, headache, increased appetite/weight gain.
To report
Cyproheptadine HCl USP, is an antihistaminic and antiserotonergic agent.
Cyproheptadine hydrochloride USP is a white to slightly yellowish crystalline solid, with a molecular weight of 350.89, which is soluble in water, freely soluble in methanol, sparingly soluble in ethanol, soluble in chloroform, and practically insoluble in ether. It is the sesquihydrate of 4-(5
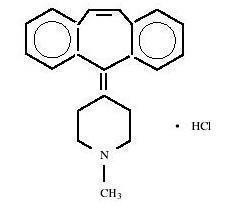
C21H21N• HCl M.W. 350.89
Cyproheptadine hydrochloride USP is available for oral administration in 4 mg tablets. Inactive ingredients include: lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and sodium starch glycolate.
Cyproheptadine is a serotonin and histamine antagonist with anticholinergic and sedative effects. Antiserotonin and antihistamine drugs appear to compete with serotonin and histamine, respectively, for receptor sites.