Dextrose
(Dextrose Monohydrate)Dextrose Prescribing Information
Dosage and Administration (
• Dextrose Injection is intended for intravenous use.• Peripheral administration of 5% dextrose is generally acceptable, however, consider central vein when administering more than 5% dextrose or with an osmolarity of at least 900 mOsm/L or when there is peripheral vein irritation, phlebitis, and/or associated pain[see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].• Do not administer Dextrose Injection simultaneously with blood products through the same administration set because of the possibility of pseudoagglutination or hemolysis.• To prevent air embolism, use a non-vented infusion set or close the vent on a vented set, avoid multiple connections, do not connect flexible containers in series, do not pressurize the flexible container to increase flow rates, and if administration is controlled by a pumping device, turn off pump before the container runs dry.• Prior to infusion, visually inspect the infusion solution for particulate matter. The solution should be clear and there should be no precipitates. Do not administer unless solution is clear and container is undamaged.• Use of a final filter is recommended during administration of parenteral solutions, where possible.• Consult the full prescribing information of the medication to be added. Prior to adding the medication, verify that it is soluble and/or stable in Dextrose Injection and that the pH range is appropriate.
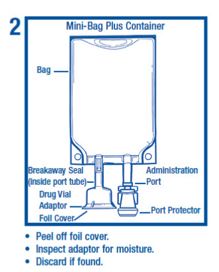
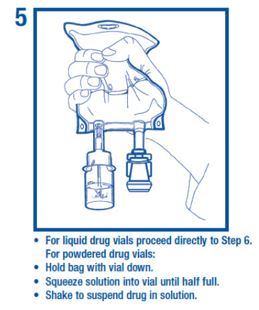
• Do not remove from overpouch until ready to use.• Tear overwrap sharply down from the slit and remove solution container. Small amounts of moisture may be found on the solution container from water permeating from inside the container. The amount of permeated water is insufficient to affect the solution significantly. If larger amounts of water are found, the container should be checked for tears or leaks.• Visually inspect the container. Some opacity of the plastic due to moisture absorption during the sterilization process may be observed. This is normal and does not affect the solution quality or safety. The opacity will diminish gradually. Evaluate the following:• If the outlet port protector is damaged, detached, or not present, discard container.• Check to ensure the solution is clear and there are no precipitates. Discard if there is a color change and/or the appearance of precipitates, insoluble complexes or crystals.• Check for leaks by separately squeezing the inner bag firmly. If leaks are found, discard container.• Check that the vial adaptor cover is intact. If the vial adaptor cover is not intact, discard product.
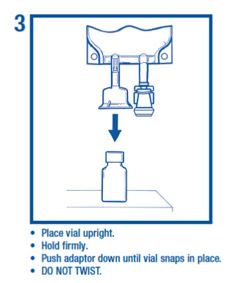
• Use aseptic technique to attach the vial to the adaptor.
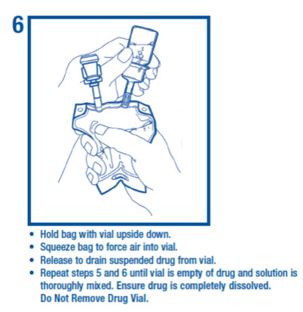
7.000000000000000e+00 Remove port protector. Attach administration set per its directions.8.000000000000000e+00 Hang container on I.V. pole and prime set per directions. Ensure that vial is empty of drug and solution. Repeat step 6 if drug and solution remain in vial.Warning: Do not use in series connections.
9.000000000000000e+00 Administer medication per institutional practices.1.000000000000000e+01 Use within specified time for drug stability.1.100000000000000e+01 Discard unused portion.
Consult the full prescribing information of the added medication.






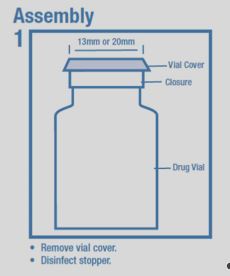
Dextrose Injection is indicated as source of water and calories and may also be used as diluent for reconstitution of a powdered or liquid (up to 10 mL) drug product packaged in a vial with a 13 mm or 20 mm closure.
• Only for intravenous infusion. ()2.1 Important Administration Instructions• Dextrose Injection is intended for intravenous use.• Peripheral administration of 5% dextrose is generally acceptable, however, consider central vein when administering more than 5% dextrose or with an osmolarity of at least 900 mOsm/L or when there is peripheral vein irritation, phlebitis, and/or associated pain[see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].• Do not administer Dextrose Injection simultaneously with blood products through the same administration set because of the possibility of pseudoagglutination or hemolysis.• To prevent air embolism, use a non-vented infusion set or close the vent on a vented set, avoid multiple connections, do not connect flexible containers in series, do not pressurize the flexible container to increase flow rates, and if administration is controlled by a pumping device, turn off pump before the container runs dry.• Prior to infusion, visually inspect the infusion solution for particulate matter. The solution should be clear and there should be no precipitates. Do not administer unless solution is clear and container is undamaged.• Use of a final filter is recommended during administration of parenteral solutions, where possible.• Consult the full prescribing information of the medication to be added. Prior to adding the medication, verify that it is soluble and/or stable in Dextrose Injection and that the pH range is appropriate.
• See full prescribing information for information on preparation, administration, dosing considerations and instructions for use. (,2.1 Important Administration Instructions• Dextrose Injection is intended for intravenous use.• Peripheral administration of 5% dextrose is generally acceptable, however, consider central vein when administering more than 5% dextrose or with an osmolarity of at least 900 mOsm/L or when there is peripheral vein irritation, phlebitis, and/or associated pain[see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].• Do not administer Dextrose Injection simultaneously with blood products through the same administration set because of the possibility of pseudoagglutination or hemolysis.• To prevent air embolism, use a non-vented infusion set or close the vent on a vented set, avoid multiple connections, do not connect flexible containers in series, do not pressurize the flexible container to increase flow rates, and if administration is controlled by a pumping device, turn off pump before the container runs dry.• Prior to infusion, visually inspect the infusion solution for particulate matter. The solution should be clear and there should be no precipitates. Do not administer unless solution is clear and container is undamaged.• Use of a final filter is recommended during administration of parenteral solutions, where possible.• Consult the full prescribing information of the medication to be added. Prior to adding the medication, verify that it is soluble and/or stable in Dextrose Injection and that the pH range is appropriate.
,2.2 Recommended DosageThe choice of dextrose concentration, rate and volume depends on the age, weight, clinical and metabolic conditions of the patient and concomitant therapy. Electrolyte supplementation may be indicated according to the clinical needs of the patient.
The administration rate should be governed, especially for premature infants with low birth weight, during the first few days of therapy, by the patient’s tolerance to dextrose.
Increase the infusion rate gradually as indicated by frequent monitoring of blood glucose concentrations
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].)2.3 Instructions for UseTo Open• Do not remove from overpouch until ready to use.• Tear overwrap sharply down from the slit and remove solution container. Small amounts of moisture may be found on the solution container from water permeating from inside the container. The amount of permeated water is insufficient to affect the solution significantly. If larger amounts of water are found, the container should be checked for tears or leaks.• Visually inspect the container. Some opacity of the plastic due to moisture absorption during the sterilization process may be observed. This is normal and does not affect the solution quality or safety. The opacity will diminish gradually. Evaluate the following:• If the outlet port protector is damaged, detached, or not present, discard container.• Check to ensure the solution is clear and there are no precipitates. Discard if there is a color change and/or the appearance of precipitates, insoluble complexes or crystals.• Check for leaks by separately squeezing the inner bag firmly. If leaks are found, discard container.• Check that the vial adaptor cover is intact. If the vial adaptor cover is not intact, discard product.
Preparation for Administration• Use aseptic technique to attach the vial to the adaptor.






7.000000000000000e+00 Remove port protector. Attach administration set per its directions.8.000000000000000e+00 Hang container on I.V. pole and prime set per directions. Ensure that vial is empty of drug and solution. Repeat step 6 if drug and solution remain in vial.Warning: Do not use in series connections.
9.000000000000000e+00 Administer medication per institutional practices.1.000000000000000e+01 Use within specified time for drug stability.1.100000000000000e+01 Discard unused portion.
Storage of the infusion solutionConsult the full prescribing information of the added medication.

Assembly 1 
Assembly step 2 
Assembly part 3 
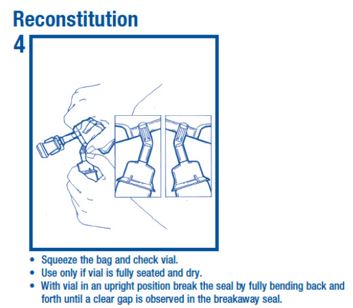
Reconstitution Step 4 
Reconstitution Step 5 
Reconstitution Step 6
Dextrose Injection, USP is a clear, sterile, non-pyrogenic solution supplied as 5 grams of dextrose hydrous per 100 mL (0.05 grams/mL) in 50 mL and 100 mL single-dose, flexible containers.
The safety profile of Dextrose Injection in pediatric patients is similar to adults.
Neonates, especially premature infants with low birth weight, are at increased risk of developing hypo- or hyperglycemia and therefore need close monitoring during treatment with intravenous glucose infusions to ensure adequate glycemic control in order to avoid potential long-term adverse effects.
Closely monitor plasma electrolyte concentrations in pediatric patients who may have impaired ability to regulate fluids and electrolytes. In very low birth weight infants, excessive or rapid administration of Dextrose Injection may result in increased serum osmolality and risk of intracerebral hemorrhage.
Children (including neonates and older children) are at increased risk of developing hyponatremia as well as for developing hyponatremic encephalopathy
The use of Dextrose Injection is contraindicated in patients with:
• Clinically significant hyperglycemia[see].5.1 Hyperglycemia and Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic StateThe use of dextrose infusions in patients with impaired glucose tolerance may worsen hyperglycemia. Administration of dextrose at a rate exceeding the patient’s utilization rate may lead to hyperglycemia, coma, and death.
Hyperglycemia is associated with an increase in serum osmolality, resulting in osmotic diuresis, dehydration and electrolyte losses
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]. Patients with underlying CNS disease and renal impairment who receive dextrose infusions, may be at greater risk of developing hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state.Monitor blood glucose levels and treat hyperglycemia to maintain levels within normal limits while administering Dextrose Injection. Insulin may be administered or adjusted to maintain optimal blood glucose levels during Dextrose Injection administration.
• Known hypersensitivity to dextrose[see].5.2 Hypersensitivity ReactionsHypersensitivity and infusion reactions including anaphylaxis, have been reported with Dextrose Injection
[see Adverse Reactions (6)]. Stop infusion immediately and treat patient accordingly if signs or symptoms of a hypersensitivity reaction develop. Appropriate therapeutic countermeasures must be instituted as clinically indicated.