Diltiazem Hydrochloride
Diltiazem Hydrochloride Prescribing Information
Diltiazem hydrochloride extended-release capsules, USP is indicated for the treatment of hypertension. It may be used alone or in combination with other antihypertensive medications.
Diltiazem hydrochloride extended-release capsules, USP is indicated for the management of chronic stable angina and angina due to coronary artery spasm.
Patients controlled on diltiazem alone or in combination with other medications may be switched to Diltiazem Hydrochloride Extended-Release Capsules, USP at the nearest equivalent total daily dose. Higher doses of diltiazem hydrochloride extended-release capsules may be needed in some patients. Monitor patients closely. Subsequent titration to higher or lower doses may be necessary. There is limited general clinical experience with doses above 360 mg, but doses to 540 mg have been studied in clinical trials. The incidence of side effects increases as the dose increases with first-degree AV block, dizziness, and sinus bradycardia bearing the strongest relationship to dose.
Diltiazem hydrochloride tablets is extensively metabolized by the liver and excreted by the kidneys and in bile. Laboratory parameters of renal and hepatic function should be monitored at regular intervals. In subacute and chronic dog and rat studies designed to produce toxicity, high doses of diltiazem were associated with hepatic damage. In special subacute hepatic studies, oral doses of 125 mg/kg and higher in rats were associated with histological changes in the liver which were reversible when the drug was discontinued. In dogs, doses of 20 mg/kg were also associated with hepatic changes; however, these changes were reversible with continued dosing.
Dermatological events (see
Because of the potential for additive effects, slow titration is warranted in patients receiving diltiazem hydrochloride tablets concomitantly with other agents known to affect cardiac contractility and/or conduction (see
Diltiazem is both a substrate and an inhibitor of the cytochrome P450 3A4 enzyme system. Other drugs that are specific substrates, inhibitors, or inducers of this enzyme system may have a significant impact on the efficacy and side effect profile of diltiazem. Patients taking other drugs that are substrates of CYP450 3A4, especially patients with renal and/or hepatic impairment, may require dosage adjustment when starting or stopping concomitantly administered diltiazem in order to maintain optimum therapeutic blood levels.
Administration of diltiazem hydrochloride tablets concomitantly with propranolol in five normal volunteers resulted in increased propranolol levels in all subjects and bioavailability of propranolol was increased approximately 50%.
5.5-fold and Cmax4.1-fold compared to placebo. The T1/2and Tmaxof buspirone were not significantly affected by diltiazem. Enhanced effects and increased toxicity of buspirone may be possible during concomitant administration with diltiazem. Subsequent dose adjustments may be necessary during coadministration, and should be based on clinical assessment.
The effect of cyclosporine on diltiazem plasma concentrations has not been evaluated.
In a healthy volunteer crossover study (N=10), coadministration of a single 20 mg dose of simvastatin at the end of a 14-day regimen with 120 mg BID diltiazem SR resulted in a 5-fold increase in mean simvastatin AUC versus simvastatin alone. Subjects with increased average steady-state exposures of diltiazem showed a greater fold increase in simvastatin exposure. Computer-based simulations showed that at a daily dose of 480 mg of diltiazem, an 8- to 9-fold mean increase in simvastatin AUC can be expected. If coadministration of simvastatin with diltiazem is required, limit the daily doses of simvastatin to 10 mg and diltiazem to 240 mg.
In a ten-subject randomized, open-label, 4-way crossover study, coadministration of diltiazem (120 mg BID diltiazem SR for 2 weeks) with a single 20 mg dose of lovastatin resulted in 3- to 4-fold increase in mean lovastatin AUC and Cmaxversus lovastatin alone. In the same study, there was no significant change in 20 mg single dose pravastatin AUC and Cmaxduring diltiazem coadministration. Diltiazem plasma levels were not significantly affected by lovastatin or pravastatin.
A 24-month study in rats at oral dosage levels of up to 100 mg/kg/day and a 21-month study in mice at oral dosage levels of up to 30 mg/kg/day showed no evidence of carcinogenicity. There was also no mutagenic response
Reproduction studies have been conducted in mice, rats, and rabbits. Administration of doses ranging from five to ten times greater (on a mg/kg basis) than the daily recommended therapeutic dose has resulted in embryo and fetal lethality. These doses, in some studies, have been reported to cause skeletal abnormalities. In the perinatal/postnatal studies, there was an increased incidence of stillbirths at doses of 20 times the human dose or greater.
There are no well-controlled studies in pregnant women; therefore, use diltiazem hydrochloride tablets in pregnant women only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Diltiazem is excreted in human milk. One report suggests that concentrations in breast milk may approximate serum levels. If use of diltiazem hydrochloride tablets is deemed essential, an alternative method of infant feeding should be instituted.
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Clinical studies of diltiazem did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
Diltiazem hydrochloride tablets are contraindicated in (1) patients with sick sinus syndrome except in the presence of a functioning ventricular pacemaker, (2) patients with second- or third-degree AV block except in the presence of a functioning ventricular pacemaker, (3) patients with hypotension (less than 90 mm Hg systolic), (4) patients who have demonstrated hypersensitivity to the drug, and (5) patients with acute myocardial infarction and pulmonary congestion documented by x-ray on admission.
Serious adverse reactions have been rare in studies carried out to date, but it should be recognized that patients with impaired ventricular function and cardiac conduction abnormalities have usually been excluded from these studies.
The following table presents the most common adverse reactions reported in placebo-controlled angina and hypertension trials in patients receiving diltiazem hydrochloride extended-release capsules up to 360 mg with rates in placebo patients shown for comparison.
| Adverse Reactions | Diltiazem Hydrochloride Extended-Release Capsules (n=607) | Placebo (n=301) |
| Headache | 5.4% | 5.0% |
| Dizziness | 3.0% | 3.0% |
| Bradycardia | 3.3% | 1.3% |
| AV Block First Degree | 3.3% | 0.0% |
| Edema | 2.6% | 1.3% |
| Asthenia | 1.8% | 1.7% |
In addition, the following events were reported infrequently (less than 1%) in angina or hypertension trials:
The following postmarketing events have been reported infrequently in patients receiving diltiazem hydrochloride tablets: acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis, allergic reactions, alopecia, angioedema (including facial or periorbital edema), asystole, erythema multiforme (including Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis), exfoliative dermatitis, extrapyramidal symptoms, gingival hyperplasia, hemolytic anemia, increased bleeding time, leukopenia, photosensitivity (including lichenoid keratosis and hyperpigmentation at sun-exposed skin areas), purpura, retinopathy, myopathy, and thrombocytopenia. In addition, events such as myocardial infarction have been observed which are not readily distinguishable from the natural history of the disease in these patients. A number of well-documented cases of generalized rash, some characterized as leukocytoclastic vasculitis, have been reported. However, a definitive cause and effect relationship between these events and diltiazem hydrochloride tablets therapy is yet to be established.
Because of the potential for additive effects, slow titration is warranted in patients receiving diltiazem hydrochloride tablets concomitantly with other agents known to affect cardiac contractility and/or conduction (see
Diltiazem is both a substrate and an inhibitor of the cytochrome P450 3A4 enzyme system. Other drugs that are specific substrates, inhibitors, or inducers of this enzyme system may have a significant impact on the efficacy and side effect profile of diltiazem. Patients taking other drugs that are substrates of CYP450 3A4, especially patients with renal and/or hepatic impairment, may require dosage adjustment when starting or stopping concomitantly administered diltiazem in order to maintain optimum therapeutic blood levels.
Administration of diltiazem hydrochloride tablets concomitantly with propranolol in five normal volunteers resulted in increased propranolol levels in all subjects and bioavailability of propranolol was increased approximately 50%.
5.5-fold and Cmax 4.1-fold compared to placebo. The T1/2 and Tmax of buspirone were not significantly affected by diltiazem. Enhanced effects and increased toxicity of buspirone may be possible during concomitant administration with diltiazem. Subsequent dose adjustments may be necessary during coadministration, and should be based on clinical assessment.
The effect of cyclosporine on diltiazem plasma concentrations has not been evaluated.
In a healthy volunteer crossover study (N=10), coadministration of a single 20 mg dose of simvastatin at the end of a 14-day regimen with 120 mg BID diltiazem SR resulted in a 5-fold increase in mean simvastatin AUC versus simvastatin alone. Subjects with increased average steady-state exposures of diltiazem showed a greater fold increase in simvastatin exposure. Computer-based simulations showed that at a daily dose of 480 mg of diltiazem, an 8- to 9-fold mean increase in simvastatin AUC can be expected. If coadministration of simvastatin with diltiazem is required, limit the daily doses of simvastatin to 10 mg and diltiazem to 240 mg.
In a ten-subject randomized, open-label, 4-way crossover study, coadministration of diltiazem (120 mg BID diltiazem SR for 2 weeks) with a single 20 mg dose of lovastatin resulted in 3- to 4-fold increase in mean lovastatin AUC and Cmax versus lovastatin alone. In the same study, there was no significant change in 20 mg single dose pravastatin AUC and Cmax during diltiazem coadministration. Diltiazem plasma levels were not significantly affected by lovastatin or pravastatin.
Diltiazem Hydrochloride Extended-Release Capsules, USP is a calcium ion cellular influx inhibitor (slow channel blocker or calcium antagonist). Chemically, diltiazem hydrochloride is 1,5-Benzothiazepin-4(5
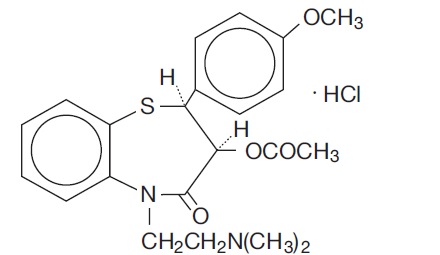
Diltiazem hydrochloride is a white to off-white crystalline powder with a bitter taste. It is soluble in water, methanol, and chloroform. It has a molecular weight of 450.98. Diltiazem Hydrochloride Extended-Release Capsules, USP is formulated as a once-a-day extended-release capsule containing 120 mg diltiazem hydrochloride (equivalent to 110.3 mg diltiazem), 180 mg diltiazem hydrochloride (equivalent to 165.45 mg diltiazem), 240 mg diltiazem hydrochloride (equivalent to 220.6 mg diltiazem) or 300 mg diltiazem hydrochloride (equivalent to 275.75 mg diltiazem).
Each diltiazem hydrochloride extended-release capsule, contains the following inactive ingredients: ammonio methacrylate copolymer NF, type A, ammonio methacrylate copolymer NF, type B, ammonium hydroxide, gelatin, hydroxypropyl cellulose, propylene glycol, shellac, sodium lauryl sulfate, sucrose, corn starch, talc, titanium dioxide, triethyl citrate and black iron oxide. In addition, the 180 mg capsules contains D&C yellow #10, FD&C blue #1, FD&C green #3, 240 mg capsules contains D&C yellow #10, FD&C green #3 and 300 mg capsules contains black iron oxide, D&C yellow #10, FD&C green #3.
For oral administration.
This drug product conforms to USP Drug release test #11.