Diphenhydramine
(Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride)Diphenhydramine Prescribing Information
For use in parkinsonism, when oral therapy is impossible or contraindicated, as follows: parkinsonism in the elderly who are unable to tolerate more potent agents; mild cases of parkinsonism in other age groups, and in other cases of parkinsonism in combination with centrally acting anticholinergic agents.
THIS PRODUCT IS FOR INTRAVENOUS OR INTRAMUSCULAR ADMINISTRATION ONLY.
Diphenhydramine hydrochloride in the injectable form is indicated when the oral form is impractical.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
DOSAGE SHOULD BE INDIVIDUALIZED ACCORDING TO THE NEEDS AND THE RESPONSE OF THE PATIENT.
2/24 hr. Maximum daily dosage is 300 mg. Divide into four doses, administered intravenously at a rate generally not exceeding 25 mg/min, or deep intramuscularly.
Because of the risk of local necrosis, this drug should not be used as a local anesthetic.
- Urticaria, drug rash, anaphylactic shock, photosensitivity, excessive perspiration, chills, dryness of mouth, nose and throat.General:
- Hypotension, headache, palpitations, tachycardia, extrasystoles.Cardiovascular System:
- Hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis.Hematologic System:
- Nervous System:Sedation,sleepiness,dizziness,disturbed coordination, fatigue, confusion, restlessness, excitation, nervousness, tremor, irritability, insomnia, euphoria, paresthesia, blurred vision, diplopia, vertigo, tinnitus, acute labyrinthitis, neuritis, convulsions.
- GI System:Epigastric distress, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation.
- Urinary frequency, difficult urination, urinary retention, early menses.GU System:
- Respiratory System:Thickeningofbronchialsecretions, tightness of chest or throat and wheezing, nasal stuffiness.
Diphenhydramine hydrochloride is an antihistamine drug having the chemical name 2-(Diphenylmethoxy)-N,N-dimethylethylamine hydrochloride. It occurs as a white, crystalline powder, is freely soluble in water and alcohol.
The structural formula is as follows:
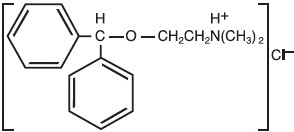
Diphenhydramine hydrochloride in the parenteral form is a sterile, pyrogen-free solution available in a concentration of 50 mg of diphenhydramine hydrochloride per mL. pH 4.0 to 6.5; sodium hydroxide and/or hydrochloric acid added, if needed, for pH adjustment.
Diphenhydramine hydrochloride is an antihistamine with anticholinergic (drying) and sedative side effects. Antihistamines appear to compete with histamine for cell receptor sites on effector cells.
Diphenhydramine hydrochloride in the injectable form has a rapid onset of action. Diphenhydramine hydrochloride is widely distributed throughout the body, including the CNS. A portion of the drug is excreted unchanged in the urine, while the rest is metabolized via the liver. Detailed information on the pharmacokinetics of diphenhydramine hydrochloride injection is not available.