Ertapenem Sodium - Ertapenem injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution
(Ertapenem)Ertapenem Sodium - Ertapenem injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution Prescribing Information
For Injection: Vials
Ertapenem for injection is a sterile lyophilized powder in a single-dose vial containing 1 g ertapenem equivalent to 1.046 g ertapenem sodium for intravenous infusion or for intramuscular injection after reconstitution.
- Ertapenem for injection is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to any component of this product or to other drugs in the same class or in patients who have demonstrated anaphylactic reactions to beta-lactams.
- Due to the use of lidocaine HCl as a diluent, Ertapenem for injection administered intramuscularly is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to local anesthetics of the amide type.
The following are described in greater detail in the Warnings and Precautions section
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions ()]5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Serious and occasionally fatal hypersensitivity (anaphylactic) reactions have been reported in patients receiving therapy with beta-lactams. These reactions are more likely to occur in individuals with a history of sensitivity to multiple allergens. There have been reports of individuals with a history of penicillin hypersensitivity who have experienced severe hypersensitivity reactions when treated with another beta-lactam. Before initiating therapy with Ertapenem for injection, careful inquiry should be made concerning previous hypersensitivity reactions to penicillins, cephalosporins, other beta-lactams and other allergens. If an allergic reaction to Ertapenem for injection occurs, discontinue the drug immediately. Serious anaphylactic reactions require immediate emergency treatment as clinically indicated.
- Seizure Potential [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]Interaction with Valproic Acid [see Warnings and Precautions ()]5.3 Interaction with Valproic Acid
Case reports in the literature have shown that co-administration of carbapenems, including ertapenem, to patients receiving valproic acid or divalproex sodium results in a reduction in valproic acid concentrations. The valproic acid concentrations may drop below the therapeutic range as a result of this interaction, therefore increasing the risk of breakthrough seizures. Increasing the dose of valproic acid or divalproex sodium may not be sufficient to overcome this interaction. The concomitant use of ertapenem and valproic acid/divalproex sodium is generally not recommended. Anti-bacterials other than carbapenems should be considered to treat infections in patients whose seizures are well controlled on valproic acid or divalproex sodium. If administration of Ertapenem for injection is necessary, supplemental anti-convulsant therapy should be considered [see Drug Interactions ].
- Clostridioides difficile-Associated Diarrhea (CDAD) [see Warnings and Precautions ()]5.4Clostridioides difficile-Associated Diarrhea (CDAD)
CDAD has been reported with use of nearly all antibacterial agents, including ertapenem, and may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon leading to overgrowth of
Clostridioides difficile.Clostridioides difficileproduces toxins A and B which contribute to the development of CDAD. Hypertoxin producing strains ofClostridioides difficilecause increased morbidity and mortality, as these infections can be refractory to antimicrobial therapy and may require colectomy. CDAD must be considered in all patients who present with diarrhea following antibiotic use. Careful medical history is necessary since CDAD has been reported to occur over two months after the administration of antibacterial agents.If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing antibiotic use not directed against
Clostridioides difficilemay need to be discontinued. Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibiotic treatment ofClostridioides difficile, and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically indicated. - Caution with Intramuscular Administration [see Warnings and Precautions ()]5.5 Caution with Intramuscular Administration
Caution should be taken when administering Ertapenem for injection intramuscularly to avoid inadvertent injection into a blood vessel [see Dosage and Administration ].
- Development of Drug-Resistant Bacteria [see Warnings and Precautions ()]5.6 Development of Drug-Resistant Bacteria
As with other antibiotics, prolonged use of Ertapenem for injection may result in overgrowth of non-susceptible organisms. Repeated evaluation of the patient's condition is essential. If superinfection occurs during therapy, appropriate measures should be taken.
Prescribing Ertapenem for injection in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection or a prophylactic indication is unlikely to provide benefit to the patient and increases the risk of the development of drug-resistant bacteria.
- Laboratory Tests [see Warnings and Precautions ()]5.7 Laboratory Tests
While Ertapenem for injection possesses toxicity similar to the beta-lactam group of antibiotics, periodic assessment of organ system function, including renal, hepatic, and hematopoietic, is advisable during prolonged therapy.
Ertapenem for injection is a sterile, synthetic, parenteral, 1-β methyl-carbapenem that is structurally related to beta-lactam antibiotics.
Chemically, Ertapenem for injection is described as [4R-[3(3S*,5S*),4α,5β,6β(R*)]]-3-[[5-[[(3-carboxyphenyl)amino]carbonyl]-3-pyrrolidinyl]thio]-6-(1-hydroxyethyl)-4-methyl-7-oxo-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]hept-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid monosodium salt. Its molecular weight is 497.50. The empirical formula is C22H24N3O7SNa, and its structural formula is:
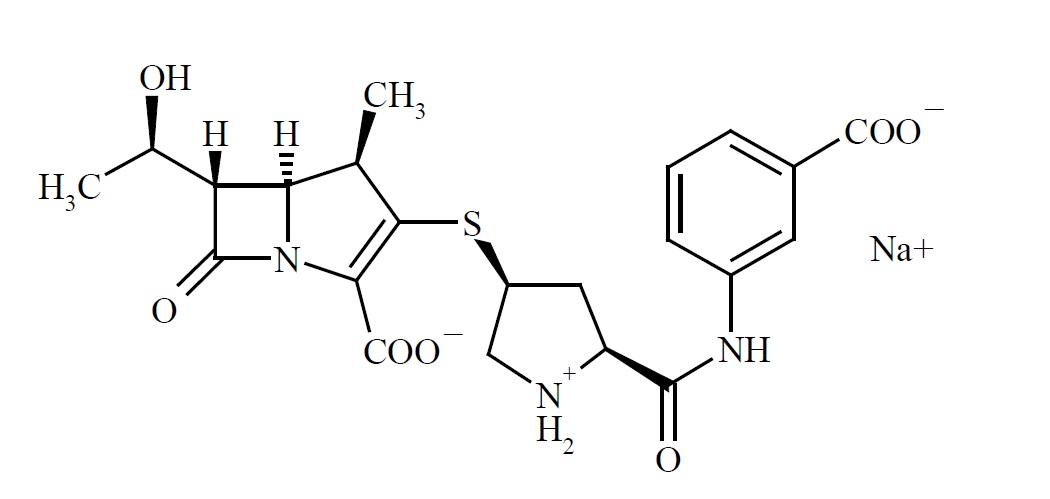 Ertapenem sodium is a white to off-white hygroscopic, weakly crystalline powder. It is soluble in water and 0.9% sodium chloride solution, practically insoluble in ethanol, and insoluble in isopropyl acetate and tetrahydrofuran.
Ertapenem sodium is a white to off-white hygroscopic, weakly crystalline powder. It is soluble in water and 0.9% sodium chloride solution, practically insoluble in ethanol, and insoluble in isopropyl acetate and tetrahydrofuran.
Ertapenem for Injection is supplied as sterile lyophilized powder for intravenous infusion after reconstitution with appropriate diluent [see Dosage and Administration (
DO NOT MIX OR CO-INFUSE ERTAPENEM FOR INJECTION WITH OTHER MEDICATIONS. DO NOT USE DILUENTS CONTAINING DEXTROSE (α-D-GLUCOSE).
- Reconstitute the contents of a 1 g vial of Ertapenem for injection with 10 mL of one of the following: Water for Injection, 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection or Bacteriostatic Water for Injection, using a syringe equipped with a 21-gauge or smaller diameter needle. NOTE: Use with a needleless IV system is not recommended.
- Shake well to dissolve and immediately transfer contents of the reconstituted vial to 50 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection.
- Complete the infusion within 6 hours of reconstitution.Preparation for intramuscular administration:ERTAPENEM FOR INJECTION MUST BE RECONSTITUTED PRIOR TO ADMINISTRATION.
- Reconstitute the contents of a 1 g vial of Ertapenem for injection with 3.2 mL of 1.0% lidocaine HCl injection [1](without epinephrine). Shake vial thoroughly to form solution.
- Immediately withdraw the contents of the vial and administer by deep intramuscular injection into a large muscle mass (such as the gluteal muscles or lateral part of the thigh).
- The reconstituted IM solution should be used within 1 hour after preparation.NOTE: THE RECONSTITUTED SOLUTION SHOULD NOT BE ADMINISTERED INTRAVENOUSLY.Pediatric patients 3 months to 12 years of agePreparation for intravenous administration:DO NOT MIX OR CO-INFUSE ERTAPENEM FOR INJECTION WITH OTHER MEDICATIONS.
DO NOT USE DILUENTS CONTAINING DEXTROSE (α-D-GLUCOSE).
ERTAPENEM FOR INJECTION MUST BE RECONSTITUTED AND THEN DILUTED PRIOR TO ADMINISTRATION. - Reconstitute the contents of a 1 g vial of Ertapenem for injection with 10 mL of one of the following: Water for Injection, 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection or Bacteriostatic Water for Injection, using a syringe equipped with a 21-gauge or smaller diameter needle. NOTE: Use with a needleless IV system is not recommended.
- Shake well to dissolve and immediately withdraw a volume equal to 15 mg/kg of body weight (not to exceed 1 g/day) and dilute in 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection to a final concentration of 20 mg/mL or less. Discard vial with unused portion of Ertapenem for injection reconstituted solution.
- Complete the infusion within 6 hours of reconstitution.Preparation for intramuscular administration:ERTAPENEM FOR INJECTION MUST BE RECONSTITUTED PRIOR TO ADMINISTRATION.
- Reconstitute the contents of a 1 g vial of Ertapenem for injection with 3.2 mL of 1.0% lidocaine HCl injection (without epinephrine). Shake vial thoroughly to form solution.
- Immediately withdraw a volume equal to 15 mg/kg of body weight (not to exceed 1 g/day) and administer by deep intramuscular injection into a large muscle mass (such as the gluteal muscles or lateral part of the thigh). Discard vial with unused portion of Ertapenem for injection reconstituted solution.
- The reconstituted IM solution should be used within 1 hour after preparation.NOTE: THE RECONSTITUTED SOLUTION SHOULD NOT BE ADMINISTERED INTRAVENOUSLY.StorageWhen prepared with the diluent, Ertapenem for injection maintains satisfactory potencyfor 6 hours at room temperature (25°C) or for 24 hours under refrigeration (5°C) and used within 4 hours after removal from refrigeration. Solutions of Ertapenem for injection should not be frozen.Before administering, see accompanying package circular for Ertapenem for injection.Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to use, whenever solution and container permit. Solutions of Ertapenem for injection range from colorless to pale yellow. Variations of color within this range do not affect the potency of the product.
Each single-dose vial contains 1 gram ertapenem, equivalent to 1.046 grams ertapenem sodium. The sodium content is approximately 137 mg (approximately 6.0 mEq).
Each vial of Ertapenem for Injection contains the following inactive ingredients: 175 mg sodium bicarbonate and sodium hydroxide to adjust pH to 7.5.
Ertapenem sodium is a carbapenem antibiotic [see Clinical Pharmacology (
Mechanism of Action
Ertapenem has
Resistance
Ertapenem is stable against hydrolysis by a variety of beta-lactamases, including penicillinases, and cephalosporinases and extended spectrum beta-lactamases. Ertapenem is hydrolyzed by metallo-betalactamases.
Antimicrobial Activity
Ertapenem has been shown to be active against most isolates of the following microorganisms both
Bacteroides fragilis
Bacteroides distasonis
Bacteroides ovatus
Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron
Bacteroides uniformis
Clostridium clostridioforme
Eubacterium lentum
Peptostreptococcus species
Porphyromonas asaccharolytica
Prevotella bivia
The following
For specific information regarding susceptibility testing methods, interpretive criteria, and associated test methods and quality control standards recognized by FDA for ertapenem, please see: https://www.fda.gov/STIC.