Ephedrine Sulfate
Ephedrine Sulfate Prescribing Information
Ephedrine Sulfate Injection is indicated for the treatment of clinically important hypotension occurring in the setting of anesthesia.
Ephedrine Sulfate Injection, 5 mg/mL is a clear, colorless solution available in:
- a single‑dose, 10 mL vial that contains 50 mg/10 mL ephedrine sulfate, equivalent to 38 mg ephedrine base;
- a single‑dose, 5 mL prefilled syringe that contains 25 mg/5 mL ephedrine sulfate, equivalent to 19 mg ephedrine base.
None
The following adverse reactions associated with the use of ephedrine sulfate were identified in the literature. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to estimate their frequency reliably or to establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Interactions that Augment the Pressor Effect | |
Oxytocin and oxytocic drugs | |
Clinical Impact: | Serious postpartum hypertension has been described in patients who received both a vasopressor (i.e., methoxamine, phenylephrine, ephedrine) and an oxytocic (i.e., methylergonovine, ergonovine). Some of these patients experienced a stroke. |
Intervention: | Carefully monitor the blood pressure of individuals who have received both ephedrine and an oxytocic. |
Clonidine, propofol, monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), atropine | |
Clinical Impact: | These drugs augment the pressor effect of ephedrine. |
Intervention: | Carefully monitor the blood pressure of individuals who have received both ephedrine and any of these drugs. |
Interactions that Antagonize the Pressor Effect | |
Clinical Impact: | These drugs antagonize the pressor effect of ephedrine. |
Intervention: | Carefully monitor the blood pressure of individuals who have received both ephedrine and any of these drugs. |
Examples: | α-adrenergic antagonists, β-adrenergic receptor antagonists, reserpine, quinidine, mephentermine |
Other Drug Interactions | |
Guanethidine | |
Clinical Impact: | Ephedrine may inhibit the neuron blockage produced by guanethidine, resulting in loss of antihypertensive effectiveness. |
Intervention: | Clinician should monitor patient for blood pressor response and adjust the dosage or choice of pressor accordingly. |
Rocuronium | |
Clinical Impact: | Ephedrine may reduce the onset time of neuromuscular blockade when used for intubation with rocuronium if administered simultaneously with anesthetic induction. |
Intervention: | Be aware of this potential interaction. No treatment or other interventions are needed. |
Epidural anesthesia | |
Clinical Impact: | Ephedrine may decrease the efficacy of epidural blockade by hastening the regression of sensory analgesia. |
Intervention: | Monitor and treat the patient according to clinical practice. |
Theophylline | |
Clinical Impact: | Concomitant use of ephedrine may increase the frequency of nausea, nervousness, and insomnia. |
Intervention: | Monitor patient for worsening symptoms and manage symptoms according to clinical practice. |
Cardiac glycosides | |
Clinical Impact: | Giving ephedrine with a cardiac glycoside, such as digitalis, may increase the possibility of arrhythmias. |
Intervention: | Carefully monitor patients on cardiac glycosides who are also administered ephedrine. |
Ephedrine is an alpha- and beta-adrenergic agonist and a norepinephrine-releasing agent. Ephedrine Sulfate Injection, 5 mg/mL is a clear, colorless, sterile, ready-to-use solution for intravenous injection. The chemical name of ephedrine sulfate is (1
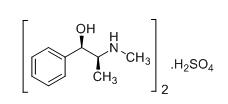
Ephedrine sulfate is freely soluble in water and ethanol, very slightly soluble in chloroform, and practically insoluble in ether. Each mL contains ephedrine sulfate 5 mg (equivalent to 3.8 mg ephedrine base), sodium chloride 9 mg, and sodium hydroxide and/or acetic acid for pH adjustment, if necessary. The pH range is 4.5 to 7.0.