Edaravone
Edaravone Prescribing Information
Edaravone injection is indicated for the treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
Edaravone injection is supplied for intravenous infusion in a single-dose USP Type 1 Glass Vial containing
Edaravone injection is contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to edaravone or any of the inactive ingredients in this product. Hypersensitivity reactions and anaphylactic reactions have occurred
Hypersensitivity reactions (redness, wheals, and erythema multiforme) and cases of anaphylaxis (urticaria, decreased blood pressure, and dyspnea) have been reported in spontaneous postmarketing reports with edaravone injection.
Patients should be monitored carefully for hypersensitivity reactions. If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue edaravone injection, treat per standard of care, and monitor until the condition resolves
Edaravone injection contains sodium bisulfite, a sulfite that may cause allergic type reactions, including anaphylactic symptoms and life-threatening or less severe asthmatic episodes in susceptible people. The overall prevalence of sulfite sensitivity in the general population is unknown. Sulfite sensitivity occurs more frequently in asthmatic than non-asthmatic people.
The following serious adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see]5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions (redness, wheals, and erythema multiforme) and cases of anaphylaxis (urticaria, decreased blood pressure, and dyspnea) have been reported in spontaneous postmarketing reports with edaravone injection.
Patients should be monitored carefully for hypersensitivity reactions. If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue edaravone injection, treat per standard of care, and monitor until the condition resolves
[see CONTRAINDICATIONS (4)]. - Sulfite Allergic Reactions [see]5.2 Sulfite Allergic Reactions
Edaravone injection contains sodium bisulfite, a sulfite that may cause allergic type reactions, including anaphylactic symptoms and life-threatening or less severe asthmatic episodes in susceptible people. The overall prevalence of sulfite sensitivity in the general population is unknown. Sulfite sensitivity occurs more frequently in asthmatic than non-asthmatic people.
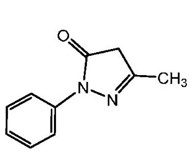
The active ingredient in edaravone injection is edaravone, which is a member of the substituted 2-pyrazolin-5-one class. The chemical name of edaravone is [3-methyl-1-phenyl-2-pyrazolin-5-one]. The molecular formula is C
10H
10N
2O and the molecular weight is 174.20.
The chemical structure is:
Edaravone is a white crystalline powder with a melting point of 129.7°C. It is freely soluble in acetic acid, methanol, or ethanol and slightly soluble in water or diethyl ether.
Edaravone injection is a clear, colorless liquid provided as a sterile solution.
The efficacy of edaravone injection for the treatment of ALS was established in a 6-month, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study conducted in Japanese patients with ALS who were living independently and met the following criteria at screening:
- Functionality retained most activities of daily living (defined as scores of 2 points or better on each individual item of the ALS Functional Rating Scale - Revised [ALSFRS-R; described below])
- Normal respiratory function (defined as percent-predicted forced vital capacity values of [%FVC] ≥80%)
- Definite or Probable ALS based on El Escorial revised criteria
- Disease duration of 2 years or less
The study enrolled 69 patients in the edaravone injection arm and 68 in the placebo arm. Baseline characteristics were similar between these groups, with over 90% of patients in each group being treated with riluzole.
Edaravone injection was administered as an intravenous infusion of 60 mg given over a 60-minute period according to the following schedule:
- An initial treatment cycle with daily dosing for 14 days, followed by a 14-day drug-free period (Cycle 1)
- Subsequent treatment cycles with daily dosing for 10 days out of 14-day periods, followed by 14-day drug-free periods (Cycles 2-6).
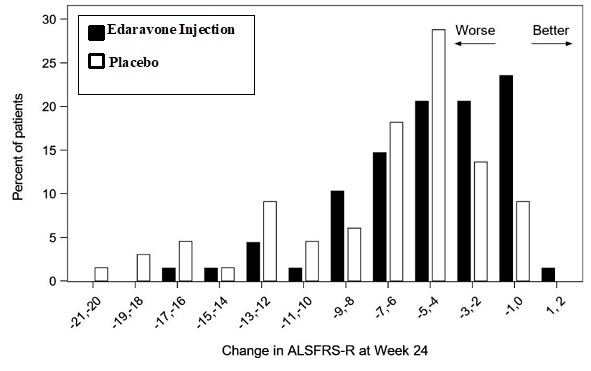
The primary efficacy endpoint was a comparison of the change between treatment arms in the ALSFRS-R total scores from baseline to Week 24. The ALSFRS-R scale consists of 12 questions that evaluate the fine motor, gross motor, bulbar, and respiratory function of patients with ALS (speech, salivation, swallowing, handwriting, cutting food, dressing/hygiene, turning in bed, walking, climbing stairs, dyspnea, orthopnea, and respiratory insufficiency). Each item is scored from 0-4, with higher scores representing greater functional ability. The decline in ALSFRS-R scores from baseline was significantly less in the edaravone injection-treated patients as compared to placebo (see Table 3). The distribution of change in ALSFRS-R scores from baseline to Week 24 by percent of patients is shown in Figure 1.
Treatment | Change from Baseline LS Mean ± SE(95% CI) | Treatment Difference ( Edaravone Injection – placebo [95% CI]) | p -value |
| Edaravone Injection | −5.01±0.64 | 2.49 (0.99, 3.98) | 0.0013 |
| Placebo | −7.50±0.66 |