Deferoxamine
(Deferoxamine Mesylate)Deferoxamine Prescribing Information
Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection is an iron-chelating agent indicated:
• As an adjunct to standard measures for the treatment of acute iron intoxication. ()1.1 Acute Iron IntoxicationDeferoxamine Mesylate for Injection is indicated as an adjunct to standard measures for the treatment of acute iron intoxication.
• For the treatment of transfusional iron overload in patients with chronic anemia. ()1.2 Chronic Iron OverloadDeferoxamine Mesylate for Injection is indicated for the treatment of transfusional iron overload in patients with chronic anemia.
Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection is not indicated for the treatment of primary hemochromatosis (since phlebotomy is the method of choice for removing excess iron in this disorder).
The dosage (based on body weight in mg/kg/day), rates of administration, and mode of administration for both adults and pediatric patients are individually determined and adapted during the course of therapy based on the severity of the patient's iron overload. The minimum daily dose of Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection is 20 mg/kg/day for both adults and pediatric patients. The maximum daily dose is 40 mg/kg/day for pediatric patients and 60 mg/kg/day for adults.
For injection: 500 mg of deferoxamine mesylate (corresponding to 426.82 mg of deferoxamine as free base) is a white to off-white lyophilized powder in a single-dose vial for reconstitution.
For injection: 2 grams of deferoxamine mesylate (corresponding to 1.707 g of deferoxamine as free base) is a white to off-white lyophilized powder in a single-dose vial for reconstitution.
• Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed ()8.2 LactationThere are no data on the presence of deferoxamine or its metabolite in either human or animal milk, the effects on the breastfed child, or the effects on milk production. It is not known whether deferoxamine is excreted in human milk. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in the breastfed child, advise patients not to breastfeed during treatment with Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection, and for one week after the last dose.
• Geriatric Use: Increased risk of ocular disorders ()8.5 Geriatric UseClinical Studies of Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 years and over to determine whether they respond differently from the younger subjects. Postmarketing reports suggest a possible trend for an increased risk of eye disorders in the geriatric population, specifically the occurrence of color blindness, maculopathy, and scotoma.
However, it is unclear if these eye disorders were dose related. Although the number of reports was very small, certain elderly patients may be predisposed to eye disorders when taking Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection. Postmarketing reports also suggest that there may be an increased risk of deafness and hearing loss in the geriatric population
[see Adverse Reactions ]. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection is contraindicated in patients with:
• A history of a hypersensitivity reaction to deferoxamine or any of its inactive ingredients[see Description (. Reactions have included anaphylaxis)]11 DESCRIPTIONDeferoxamine Mesylate for Injection, USP is an iron-chelating agent, available in vials for injection via intramuscular, subcutaneous, and intravenous administration. Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection, USP is supplied as vials containing 500 mg and 2 g of deferoxamine mesylate USP (corresponding to 426.82 mg and 1.707 g of deferoxamine as free base) in sterile, lyophilized form. Deferoxamine mesylate is
N- [5-[3-[(5-aminopentyl)hydroxycarbamoyl]propionamido]pentyl]-3-[[5-(N-hydroxyacetamido)pentyl]carbamoyl]propionohydroxamic acid monomethanesul-fonate (salt), and its structural formula is: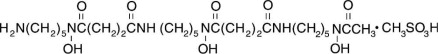
Deferoxamine mesylate is a white to almost white powder. It is freely soluble in water and slightly soluble in methanol. Its molecular weight is 656.79 g/mol.

Structural Formula [see Warnings and Precautions (.)]5.1 Hypersensitivity ReactionsHypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, have occurred in Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection-treated patients. Reactions have included flushing of the skin, urticaria, hypotension, and shock. These reactions typically occur when Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection was administered by rapid intravenous injection. Therefore, administer Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection intramuscularly or by slow subcutaneous or intravenous infusion.
• Severe renal disease or anuria since the drug and the iron chelate are excreted primarily by the kidney[see Warnings and Precautions (.)]5.3 Renal ToxicityRenal toxicity, including increases in serum creatinine (possibly dose-related), acute renal failure and renal tubular disorders has occurred in Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection-treated patients. Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection is contraindicated in patients with severe renal disease
[see Contraindications ]. Monitor serum creatinine to assess for changes in renal function.
• Hypersensitivity Reactions: More common with rapid intravenous infusion. Administer intramuscularly or by slow subcutaneous or intravenous infusion. () Auditory and Ocular Toxicity: Have been reported when administered over prolonged periods of time, at high doses, or in patients with low ferritin levels. (5.1 Hypersensitivity ReactionsHypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, have occurred in Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection-treated patients. Reactions have included flushing of the skin, urticaria, hypotension, and shock. These reactions typically occur when Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection was administered by rapid intravenous injection. Therefore, administer Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection intramuscularly or by slow subcutaneous or intravenous infusion.
)5.2 Auditory and Ocular ToxicityOcular and auditory toxicities have been reported in Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection-treated patients. The ocular toxicities observed have included blurring of vision; cataracts after prolonged administration in chronic iron overload; decreased visual acuity, including visual loss, visual defects, scotoma; impaired peripheral, color, and night vision; optic neuritis, cataracts, corneal opacities, and retinal pigmentary abnormalities. The auditory toxicities reported have been tinnitus and hearing loss, including high frequency sensorineural hearing loss. Risk factors for both ocular and auditory disturbances include prolonged treatment duration, higher doses, or low ferritin levels. In most cases, both ocular and auditory disturbances were reversible upon immediate cessation of treatment
[see Adverse Reactions ].Visual acuity tests, slit-lamp examinations, funduscopy and audiometry are recommended periodically in patients treated for prolonged periods of time. Toxicity is more likely to be reversed if symptoms or test abnormalities are detected early.
• Renal Toxicity: Cases of acute renal failure, renal tubular disorders and increase in serum creatinine have occurred. Monitor patients for changes in renal function. ()5.3 Renal ToxicityRenal toxicity, including increases in serum creatinine (possibly dose-related), acute renal failure and renal tubular disorders has occurred in Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection-treated patients. Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection is contraindicated in patients with severe renal disease
[see Contraindications ]. Monitor serum creatinine to assess for changes in renal function.• Respiratory Toxicity: Acute respiratory distress syndrome has occurred. Risk increased with high intravenous doses. Recommended daily dose should not be exceeded. ()5.4 Respiratory ToxicityAcute respiratory distress syndrome has occurred in Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection-treated patients following treatment with excessively high intravenous doses of Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection in patients with acute iron intoxication or thalassemia. The recommended daily doses should therefore not be exceeded.
• Growth Suppression: Has occurred in pediatric patients treated with high doses and concomitant low ferritin levels. Dose reduction may partially resume growth velocity to pre-treatment rates. ()5.5 Growth SuppressionHigh doses of Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection and concomitant low ferritin levels have also been associated with growth suppression in pediatric patients. After reduction of Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection dose, growth velocity may partially resume to pre-treatment rates. Monitor growth (weight and height) in pediatric patients treated with Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection every 3 months.
• Serious Infections: Cases of mucormycosis and Yersinia infections, some fatal, have occurred. Discontinue Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection and initiate appropriate treatment immediately. ()5.6 Serious InfectionsYersinia InfectionsDeferoxamine Mesylate for Injection may increase the risk of
Yersinia enterocoliticaandYersinia pseudotuberculosisinfections. Avoid starting Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection treatment in patients with active Yersinia infections. Should Yersinia infection develop, interrupt Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection treatment until the infection is resolved.MucormycosisCases of mucormycosis, some with a fatal outcome, have occurred in Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection-treated patients. Signs or symptoms are specific to the site of infection. If mucormycosis is suspected, discontinue Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection, conduct mycological testing, and treat immediately.
• Cardiac Dysfunction with Concomitant Use of Vitamin C: Avoid coadministration in patients with cardiac failure. Delay Vitamin C for one month after start of Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection. Avoid exceeding 200 mg daily in adults. Monitor cardiac function with combined treatment. ()5.7 Cardiac Dysfunction with Concomitant Use of Vitamin CCardiac dysfunction has occurred in Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection-treated patients with severe chronic iron overload following concomitant treatment with high doses of vitamin C (more than 500 mg daily in adults). The cardiac dysfunction was reversible when vitamin C was discontinued. The following precautions should be taken when vitamin C and Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection are to be used concomitantly:
• Vitamin C supplements should not be given to patients with cardiac failure.• Start supplemental vitamin C only after an initial month of regular treatment with Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection.• Give vitamin C only if the patient is receiving Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection regularly, ideally soon after setting up the infusion pump.• Do not exceed a daily vitamin C dose of 200 mg in adults, given in divided doses. In general, 50 mg daily suffices for pediatric patients under 10 years old and 100 mg for older pediatric patients.• Clinical monitoring of cardiac function is advisable during such combined therapy.
• Risks of Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection Treatment in Patients with Aluminum Overload: Risks include neurological dysfunction (including seizures), dialysis dementia, and aggravation of hyperparathyroidism. ()5.8 Risks of Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection Treatment in Patients with Aluminum OverloadDeferoxamine Mesylate for Injection may cause neurological dysfunction (including seizures) in patients with aluminum-related encephalopathy and receiving dialysis, possibly due to an acute increase in circulating aluminum
[see Adverse Reactions ].Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection may precipitate the onset of dialysis dementia.
Treatment with Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection in the presence of aluminum overload may result in decreased serum calcium and aggravation of hyperparathyroidism.
• Effects on Ability to Drive and Use Machines: May cause dizziness. ()5.9 Effects on Ability to Drive and Use MachinesDeferoxamine Mesylate for Injection may cause dizziness, which may impair the ability to drive a car or operate machinery. Patients should not drive or operate machinery until they know how Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection will affect their ability to engage in these activities.
• Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Can cause fetal harm. Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus and use effective contraception (,5.10 Embryo-Fetal ToxicityBased on findings in animals, Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. In animal reproduction studies, administration of deferoxamine to pregnant mice and rabbits during the period of organogenesis caused adverse developmental outcomes including decreased fetal body weights and malformations at maternal doses less than those in patients at maximum recommended human dose (MRHD). Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential and males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection and for one month after the last dose
[see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3), Nonclinical Toxicology ].,8.1 PregnancyRisk SummaryThere are no available data on Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection use in pregnant women to evaluate for a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriages or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes.
In animal reproduction studies subcutaneous administration of deferoxamine to pregnant animals (mice or rabbits) during organogenesis at doses approximately ≥0.2- (mice) and ≥0.7 (rabbits) times the maximum recommended human dose resulted in maternal toxicity and adverse developmental outcomes
(see Data). Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Consider the benefits and risks of Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection for the mother and possible risks to the fetus when prescribing Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection to a pregnant woman.The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population(s) is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
DataAnimal DataIn an embryo-fetal developmental study in mice, pregnant animals administered subcutaneous doses of deferoxamine at 180, and 540 mg/kg/day from gestation day 7 to gestation day 12 resulted in a dose dependent delay and irregularities of fetal skeletal maturation at doses ≥0.2 times the MRHD. At the highest dose of 540 mg/kg, in 1/23 fetuses had a unilateral lesion to the eye lens (approximately 0.5 times the MRHD).
In the embryo-fetal developmental studies in rabbits, pregnant animals administered subcutaneous doses of deferoxamine either 200 mg/kg or 200, 300, and 540 mg/kg from gestation day 6 to gestation day 14 resulted in maternal toxicity and embryo-fetal developmental effects at 0.7 times the MRHD). Maternal toxicity included reduced fetal body weights and embryo-fetal effects included malformations of spina bifida, and increased incidence of abnormally ossified ribs and vertebrae.
No maternal toxicity or embryo-fetal effects were observed in rats at deferoxamine doses tested (up to 0.9 times the MRHD).
)8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive PotentialBased on animal data, Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection can cause malformations at doses less than the human dose
[see Use in Specific Populations ].ContraceptionFemalesDeferoxamine Mesylate for Injection can cause embryo-fetal harm when administered to pregnant women
[see Use in Specific Populations ].Advise female patients of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection and for one month after the last dose.