Emrosi
(Minocycline Hydrochloride Extended-Release)Emrosi Prescribing Information
EMROSI is indicated to treat inflammatory lesions (papules and pustules) of rosacea in adults.
- This formulation of minocycline has not been evaluated in the treatment or prevention of infections.
- To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria as well as to maintain the effectiveness of other antibacterial drugs, use EMROSI only as indicated.
The recommended dosage of EMROSI is one capsule taken orally, once daily. Higher doses have not shown to be of additional benefit in the treatment of rosacea.
EMROSI may be taken with or without food
EMROSI is not bioequivalent to any other minocycline products. The pharmacokinetics of minocycline following administration of EMROSI was investigated in two studies that enrolled 32 healthy, adult subjects. In Study 1, the plasma pharmacokinetic parameters for EMROSI following single dose administration under fasting and fed states are presented in Table 1.
N | Cmax (ng/mL) | Tmax* (hr) | AUCinf (ng.hr/mL) | t1/2 (hr) | |
EMROSI (Fasting) | 23 | 243.9 | 1.50 | 3933.6 | 14.67 |
EMROSI (Fed) | 23 | 225.0 | 4.50 | 4404.1 | 14.93 |
Note: * Median (Range)
In Study 2, minocycline plasma PK following EMROSI single (Day 1) and after repeated (Day 21) once daily administrations in eight (8) subjects were found to be similar with overlapping ranges. The mean Cmaxwas 382.83 ng/mL versus 337.74 ng/mL and AUC0-24was 3549.64 ng*hr/mL versus 3957.62 ng*hr/mL, respectively on Day 1 versus Day 21.
Swallow the capsule whole. Do not crush or chew the extended-release capsule.
Extended-release capsules: 40 mg.
EMROSI is contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to any of the tetracyclines
Cases of anaphylaxis, serious skin reactions (e.g., Stevens-Johnson syndrome), erythema multiforme, and drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome have been reported postmarketing with minocycline use in patients with acne. DRESS syndrome consists of cutaneous reaction (such as rash or exfoliative dermatitis), eosinophilia, and one or more of the following visceral complications such as: hepatitis, pneumonitis, nephritis, myocarditis, and pericarditis. Fever and lymphadenopathy may be present. In some cases, death has been reported. If this syndrome is recognized, discontinue EMROSI immediately.
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Serious Skin/Hypersensitivity Reactions[see]
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reaction and Serious Skin ReactionsCases of anaphylaxis, serious skin reactions (e.g., Stevens-Johnson syndrome), erythema multiforme, and drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome have been reported postmarketing with minocycline use in patients with acne. DRESS syndrome consists of cutaneous reaction (such as rash or exfoliative dermatitis), eosinophilia, and one or more of the following visceral complications such as: hepatitis, pneumonitis, nephritis, myocarditis, and pericarditis. Fever and lymphadenopathy may be present. In some cases, death has been reported. If this syndrome is recognized, discontinue EMROSI immediately.
- Clostridioides difficile-Associated Diarrhea (Antibiotic-Associated Colitis)[see
Warnings and Precautions (5.4)] - Hepatotoxicity[see]
5.5 HepatotoxicityPostmarketing cases of serious liver injury, including irreversible drug-induced hepatitis and fulminant hepatic failure (sometimes fatal) have been reported with minocycline use in the treatment of acne. Discontinue EMROSI if liver injury is suspected.
- Central Nervous System Effects[see]
5.6 Central Nervous System EffectsCentral nervous system side effects including light-headedness, dizziness or vertigo have been reported with minocycline therapy. Caution patients who experience these symptoms about driving vehicles or using hazardous machinery while on EMROSI. These symptoms may disappear during therapy and usually rapidly disappear when the drug is discontinued.
- Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension[see]
5.7 Idiopathic Intracranial HypertensionIdiopathic Intracranial hypertension has been associated with the use of tetracyclines. Clinical manifestations of idiopathic intracranial hypertension include headache, blurred vision, diplopia, and vision loss; papilledema can be found on fundoscopy. Women of childbearing age who are overweight or have a history of idiopathic intracranial hypertension are at a greater risk for developing idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Avoid concomitant use of isotretinoin and EMROSI because isotretinoin, a systemic retinoid, is also known to cause idiopathic intracranial hypertension.
Permanent visual loss may exist, even after the medication is discontinued. If visual disturbance occurs during treatment, prompt ophthalmologic evaluation is warranted. Because intracranial pressure can remain elevated for weeks after drug cessation, monitor patients until they stabilize.
Minocycline hydrochloride, a semi synthetic derivative of tetracycline, is [4S-(4α,4aα,5aα,12aα)]-4,7-Bis(dimethylamino)-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydro-3,10,12,12a- tetrahydroxy-1,11-dioxo-2-naphthacenecarboxamide mono hydrochloride. Its molecular formula is C
23H
27N
3O
7•HCl with a molecular weight of 493.95. Minocycline hydrochloride has the following structure: 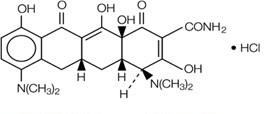
Minocycline hydrochloride is a yellow, hygroscopic, crystalline powder. It is sparingly soluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol (96%). A 1% w/v solution in water has pH between 3.5 and 4.5.
Each EMROSI extended-release capsule contains 40 mg of minocycline (equivalent to 43.19 mg of minocycline hydrochloride) as 10 mg immediate-release and 30 mg extended-release beads and the following inactive ingredients: ethyl cellulose, hypromellose, isopropyl alcohol, microcrystalline cellulose, Opadry
®clear, polyethylene glycol 400, triethyl citrate and talc. Opadry
®clear contains: hydroxypropyl cellulose and hypromellose. Capsule shell contains gelatin, iron oxide red and titanium dioxide. White ink contains ammonia, butyl alcohol, dehydrated alcohol, isopropyl alcohol, potassium hydroxide, propylene glycol, titanium dioxide and shellac.