Doxycycline Hyclate
Doxycycline Hyclate Prescribing Information
Doxycycline hyclate tablets are indicated for use as an adjunct to scaling and root planing to promote attachment level gain and to reduce pocket depth in patients with adult periodontitis.
THE DOSAGE OF DOXYCYCLINE HYCLATE TABLETS DIFFERS FROM THAT OF DOXYCYCLINE USED TO TREAT INFECTIONS. EXCEEDING THE RECOMMENDED DOSAGE MAY RESULT IN AN INCREASED INCIDENCE OF SIDE EFFECTS INCLUDING THE DEVELOPMENT OF RESISTANT MICROORGANISMS.
Doxycycline hyclate tablets 20 mg twice daily as an adjunct following scaling and root planing may be administered for up to 9 months. Doxycycline hyclate tablets should be taken twice daily at 12 hour intervals, usually in the morning and evening. It is recommended that if Doxycycline hyclate tablet is taken close to meal times, allow at least one hour prior to or two hours after meals. Safety beyond 12 months and efficacy beyond 9 months have not been established.
Administration of adequate amounts of fluid along with the tablets is recommended to wash down the drug and reduce the risk of esophageal irritation and ulceration. (See
This drug is contraindicated in persons who have shown hypersensitivity to doxycycline or any of the other tetracyclines.
In clinical trials of adult patients with periodontal disease 213 patients received 20 mg BID over a 9 to 12 month period. The most frequent adverse reactions occurring in studies involving treatment with a bioequivalent form of doxycycline hyclate capsules or placebo are listed below:
Adverse Reaction | Doxycycline Hyclate Capsules 20 mg BID (n=213) | Placebo (n=215) |
| Headache | 55 (26%) | 56 (26%) |
| Common Cold | 47 (22%) | 46 (21%) |
| Flu Symptoms | 24 (11%) | 40 (19%) |
| Tooth Ache | 14 (7%) | 28 (13%) |
| Periodontal Abscess | 8 (4%) | 21 (10%) |
| Tooth Disorder | 13 (6%) | 19 (9%) |
| Nausea | 17 (8%) | 12 (6%) |
| Sinusitis | 7 (3%) | 18 (8%) |
| Injury | 11 (5%) | 18 (8%) |
| Dyspepsia | 13 (6%) | 5 (2%) |
| Sore Throat | 11 (5%) | 13 (6%) |
| Joint Pain | 12 (6%) | 8 (4%) |
| Diarrhea | 12 (6%) | 8 (4%) |
| Sinus Congestion | 11 (5%) | 11 (5%) |
| Coughing | 9 (4%) | 11 (5%) |
| Sinus Headache | 8 (4%) | 8 (4%) |
| Rash | 8 (4%) | 6 (3%) |
| Back Pain | 7 (3%) | 8 (4%) |
| Back Ache | 4 (2%) | 9 (4%) |
| Menstrual Cramp | 9 (4%) | 5 (2%) |
| Acid Indigestion | 8 (4%) | 7 (3%) |
| Pain | 8 (4%) | 5 (2%) |
| Infection | 4 (2%) | 6 (3%) |
| Gum Pain | 1(<1%) | 6 (3%) |
| Bronchitis | 7 (3%) | 5 (2%) |
| Muscle Pain | 2 (1%) | 6 (3%) |
Note: Percentages are based on total number of study participants in each treatment group.
The following adverse reactions have been observed in patients receiving tetracyclines:
Gastrointestinal: anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, glossitis, dysphagia, enterocolitis, and inflammatory lesions (with vaginal candidiasis) in the anogenital region. Hepatotoxicity has been reported rarely. Rare instances of esophagitis and esophageal ulcerations have been reported in patients receiving the capsule forms of the drugs in the tetracycline class. Most of these patients took medications immediately before going to bed. (See
Skin: maculopapular and erythematous rashes. Exfoliative dermatitis has been reported but is uncommon. Photosensitivity is discussed above. (See
Renal toxicity: Rise in BUN has been reported and is apparently dose related. (See
Hypersensitivity reactions: urticaria, angioneurotic edema, anaphylaxis, anaphylactoid purpura, serum sickness, pericarditis, and exacerbation of systemic lupus erythematosus.
Blood: Hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, and eosinophilia have been reported.
Psychiatric: Depression, anxiety, suicidal ideation, insomnia, abnormal dreams, hallucination.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Alembic Pharmaceuticals Limited at 1-866-210-9797 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Because tetracyclines have been shown to depress plasma prothrombin activity, patients who are on anticoagulant therapy may require downward adjustment of their anticoagulant dosage. Since bacterial antibiotics, such as the tetracycline class of antibiotics, may interfere with the bactericidal action of members of the β-lactam (e.g. penicillin) class of antibiotics, it is not advisable to administer these antibiotics concomitantly. Absorption of tetracyclines is impaired by antacids containing aluminum, calcium, or magnesium, and iron-containing preparations, and by bismuth subsalicylate. Barbiturates, carbamazepine, and phenytoin decrease the half-life of doxycycline. The concurrent use of tetracycline and methoxyflurane has been reported to result in fatal renal toxicity. Concurrent use of tetracyclines may render oral contraceptives less effective.
Doxycycline hyclate tablets, USP are available as a 20 mg formulation of doxycycline for oral administration.
The structural formula of doxycycline hyclate is: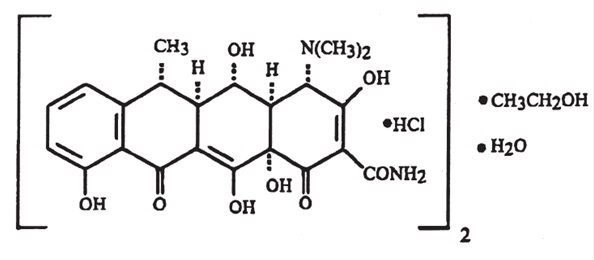
with an empirical formula of (C22H24N2O8•HCl)2•C2H6O•H2O and a molecular weight of 1025.89.
The chemical designation for doxycycline is 4-(dimethylamino)-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a–octahydro-3,5,10,12,12a–pentahydroxy-6-methyl-1,11-dioxo-2-naphthacenecarboxamide monohydrochloride, compound with ethyl alcohol (2:1), monohydrate.
Doxycycline hyclate, USP is a yellow to light-yellow powder which is freely soluble in water and in methanol; sparingly soluble in alcohol; practically insoluble in chloroform and in ether. It dissolves in aqueous solutions of alkali hydroxides and carbonates.
Inert ingredients in the formulation are: colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, lactose anhydrous, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol, talc, and titanium dioxide. Each tablet contains 23 mg of doxycycline hyclate equivalent to 20 mg of doxycycline.
Doxycycline hyclate tablets, USP meets USP