Darunavir
Darunavir Prescribing Information
Darunavir, co-administered with ritonavir (darunavir/ritonavir), in combination with other antiretroviral agents, is indicated for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) infection in adult and pediatric patients 3 years of age and older
- Darunavir tablets, 600 mgare supplied as orange colored, oval shaped, film-coated tablets, debossed with “AC13” on one side and plain on the other side.
- Darunavir tablets, 800 mgare supplied as dark red colored, oval shaped, film-coated tablets, debossed with “AC14” on one side and plain on the other side.
Co-administration of darunavir/ritonavir is contraindicated with drugs that are highly dependent on CYP3A for clearance and for which elevated plasma concentrations are associated with serious and/or life-threatening events (narrow therapeutic index). Examples of these drugs and other contraindicated drugs (which may lead to reduced efficacy of darunavir) are listed below
- Alpha 1-adrenoreceptor antagonist: alfuzosin
- Anti-gout: colchicine, in patients with renal and/or hepatic impairment
- Antimycobacterial: rifampin
- Antipsychotics: lurasidone, pimozide
- Cardiac Disorders: dronedarone, ivabradine, ranolazine
- Ergot derivatives, e.g., dihydroergotamine, ergotamine, methylergonovine
- Herbal product: St. John’s wort (Hypericum perforatum)
- Hepatitis C direct acting antiviral: elbasvir/grazoprevir
- Lipid modifying agents: lomitapide, lovastatin, simvastatin
- Opioid Antagonist: naloxegol
- PDE-5 inhibitor: sildenafil when used for treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension
- Sedatives/hypnotics: orally administered midazolam, triazolam
The following adverse reactions are discussed in other sections of labeling:
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Severe Skin Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Diabetes Mellitus/Hyperglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Fat Redistribution [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Immune Reconstitution Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Hemophilia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
Due to the need for co-administration of darunavir with ritonavir, please refer to ritonavir prescribing information for ritonavir-associated adverse reactions.
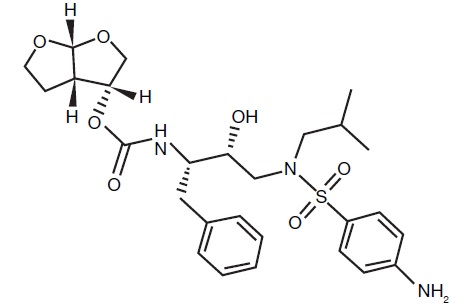
Darunavir is an inhibitor of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) protease. It has the following chemical name: [(1S,2R)-3-[[(4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl](2-methylpropyl)amino]-2-hydroxy-1-(phenylmethyl)propyl]carbamic acid (3R,3aS,6aR)-hexahydrofuro[2,3-b]furan-3-yl ester. Its molecular formula is C27H37N3O7S and its molecular weight is 547.66 g/mol. Darunavir has the following structural formula:
Darunavir is a white to creamish solid. It is freely soluble in ethyl acetate and in dichloromethane; practically insoluble in water.
Each darunavir tablet contains 600 mg or 800 mg of darunavir. It also contains the inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone Type A, hydroxypropyl cellulose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose and sodium starch glycolate Type A. The 600 mg tablet film-coating, OPADRY-II Orange, contains FD&C Yellow No. 6, polyethylene glycol 3350, polyvinyl alcohol-partially hydrolyzed, talc, and titanium dioxide. The 800 mg tablet film-coating, OPADRY-II Brown, contains ferric oxide red, polyethylene glycol 3350, polyvinyl alcohol-partially hydrolyzed, talc, and titanium dioxide.
Darunavir was evaluated for carcinogenic potential by oral gavage administration to mice and rats up to 104 weeks. Daily doses of 150, 450 and 1,000 mg/kg were administered to mice and doses of 50, 150 and 500 mg/kg was administered to rats. A dose-related increase in the incidence of hepatocellular adenomas and carcinomas were observed in males and females of both species as well as an increase in thyroid follicular cell adenomas in male rats. The observed hepatocellular findings in rodents are considered to be of limited relevance to humans. Repeated administration of darunavir to rats caused hepatic microsomal enzyme induction and increased thyroid hormone elimination, which predispose rats, but not humans, to thyroid neoplasms. At the highest tested doses, the systemic exposures to darunavir (based on AUC) were between 0.4- and 0.7-fold (mice) and 0.7- and 1-fold (rats), relative to those observed in humans at the recommended therapeutic doses (600 mg/100 mg twice daily or 800 mg/100 mg once daily).
Darunavir was not mutagenic or genotoxic in a battery of
No effects on fertility or early embryonic development were observed with darunavir in rats.