Dipentum
(Olsalazine Sodium)Dipentum Prescribing Information
DIPENTUM is indicated for the maintenance of remission of ulcerative colitis in adult patients who are intolerant of sulfasalazine.
Evaluate renal function before initiating therapy with DIPENTUM
Renal impairment, including minimal change disease, acute and chronic interstitial nephritis, and renal failure have been reported in patients given DIPENTUM or other products that contain mesalamine or are converted to mesalamine. In animal studies, the kidney was the principal organ of mesalamine toxicity
Evaluate the risks and benefits of using DIPENTUM in patients with known renal impairment or a history of renal disease or taking concomitant nephrotoxic drugs. Evaluate renal function in all patients prior to initiation and periodically while on DIPENTUM therapy. Discontinue DIPENTUM if renal function deteriorates while on therapy
The recommended dosage is 500 mg orally twice daily.
Drink an adequate amount of fluids during treatment
Cases of nephrolithiasis have been reported with the use of mesalamine, the active moiety in DIPENTUM, including stones with 100% mesalamine content. Mesalamine‑containing stones are radiotransparent and undetectable by standard radiography or computed tomography (CT). Ensure adequate fluid intake during treatment.
Capsules: 250 mg olsalazine sodium in beige capsules imprinted with DIPENTUM® 250 mg on the capsule shell
Clinical studies of DIPENTUM did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Reports from uncontrolled clinical studies and postmarketing reporting systems suggested a higher incidence of blood dyscrasias (i.e., agranulocytosis, neutropenia and pancytopenia) in patients receiving mesalamine-containing products such as DIPENTUM who were 65 years or older compared to younger adult patients, which may also be associated with ulcerative colitis, use of interacting drugs, or reduced renal function.
Consider monitoring of complete blood cell counts and platelet counts in patients 65 years and over during treatment with DIPENTUM. In general, consider the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concurrent disease or other drug therapy in patients 65 years and over when prescribing DIPENTUM.
DIPENTUM is contraindicated in patients with known or suspected hypersensitivity to salicylates, aminosalicylates, or to any of the excipients in DIPENTUM
Some patients who have experienced a hypersensitivity reaction to sulfasalazine may have a similar reaction to DIPENTUM or to other compounds that contain or are converted to mesalamine. Mesalamine‑induced hypersensitivity reactions may present as internal organ involvement, including myocarditis, pericarditis, nephritis, hepatitis, pneumonitis, and hematologic abnormalities. Evaluate patients immediately if signs or symptoms of a hypersensitivity reaction are present. Discontinue DIPENTUM if an alternative etiology for the signs and symptoms cannot be established.
The active ingredient in DIPENTUM (olsalazine sodium) is the sodium salt of a salicylate, disodium 3,3'-azobis (6-hydroxybenzoate) a compound that is effectively bioconverted to mesalamine (5-aminosalicylic acid,5-ASA), an aminosalicylate. Its empirical formula is C14H8N2Na2O6 with a molecular weight of 346.21.
The structural formula is:
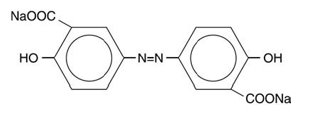
Olsalazine sodium is a yellow crystalline powder, which melts with decomposition at 240°C. It is the sodium salt of a weak acid, soluble in water and DMSO, and practically insoluble in ethanol, chloroform, and ether. Olsalazine sodium has acceptable stability under acidic or basic conditions.
DIPENTUM is supplied in capsules for oral administration. Each DIPENTUM hard gelatin capsule contains 250 mg olsalazine sodium (equivalent to 233.4 mg of olsalazine). The inert ingredient in each capsule is magnesium stearate. The capsule shell contains the following inactive ingredients: black iron oxide, caramel, gelatin, and titanium dioxide.

• Renal Impairment: Assess renal function at the beginning of treatment and periodically during treatment. Discontinue DIPENTUM if renal function deteriorates while on therapy. (,5.1 Renal ImpairmentRenal impairment, including minimal change disease, acute and chronic interstitial nephritis, and renal failure have been reported in patients given DIPENTUM or other products that contain mesalamine or are converted to mesalamine. In animal studies, the kidney was the principal organ of mesalamine toxicity
[see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.2)].Evaluate the risks and benefits of using DIPENTUM in patients with known renal impairment or a history of renal disease or taking concomitant nephrotoxic drugs. Evaluate renal function in all patients prior to initiation and periodically while on DIPENTUM therapy. Discontinue DIPENTUM if renal function deteriorates while on therapy
[see Drug Interactions (7.1), Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].)7.1 Nephrotoxic Agents, Including Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory DrugsThe concurrent use of mesalamine with known nephrotoxic agents, including non‑steroidal anti‑inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), may increase the risk of nephrotoxicity. Monitor patients taking nephrotoxic drugs for changes in renal function and mesalamine-related adverse reactions
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].• Mesalamine-Induced Acute Intolerance Syndrome: Discontinue treatment if acute intolerance syndrome (cramping, acute abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea, sometimes fever, headache and rash) is suspected. ()5.2 Mesalamine-Induced Acute Intolerance SyndromeOlsalazine is converted to mesalamine, which has been associated with an acute intolerance syndrome that may be difficult to distinguish from an exacerbation of ulcerative colitis. Symptoms include cramping, acute abdominal pain and bloody diarrhea, sometimes fever, headache, and rash. Monitor patients for worsening of these symptoms while on treatment. If acute intolerance syndrome is suspected, promptly discontinue treatment with DIPENTUM.
• Hypersensitivity Reactions, including myocarditis and pericarditis: Discontinue DIPENTUM if a hypersensitivity reaction is suspected. ()5.3 Hypersensitivity ReactionsSome patients who have experienced a hypersensitivity reaction to sulfasalazine may have a similar reaction to DIPENTUM or to other compounds that contain or are converted to mesalamine. Mesalamine‑induced hypersensitivity reactions may present as internal organ involvement, including myocarditis, pericarditis, nephritis, hepatitis, pneumonitis, and hematologic abnormalities. Evaluate patients immediately if signs or symptoms of a hypersensitivity reaction are present. Discontinue DIPENTUM if an alternative etiology for the signs and symptoms cannot be established.
• Hepatic Failure: Evaluate the risks and benefits of using DIPENTUM in patients with known liver impairment. ()5.4 Hepatic FailureThere have been reports of hepatic failure in patients with pre-existing liver disease who have been administered mesalamine. Because olsalazine is converted to mesalamine, evaluate the risks and benefits of using DIPENTUM in patients with known liver impairment.
• Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions: Discontinue at the first signs or symptoms of severe cutaneous adverse reactions or other signs of hypersensitivity and consider further evaluation. ()5.5 Severe Cutaneous Adverse ReactionsSevere cutaneous adverse reactions, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), and acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) have been reported with the use of mesalamine, the active moiety in DIPENTUM
[see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]. Discontinue DIPENTUM at the first signs or symptoms of severe cutaneous adverse reactions or other signs of hypersensitivity and consider further evaluation.• Photosensitivity: Avoid sun exposure if pre-existing skin conditions. ()5.6 PhotosensitivityPatients with pre‑existing skin conditions such as atopic dermatitis and atopic eczema have reported more severe photosensitivity reactions. Advise patients to avoid sun exposure, wear protective clothing, and use a broad-spectrum sunscreen when outdoors.
• Nephrolithiasis: Cases of nephrolithiasis have been reported with the use of mesalamine. Mesalamine-containing stones are undetectable by standard radiography or computed tomography (CT). Ensure adequate hydration during treatment. ()5.7 NephrolithiasisCases of nephrolithiasis have been reported with the use of mesalamine, the active moiety in DIPENTUM, including stones with 100% mesalamine content. Mesalamine‑containing stones are radiotransparent and undetectable by standard radiography or computed tomography (CT). Ensure adequate fluid intake during treatment.
• Interference with Laboratory Tests: Mesalamine may lead to elevated urinary normetanephrine test results. ()5.8 Interference with Laboratory TestsUse of DIPENTUM, which is converted to mesalamine, may lead to spuriously elevated test results when measuring urinary normetanephrine by liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection because of the similarity in the chromatograms of normetanephrine and the main metabolite of mesalamine, N‑acetyl‑5‑aminosalicylic acid (N‑Ac‑5‑ASA). Consider an alternative, selective assay for normetanephrine.