Dasatinib - Dasatinib tablet, Film Coated
(Dasatinib)Dasatinib - Dasatinib tablet, Film Coated Prescribing Information
Dasatinib tablets are indicated for the treatment of adult patients with
• newly diagnosed Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+) chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) in chronic phase.
• chronic, accelerated, or myeloid or lymphoid blast phase Ph+ CML with resistance or intolerance to prior therapy including imatinib.
• Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Ph+ ALL) with resistance or intolerance to prior therapy.
Dasatinib tablets are indicated for the treatment of pediatric patients 1 year of age and older with
• Ph+ CML in chronic phase.
• newly diagnosed Ph+ ALL in combination with chemotherapy.
Dasatinib tablets 20 mg are available as white to off-white, round shaped film-coated tablets debossed with “599” on one side and plain on other side and free from physical defects.
Dasatinib tablets 50 mg are available as white to off-white, oval shaped film-coated tablets debossed with “600” on one side and plain on other side and free from physical defects.
Dasatinib tablets 70 mg are available as white to off-white, round shaped film-coated tablets debossed with “601” on one side and plain on other side and free from physical defects.
Dasatinib tablets 80 mg are available as white to off-white, round shaped film-coated tablets debossed with “602” on one side and plain on other side and free from physical defects.
Dasatinib tablets 100 mg are available as white to off-white, oval shaped film-coated tablets debossed with “603” on one side and plain on other side and free from physical defects.
Dasatinib tablets 140 mg are available as white to off-white, round shaped film-coated tablets debossed with “604” on one side and plain on other side and free from physical defects.
None.
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in othersections of the labeling:
• Myelosuppression
In clinical studies, myelosuppression was managed by dose interruption, dose reduction, or discontinuation of study therapy. Hematopoietic growth factor has been used in patients with resistant myelosuppression. Guidelines for dose modifications for adult and pediatric patients are summarized in Tables 3 and 4, respectively.
| Chronic Phase CML(starting dose 100 mgonce daily) | ANC* <0.5 × 109/LorPlatelets <50 × 109/L | 1. Stop dasatinib tablets until ANC ≥1.0 × 109/L and platelets ≥50 × 109/L. 2. Resume treatment with dasatinib tablets at the original starting dose if recovery occurs in ≤7 days. 3. If platelets <25 × 109/L or recurrence of ANC <0.5 × 109/L for >7 days, repeat Step 1 and resume dasatinib tablets at a reduced dose of 80 mg once daily for second episode. For third episode, further reduce dose to 50 mg once daily (for newly diagnosed patients) or discontinue dasatinib tablets (for patients resistant or intolerant to prior therapy including imatinib). |
| Accelerated Phase CML, Blast Phase CML and Ph+ ALL (starting dose 140 mg once daily) | ANC* <0.5 × 109/LorPlatelets <10 × 109/L | 1. Check if cytopenia is related to leukemia (marrowaspirate or biopsy). 2. If cytopenia is unrelated to leukemia, stop dasatinib tablets until ANC ≥1.0 × 109/L and platelets ≥20 × 109/L and resume at the original starting dose. 3. If recurrence of cytopenia, repeat Step 1 and resume dasatinib tablets at a reduced dose of 100 mg once daily second episode) or 80 mg once daily (third episode). 4. If cytopenia is related to leukemia, consider dose escalation to 180 mg once daily. |
*ANC: absolute neutrophil count
Dose (maximum dose per day) | ||||
Original Starting Dose | One-Level Dose Reduction | Two-Level Dose Reduction | ||
| 1 If cytopenia persists for more than 3 weeks, check if cytopenia is related to leukemia (marrow aspirate or biopsy). 2. If cytopenia is unrelated to leukemia, stop dasatinib tablets until ANC* ≥1.0 × 109/L and platelets ≥75 × 109/L and resume at the original starting dose or at a reduced dose. 3. If cytopenia recurs, repeat marrow aspirate/biopsy and resume dasatinib tablets at a reduced dose. | Tablets | 40 mg 60 mg 70 mg 100 mg | 20 mg 40 mg 60 mg 80 mg | ** 20 mg 50 mg 70 mg |
*ANC: absolute neutrophil count
** lower tablet dose not available
For pediatric patients with chronic phase CML, if Grade ≥ 3 neutropenia or thrombocytopenia recurs during complete hematologic response (CHR), interrupt dasatinib tablets and resume at a reduced dose. Implement temporary dose reductions for intermediate degrees of cytopenia and disease response as needed.
For pediatric patients with Ph+ ALL, if neutropenia and/or thrombocytopenia result in a delay of the next block of treatment by more than 14 days, interrupt dasatinib tablets and resume at the same dose level once the next block of treatment is started. If neutropenia and/or thrombocytopenia persist and the next block of treatment is delayed another 7 days, perform a bone marrow assessment to assess cellularity and percentage of blasts. If marrow cellularity is <10%, interrupt treatment with dasatinib tablets until ANC >500/μL (0.5 x 109/L), at which time treatment may be resumed at full dose. If marrow cellularity is >10%, resumption of treatment with dasatinib tablets may be considered.
For adults with Ph+ CML and ALL, and pediatric patients with Ph+ CML, if a severe non-hematologic adverse reaction develops with dasatinib tablets use, treatment must be withheld until the adverse reaction has resolved or improved. Thereafter, treatment can be resumed as appropriate at a reduced dose depending on the severity and recurrence [see Warnings and Precautions (5)].
For pediatric patients with Ph+ ALL, interrupt treatment for cases of grade ≥3 non-hematologic adverse reactions with the exception of liver function test abnormalities, and resume at a reduced dose when resolved to grade ≤1. For elevated direct bilirubin over 5 times the institutional upper limit of normal (ULN), interrupt treatment until improvement to baseline or grade ≤1. For elevated AST/ALT over 15 times the institutional ULN, interrupt treatment until improvement to baseline or grade <1. For recurrent liver function test abnormalities as above, reduce the dose if this adverse reaction recurs after reinitiation of dasatinib tablets. Dose reduction recommendations are described in Table 5.
Dose (maximum dose per day) | ||||
Original Starting Dose | One-Level Dose Reduction | Two-Level Dose Reduction | ||
| 1. If a non-hematologic toxicity grade 2 occurs, consider interrupting dasatinib tablets if no recovery despite symptomatic therapy; once recovered to grade ≤1, resume at the original starting dose. Resume dasatinib tablets, at a reduced dose for recurrent events. 2. If a non-hematologic toxicity grade 3 occurs, stop dasatinib tablets until recovery to grade ≤1 and then resume at a reduced dose. 3. If direct bilirubin is >5 ULN or AST/ALT >15 ULN, interrupt dasatinib tablets until recovery to grade ≤1 and then resume dasatinib tablets at the original starting dose. Resume dasatinib tablets at a reduced dose for recurrent hepatotoxicity. | Tablets | 40 mg 60 mg 70 mg 100 mg | 20 mg 40 mg 60 mg 80 mg | ** 20 mg 50 mg 70 mg |
** lower tablet dose not available
Treatment with dasatinib tablets is associated with severe (NCI CTCAE Grade 3 or 4) thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, and anemia, which occur earlier and more frequently in patients with advanced phase CML or Ph+ ALL than in patients with chronic phase CML [
In patients with chronic phase CML, perform complete blood counts (CBCs) every 2 weeks for 12 weeks, then every 3 months thereafter, or as clinically indicated. In patients with advanced phase CML or Ph+ ALL, perform CBCs weekly for the first 2 months and then monthly thereafter, or as clinically indicated.
In pediatric patients with Ph+ ALL treated with dasatinib tablets in combination with chemotherapy, perform CBCs prior to the start of each block of chemotherapy and as clinically indicated. During the consolidation blocks of chemotherapy, perform CBCs every 2 days until recovery.
Myelosuppression is generally reversible and usually managed by withholding dasatinibtablets temporarily and/or dose reduction
• Bleeding-related events
Dasatinib tablets can cause serious and fatal bleeding. In all CML or Ph+ ALL clinical studies, Grade ≥3 central nervous system (CNS) hemorrhages, including fatalities, occurred in <1% of patients receiving dasatinib. The incidence of Grade 3/4 hemorrhage occurred in 5.8% of adult patients and generally required treatment interruptions and transfusions. The incidence of Grade 5 hemorrhage occurred in 0.4% of adult patients. The most frequent site of hemorrhage was gastrointestinal [
Concomitant medications that inhibit platelet function or anticoagulants may increase the risk of hemorrhage.
• Fluid retention
Dasatinib tablets may cause fluid retention [
Evaluate patients who develop symptoms of pleural effusion or other fluid retention, such as new or worsened dyspnea on exertion or at rest, pleuritic chest pain, or dry cough, promptly with a chest x-ray or additional diagnostic imaging as appropriate. Fluid retention events were typically managed by supportive care measures that may include diuretics or short courses of steroids. Severe pleural effusion may require thoracentesis and oxygen therapy. Consider dose reduction or treatment interruption
• Cardiovascular Toxicity
Dasatinib tablets can cause cardiac dysfunction [
• Pulmonary arterial hypertension
Dasatinib tablets may increase the risk of developing pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) in adult and pediatric patients which may occur any time after initiation, including after more than 1 year of treatment. Manifestations include dyspnea, fatigue, hypoxia, and fluid retention [
• QT prolongation
Dasatinib tablets may increase the risk of prolongation of QTc in patients including those with hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia, patients with congenital long QT syndrome, patients taking antiarrhythmic medicines or other medicinal products that lead to QT prolongation, and cumulative high-dose anthracycline therapy [
• Severe dermatologic reactions
Cases of severe mucocutaneous dermatologic reactions, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome [
• Tumor lysis syndrome
Tumor lysis syndrome has been reported in patients with resistance to prior imatinib therapy, primarily in advanced phase disease. Due to potential for tumor lysis syndrome, maintain adequate hydration, correct uric acid levels prior to initiating therapy with dasatinib tablets, and monitor electrolyte levels. Patients with advanced stage disease and/or high tumor burden may be at increased risk and should be monitored more frequently
• Effects on growth and development in pediatric patients [see Warnings and Precautions (
In pediatric trials of dasatinib in chronic phase CML after at least 2 years of treatment, adverse reactions associated with bone growth and development were reported in 5 (5.2%) patients, one of which was severe in intensity (Growth Retardation Grade 3). These 5 cases included cases of epiphyses delayed fusion, osteopenia, growth retardation, and gynecomastia [see Adverse Reactions and Use in Specific Populations ]. Of these 5 cases, 1 case of osteopenia and 1 case of gynecomastia resolved during treatment.
• Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (
Dasatinib may cause hepatotoxicity as measured by elevations in bilirubin, aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and alkaline phosphatase [see Adverse Reactions ]. When dasatinib tablets are administered in combination with chemotherapy, liver toxicity in the form of transaminase elevation and hyperbilirubinemia has been observed. Monitor hepatic function when dasatinib tablets are used in combination with chemotherapy.
Dasatinib is a kinase inhibitor. The chemical name for dasatinib (S)-propylene glycol is N-(2-chloro-6-methylphenyl)-2-[[6-[4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazinyl]-2-methyl-4-pyrimidinyl]amino]-5-thiazolecarboxamide S-1, 2-Propanediol. The molecular formula is C22H26ClN7O2S • C3H8O2, which corresponds to a formula weight of 564.11 ((S)-Propylene Glycol). The free base has a molecular weight of 488.01. Dasatinib (S)-propylene glycol has the following chemical structure:
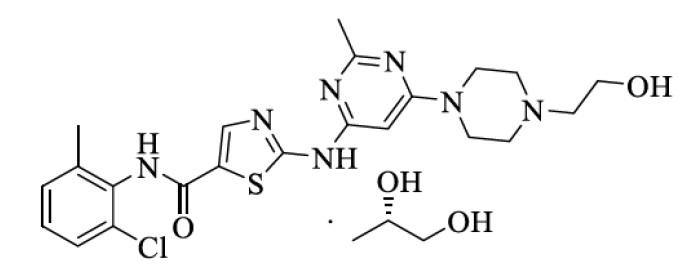
Dasatinib (S)-propylene glycol is a white to brown colored powder. The drug substance is freely soluble in dimethyl formamide & N-methyl-2-pyrrolodine while practically insoluble in dichloromethane, methanol, ethanol, acetone, n-heptane, n-hexane, tertrahydrofuran, toluene, ethyl acetate, petroleum ether, (S)-propylene glycol and water.
Dasatinib tablets are white to off-white, round/oval, film-coated tablets containing dasatinib (S)-propylene glycol, with the following inactive ingredients: anhydrous lactose, colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, hydrogenated castor oil, magnesium stearate and microcrystalline cellulose. The tablet coating consists of hypromellose, titanium dioxide, and triacetin.
Dasatinib, at nanomolar concentrations, inhibits the following kinases: BCR-ABL, SRC family (SRC, LCK, YES, FYN), c-KIT, EPHA2, and PDGFRβ. Based on modeling studies, dasatinib is predicted to bind to multiple conformations of the ABL kinase.