Delflex
(Dextrose Monohydrate, Sodium Chloride, Sodium Lactate, Calcium Chloride, Magnesium Chloride)Delflex Prescribing Information
DELFLEX® is indicated in the treatment of chronic kidney failure in patients being maintained on peritoneal dialysis.
For intraperitoneal dialysis only. (
For intraperitoneal dialysis only.
DELFLEX® is intended for intraperitoneal administration only. Not for intravenous or intra-arterial administration.
The mode of therapy, frequency of treatment, formulation, exchange volume, duration of dwell, and length of dialysis should be selected by the physician responsible for the treatment of the individual patient.
Utilize the peritoneal dialysis solution with lowest level of osmolarity consistent with the fluid removal requirements for that exchange.
Do not store solutions containing additives.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration whenever solution and container permit.
Do not heat in a microwave oven.
- Clean work surface.
- Gather supplies:
- DELFLEX peritoneal dialysis bag(s).
- Prescribed medication(s), if ordered by your healthcare provider.
- Mask.
- PVC

Tear the overwrap from the slit edge down the length of the inner bag to open. Locate pull tabs on overwrap. Grasping one tab in each hand, pull outward, down the length of the inner bag to open. 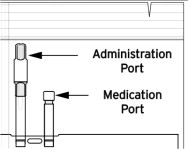
Wipe away any moisture from the solution bags. Some opacity may be observed in the plastic of the bag and/or tubing and is due to moisture absorption during the sterilization process. This is normal and does not affect the solution quality or safety. The opacity will diminish gradually. Wipe away any moisture from the solution bags. Inspect DELFLEX Solution Bag - After removing the overwrap, check your DELFLEX solution bag(s) for strength, clarity, amount, leaks, and expiration date. Do not use DELFLEX solution if leaks are found, the solution bag is damaged, and/or the solution is cloudy or discolored, or the product is expired. Color may vary from clear to slightly yellow but does not affect efficacy and may be used.
- Visually check that the solution bag tubing is free from kinks. If kinks are present, straighten tubing to allow the solution to flow freely.Note: Retain DELFLEX peritoneal dialysis bag sample for manufacturer evaluation and notify your healthcare provider if any of the above defects are found.
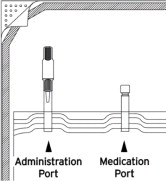
Note: DELFLEX peritoneal dialysis solutions utilize the Safe-Lock® Connection System. This unique system consists of two Safe-Lock connectors, one located on the administration port of the bag, and the mating connector is located on the cycler set. The Safe-Lock connectors were designed to reduce the potential risk of touch contamination of the internal connection components. - Put on mask. Wash your hands.
- If you will be adding medications(s):
- Clean hands (as per facility's protocol)
- Clean the medication port as instructed by your healthcare provider.
- Add the medicine(s).
- Turn the bag upside down several times to mix the medicine(s).
- To connect the bag(s) to the cycler set, unscrew the protective caps of the administration port and the cycler set solution line connector. Secure these two connectors with a twisting motion to lock in place, so that the cycler set connector is seated over the administration port O-ring to assure a firm and tight fit.
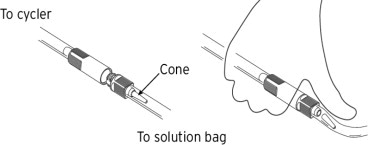
- After completing Step 8, wait for the cycler prompt to break the administration port cone and initiate solution flow. Do this by placing the thumb firmly on the tube over the cone and pressing towards the outer wall of the tube and away from the bag.
- Perform your treatment as prescribed.
- At the end of your treatment, throw away the fluid and used set as instructed by your healthcare provider.In case of cloudiness, save the fluid and the used set and immediately contact your healthcare provider.Dispose of your empty solution bag according to your local recycling program. Empty solution bags may not be recyclable in your area.




Compatible medications can be added via the medication port
DELFLEX peritoneal dialysis solutions are available in single-dose flexible bags comprised of either polyvinyl chloride (PVC), or a proprietary blend of polyolefins called Biofine®. All DELFLEX peritoneal dialysis solutions have overfills declared on the bag label.
DELFLEX peritoneal dialysis solutions are available in the sizes and formulations shown in
| PVC | Biofine® | ||||||
| 2L | 3L | 5L | 6L | 3L | 5L | 6L | |
| DELFLEX Standard with 1.5% Dextrose | X | X | X | X | |||
| DELFLEX Standard with 2.5% Dextrose | X | X | X | X | |||
| DELFLEX Low Magnesium, Low Calcium with 1.5% Dextrose | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| DELFLEX Low Magnesium, Low Calcium with 2.5% Dextrose | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| DELFLEX Low Magnesium, Low Calcium with 4.25% Dextrose | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| PVC | Biofine ® | ||||||
| 2L | 3L | 5L | 6L | 3L | 5L | 6L | |
| DELFLEX Standard with 1.5% Dextrose | X | X | X | X | |||
| DELFLEX Standard with 2.5% Dextrose | X | X | X | X | |||
| DELFLEX Low Magnesium, Low Calcium with 1.5% Dextrose | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| DELFLEX Low Magnesium, Low Calcium with 2.5% Dextrose | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| DELFLEX Low Magnesium, Low Calcium with 4.25% Dextrose | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
DELFLEX solutions consist of electrolytes, lactate, and bicarbonate at physiological levels, and glucose to facilitate ultrafiltration. While there are no adequate and well controlled studies in pregnant women, appropriate administration of DELFLEX with monitoring of fluid, electrolyte, acid-base and glucose balance, is not expected to cause fetal harm. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with DELFLEX.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population are unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
None.
- Monitor patient for electrolyte, fluid, and nutrition imbalances. ()
5.1 Electrolyte, Fluid and Nutrition ImbalancesPeritoneal dialysis may affect a patient's protein, water-soluble vitamin, potassium, sodium, chloride, bicarbonate, and magnesium levels and volume status. Monitor electrolytes and blood chemistry periodically and take appropriate clinical action.
Potassium is omitted from DELFLEX solutions because dialysis may be performed to correct hyperkalemia. In situations where there is a normal serum potassium level or hypokalemia, the addition of potassium chloride (up to a concentration of 4 mEq/L) may be indicated to prevent severe hypokalemia.
To avoid the risk of severe dehydration or hypovolemia and to minimize the loss of protein, it is advisable to select the peritoneal dialysis solution with lowest level of osmolarity consistent with the fluid removal requirements for that exchange.
Significant loss of protein, amino acids and water-soluble vitamins may occur during peritoneal dialysis. Replacement therapy should be provided as necessary.
- Encapsulating Peritonitis Sclerosis (EPS) ()
5.2 Peritonitis and Encapsulating Peritoneal SclerosisInfectious and aseptic peritonitis has been associated with peritoneal dialysis therapy. Following DELFLEX use, inspect the drained fluid for the presence of fibrin or cloudiness, which may indicate the presence of peritonitis. Improper clamping or priming sequence may result in infusion of air into the peritoneal cavity, which may result in abdominal pain and/or peritonitis. If peritonitis occurs, treat with appropriate therapy.
Encapsulating peritoneal sclerosis (EPS), sometimes fatal, is a complication of peritoneal dialysis therapy.
- Peritonitis: Initiate appropriate antimicrobial therapy ()
5.2 Peritonitis and Encapsulating Peritoneal SclerosisInfectious and aseptic peritonitis has been associated with peritoneal dialysis therapy. Following DELFLEX use, inspect the drained fluid for the presence of fibrin or cloudiness, which may indicate the presence of peritonitis. Improper clamping or priming sequence may result in infusion of air into the peritoneal cavity, which may result in abdominal pain and/or peritonitis. If peritonitis occurs, treat with appropriate therapy.
Encapsulating peritoneal sclerosis (EPS), sometimes fatal, is a complication of peritoneal dialysis therapy.
- Monitor for Lactic Acidosis in patients at risk. ()
5.3 Lactic AcidosisMonitor patients with conditions known to increase the risk of lactic acidosis [e.g., severe hypotension or sepsis that can be associated with acute kidney failure, inborn errors of metabolism, treatment with drugs such as nucleoside/nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs)] for lactic acidosis before the start of treatment and during treatment with DELFLEX.
Solutions containing the lactate ion should be used with great care in patients with metabolic or respiratory alkalosis. Lactate should be administered with great care in those conditions in which there is an increased level or an impaired utilization of this ion, such as severe hepatic insufficiency.