Dobutamine
Dobutamine Prescribing Information
Dobutamine is indicated when parenteral therapy is necessary for inotropic support in the
Whether given orally, continuously intravenously, or intermittently intravenously, neither dobutamine nor any other cyclic-AMP-dependent inotrope has been shown in controlled trials to be safe or effective in the long-term treatment of congestive heart failure. In controlled trials of chronic oral therapy with various such agents, symptoms were not consistently alleviated, and the cyclic-AMP-dependent inotropes were consistently associated with increased risk of hospitalization and death. Patients with NYHA Class IV symptoms appeared to be at particular risk.
Dobutamine is contraindicated in patients with idiopathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis and in patients who have shown previous manifestations of hypersensitivity to dobutamine.
Animal studies indicate that dobutamine may be ineffective if the patient has recently received a ß-blocking drug. In such a case, the peripheral vascular resistance may increase.
Preliminary studies indicate that the concomitant use of dobutamine and nitroprusside results in a higher cardiac output and, usually, a lower pulmonary wedge pressure than when either drug is used alone.
There was no evidence of drug interactions in clinical studies in which dobutamine was administered concurrently with other drugs, including digitalis preparations, furosemide, spironolactone, lidocaine, glyceryl trinitrate, isosorbide dinitrate, morphine, atropine, heparin, protamine, potassium chloride, folic acid, and acetaminophen.
Dobutamine Injection USP is (±)-4-[2-[[3-(
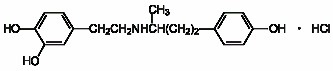
Molecular Formula: C18H23NO3•HCl
Molecular Weight: 337.84
The clinical formulation is supplied in a sterile form for intravenous use only. Each mL contains: dobutamine hydrochloride, equivalent to 12.5 mg (41.5 µmol) dobutamine; sodium metabisulfite 0.26 mg, and water for injection, q.s. Hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide may have been added during manufacture to adjust the pH (2.5 to 5.5).
Dobutamine is a direct-acting inotropic agent whose primary activity results from stimulation of the ß receptors of the heart while producing comparatively mild chronotropic, hypertensive, arrhythmogenic, and vasodilative effects. It does not cause the release of endogenous norepinephrine, as does dopamine. In animal studies, dobutamine produces less increase in heart rate and less decrease in peripheral vascular resistance for a given inotropic effect than does isoproterenol.
In patients with depressed cardiac function, both dobutamine and isoproterenol increase the cardiac output to a similar degree. In the case of dobutamine, this increase is usually not accompanied by marked increases in heart rate (although tachycardia is occasionally observed), and the cardiac stroke volume is usually increased. In contrast, isoproterenol increases the cardiac index primarily by increasing the heart rate while stroke volume changes little or declines.
Facilitation of atrioventricular conduction has been observed in human electrophysiologic studies and in patients with atrial fibrillation.
Systemic vascular resistance is usually decreased with administration of dobutamine. Occasionally, minimum vasoconstriction has been observed.
Most clinical experience with dobutamine is short-term–not more than several hours in duration. In the limited number of patients who were studied for 24, 48, and 72 hours, a persistent increase in cardiac output occurred in some, whereas output returned toward baseline values in others.
The onset of action of dobutamine is within 1 to 2 minutes; however, as much as 10 minutes may be required to obtain the peak effect of a particular infusion rate.
The plasma half-life of dobutamine in humans is 2 minutes. The principal routes of metabolism are methylation of the catechol and conjugation. In human urine, the major excretion products are the conjugates of dobutamine and 3-O-methyl dobutamine. The 3-O-methyl derivative of dobutamine is inactive.
Alteration of synaptic concentrations of catecholamines with either reserpine or tricyclic antidepressants does not alter the actions of dobutamine in animals, which indicates that the actions of dobutamine are not dependent on presynaptic mechanisms.
The effective infusion rate of dobutamine varies widely from patient to patient, and titration is always necessary (see