Donepezil Hydrochloride
Donepezil Hydrochloride Prescribing Information
Donepezil hydrochloride tablets are indicated for the treatment of dementia of the Alzheimer’s type. Efficacy has been demonstrated in patients with mild, moderate, and severe Alzheimer’s disease.
Donepezil hydrochloride tablets, USP are supplied as film-coated, round tablets containing 23 mg of donepezil hydrochloride.
The 23 mg tablets are reddish, debossed with ‘R’ on one side and ’23’ on other side.
Donepezil hydrochloride tablets are contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to donepezil hydrochloride or to piperidine derivatives.
The following serious adverse reactions are described below and elsewhere in the labeling:
- Cardiovascular Conditions [see Warnings and Precautions]
5.2 Cardiovascular ConditionsBecause of their pharmacological action, cholinesterase inhibitors may have vagotonic effects on the sinoatrial and atrioventricular nodes. This effect may manifest as bradycardia or heart block in patients both with and without known underlying cardiac conduction abnormalities. Syncopal episodes have been reported in association with the use of donepezil hydrochloride.
- Nausea and Vomiting [see Warnings and Precautions]
5.3 Nausea and VomitingDonepezil hydrochloride, as a predictable consequence of its pharmacological properties, has been shown to produce diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. These effects, when they occur, appear more frequently with the 10 mg/day dose than with the 5 mg/day dose, and more frequently with the 23 mg dose than with the 10 mg dose. Specifically, in a controlled trial that compared a dose of 23 mg/day to 10 mg/day in patients who had been treated with donepezil 10 mg/day for at least three months, the incidence of nausea in the 23 mg group was markedly greater than in the patients who continued on 10 mg/day (11.8% vs 3.4%, respectively), and the incidence of vomiting in the 23 mg group was markedly greater than in the 10 mg group (9.2% vs 2.5%, respectively). The percent of patients who discontinued treatment due to vomiting in the 23 mg group was markedly higher than in the 10 mg group (2.9% vs 0.4%, respectively).
Although in most cases, these effects have been transient, sometimes lasting one to three weeks, and have resolved during continued use of donepezil hydrochloride, patients should be observed closely at the initiation of treatment and after dose increases.
- Peptic Ulcer Disease and GI Bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions]
5.4 Peptic Ulcer Disease and GI BleedingThrough their primary action, cholinesterase inhibitors may be expected to increase gastric acid secretion due to increased cholinergic activity. Therefore, patients should be monitored closely for symptoms of active or occult gastrointestinal bleeding, especially those at increased risk for developing ulcers, e.g., those with a history of ulcer disease or those receiving concurrent nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Clinical studies of donepezil hydrochloride tablets in a dose of 5 mg/day to 10 mg/day have shown no increase, relative to placebo, in the incidence of either peptic ulcer disease or gastrointestinal bleeding. Results of a controlled clinical study with 23 mg/day showed an increase, relative to 10 mg/day, in the incidence of peptic ulcer disease (0.4% vs. 0.2%) and gastrointestinal bleeding from any site (1.1% vs. 0.6%).
- Weight Loss [see Warnings and Precautions]
5.5 Weight LossWeight loss was reported as an adverse reaction in 4.7% of patients assigned to donepezil hydrochloride in a dose of 23 mg/day compared to 2.5% of patients assigned to 10 mg/day. Compared to their baseline weights, 8.4% of patients taking 23 mg/day were found to have a weight decrease of ≥ 7% by the end of the study, while 4.9% of patients taking 10 mg/day were found to have weight loss of ≥ 7% at the end of the study.
- Genitourinary Conditions [see Warnings and Precautions]
5.6 Genitourinary ConditionsAlthough not observed in clinical trials of donepezil hydrochloride, cholinomimetics may cause bladder outflow obstruction.
- Neurological Conditions: Seizures [see Warnings and Precautions]
5.7 Neurological Conditions: SeizuresCholinomimetics are believed to have some potential to cause generalized convulsions. However, seizure activity also may be a manifestation of Alzheimer’s disease.
- Pulmonary Conditions [see Warnings and Precautions]
5.8 Pulmonary ConditionsBecause of their cholinomimetic actions, cholinesterase inhibitors should be prescribed with care to patients with a history of asthma or obstructive pulmonary disease.
Donepezil hydrochloride monohydrate USP is a reversible inhibitor of the enzyme acetylcholinesterase, known chemically as (±)-2, 3-dihydro-5, 6-dimethoxy-2-[[1-(phenylmethyl)-4-piperidinyl]methyl]-1H-inden-1-one hydrochloride monohydrate. Donepezil hydrochloride monohydrate USP is commonly referred to in the pharmacological literature as E2020. It has an molecular formula of C24H29NO3HCl.H2O and a molecular weight of 433.95. Donepezil hydrochloride monohydrate USP is a off-white to white crystalline powder and is soluble in chloroform, water and in glacial aceticacid, slightly soluble in alcohol and acetonitrile, practically insoluble in ethyl acetate and n-Hexane.
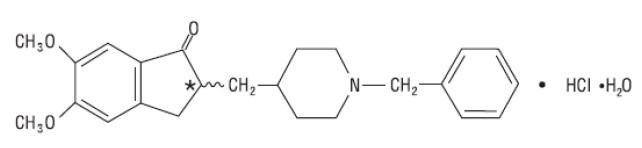
Donepezil hydrochloride tablets, USP are available for oral administration in film-coated tablets containing 23 mg of donepezil hydrochloride monohydrate USP.
Inactive ingredients are hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate and methacrylic acid copolymer. The film coating includes iron oxide red, iron oxide yellow and Opadry OY-58900 White contains hypromellose, polyethylene glycol and titanium dioxide.
Current theories on the pathogenesis of the cognitive signs and symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease attribute some of them to a deficiency of cholinergic neurotransmission.
Donepezil hydrochloride is postulated to exert its therapeutic effect by enhancing cholinergic function. This is accomplished by increasing the concentration of acetylcholine through reversible inhibition of its hydrolysis by acetylcholinesterase. There is no evidence that donepezil alters the course of the underlying dementing process.