Femlyv Prescribing Information
FEMLYV is contraindicated in females who are known to have or develop the following conditions:
• A history of, increased risk for, or current arterial or venous thrombotic/thromboembolic diseases.
Examples include women who are known to:
• Smoke, if 35 years of age and older[see Boxed Warningand Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]• Have current or history of deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]• Have cerebrovascular disease[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]• Have coronary artery disease[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]• Have thrombogenic valvular or thrombogenic rhythm diseases of the heart (for example, subacute bacterial endocarditis with valvular disease, or atrial fibrillation)[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]• Have inherited or acquired hypercoagulopathies[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]• Have uncontrolled hypertension or hypertension with vascular disease[see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]• Have diabetes mellitus with hypertension or end-organ damage; or diabetes mellitus of > 20 years duration[see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]• Have migraine headaches with aurao All women over age 35 with migraine headache[see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
• Current diagnosis of, or history of, breast cancer, which may be hormone-sensitive[see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]• Liver tumors, benign or malignant, or hepatic impairment[see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]• Use of Hepatitis C drug combinations containing ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir, due to the potential for ALT elevations[see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]• Undiagnosed abnormal uterine bleeding[see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
• A high risk of arterial or venous thrombotic diseases• Breast cancer or history of breast cancer• Liver tumors, benign or malignant, or hepatic impairment• Co-administration with Hepatitis C drug combinations containing ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir• Undiagnosed abnormal uterine bleeding
• Thromboembolic Disorders and Other Vascular Problems: Discontinue FEMLYV if a thrombotic event occurs. Discontinue at least 4 weeks before through 2 weeks after major surgery. Start no earlier than 4 weeks after delivery, in women who are not breastfeeding. Consider all cardiovascular risk factors before initiating in any female, particularly in the presence of multiple risk factors• High blood pressure: Monitor blood pressure periodically and stop use if blood pressure rises significantly. Do not prescribe for women with uncontrolled hypertension or hypertension with vascular disease• Migraine: Evaluate significant change in migraines and discontinue if new, recurrent, persistent, or severe migraines occur• Hormonally-sensitive malignancy: Discontinue FEMLYV if a hormonally-sensitive malignancy is diagnosed .• Liver disease: Discontinue use if jaundice or acute or chronic disturbances of liver function occurs• Glucose tolerance and hypertriglyceridemia: Monitor glucose in females with prediabetes and diabetes taking FEMLYV. Consider an alternative contraceptive method for women with uncontrolled dyslipidemia• Gallbladder disease and cholestasis: Consider discontinuing FEMLYV in females with symptomatic gallbladder or cholestatic disease• Uterine bleeding: Evaluate irregular bleeding or amenorrhea
Stop FEMLYV if an arterial or deep venous thrombotic event (VTE) occurs.
Stop FEMLYV if there is unexplained loss of vision, proptosis, diplopia, papilledema, or retinal vascular lesions and evaluate for retinal vein thrombosis immediately.
Discontinue FEMLYV during prolonged immobilization.
If feasible, discontinue FEMLYV at least 4 weeks before and through 2 weeks after major surgery or other surgeries known to have an elevated risk of VTE.
Start FEMLYV no earlier than 4 weeks after delivery in females who are not breastfeeding. The risk of postpartum thromboembolism decreases after the third postpartum week, whereas the likelihood of ovulation increases after the third postpartum week.
Before starting FEMLYV, evaluate any past medical history or family history of thrombotic or thromboembolic disorders and consider whether the history suggests an inherited or acquired hypercoagulopathy. FEMLYV is contraindicated in females with a high risk of arterial or venous thrombotic/thromboembolic diseases
Use of CHCs increases the risk of cardiovascular events and cerebrovascular events, such as myocardial infarction and stroke. The risk is greater among females over age 40, smokers, and females with hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes, or obesity. The risk increases with age, particularly in females 35 years of age and older, and with the number of cigarettes smoked. In addition to cigarettes, use of other nicotine-containing products – including cigars, smokeless tobacco, hookah tobacco, e-cigarettes, and nicotine replacement therapy – may also increase the risk of serious cardiovascular events from CHC use.
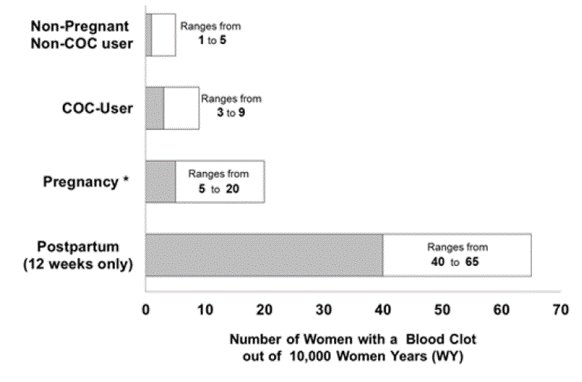
Use of CHCs also increases the risk of venous thromboembolic events (VTEs), such as deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. The rate of VTE in females using COCs has been estimated to be 3 to 9 cases per 10,000 woman-years and should be considered in the context of other female of reproductive potential subpopulations who are not taking CHCs
Risk factors for VTEs include smoking, obesity, family history of VTE, and prolonged immobilization in addition to other factors that contraindicate use of CHCs
The risk of VTE is increased during the first six weeks postpartum compared to the risk in nonpregnant, non-postpartum females. The risk is highest in the first three weeks postpartum but remains higher than baseline until at least six weeks postpartum. The presence of multiple risk factors for VTE may further increase the risk. Obstetric complications may extend the elevated risk up to 12 weeks postpartum.
Figure 1shows the risk of developing a VTE for females who are not pregnant and do not use COCs, for females who use COCs, for pregnant females, and for females in the postpartum period. To put the risk of developing a VTE into perspective: if 10,000 females who are not pregnant and do not use oral contraceptives are followed for one year, between 1 and 5 of these females will develop a VTE.

FEMLYV is contraindicated in females with uncontrolled hypertension or hypertension with vascular disease
An increase in blood pressure has been reported in females taking CHCs, and this increase is more likely in older women with extended duration of use.
FEMLYV is contraindicated in females who have migraines with aura
Migraines with aura increase the risk for stroke. This stroke risk is further increased in females who have migraines with aura with use of CHCs.
FEMLYV is contraindicated in females who currently have or have had breast cancer because breast cancer may be hormonally sensitive
Epidemiology studies have not found a consistent association between use of combined oral contraceptives (COCs) and breast cancer risk. Studies do not show an association between ever (current or past) use of COCs and risk of breast cancer. However, some studies report a small increase in the risk of breast cancer among current or recent users (<6 months since last use) and current users with longer duration of COC use
A causal relationship between the use of CHCs and the development of cervical cancer and intraepithelial neoplasia has not been clearly established. In observational studies, the use of oral hormonal contraceptives in females for five years or more, compared to females who did not use oral hormonal contraceptives, was associated with an increased risk of cervical cancer and intraepithelial neoplasia. In these studies, the use of oral hormonal contraceptives in females for 10 years or more, compared to females who received oral hormonal contraceptives for 5-9 years, was associated with an increased risk of cervical cancer and intraepithelial neoplasia. Limitations in these epidemiologic studies include potential recall bias, differences in sexual behavior, and other factors such as establishing whether there were data on persistent high-risk Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) infection.
FEMLYV is contraindicated in females with acute hepatitis or severe (decompensated) cirrhosis of the liver
FEMLYV is contraindicated in females with hepatic adenomas and malignant liver tumors
CHCs, such as FEMLYV, are contraindicated for use with Hepatitis C drug combinations containing ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir (with or without dasabuvir)
During clinical trials with the above-mentioned Hepatitis C combination drug regimen, ALT elevations greater than 5 times the upper limit of normal (ULN), including some cases greater than 20 times the ULN, were significantly more frequent in females using ethinyl estradiol (EE)-containing drugs, such as CHCs.
Carefully monitor females with prediabetes and diabetes who are using FEMLYV. FEMLYV may decrease glucose tolerance.
Consider alternative contraception for females with hypertriglyceridemia. Females with hypertriglyceridemia, or a family history thereof, may have an increase in serum triglyceride concentrations when using FEMLYV, which may increase the risk of pancreatitis.
Consider discontinuing FEMLYV in females with symptomatic gallbladder disease or cholestatic disease. Studies suggest an increased risk of developing gallbladder disease among CHC users. Use of CHCs may also worsen existing gallbladder disease.
A past history of CHC-related cholestasis predicts an increased risk with subsequent CHC use. Women with a history of pregnancy-related cholestasis may be at an increased risk for CHC-related cholestasis.
Females using FEMLYV may experience unscheduled (breakthrough or intracyclic) bleeding and spotting, especially during the first three months of use. Bleeding irregularities may resolve over time or by changing to a different contraceptive product. If bleeding persists or occurs after previously regular cycles, evaluate for causes such as pregnancy or malignancy.
Based on patient diaries from a clinical trial evaluating the safety and efficacy of a 24-day regimen of norethindrone acetate 1 mg/ethinyl estradiol 0.020 mg tablets, 24-35% of women experienced unscheduled bleeding per cycle. A total of 10 subjects out of 743 (1.3%) discontinued due to bleeding or spotting
If scheduled (withdrawal) bleeding does not occur, consider the possibility of pregnancy. If the patient has not adhered to the prescribed dosing schedule (missed one or more active tablets or started taking them on a day later than she should have), consider the possibility of pregnancy at the time of the first missed period and take appropriate diagnostic measures. If the patient has adhered to the prescribed regimen and misses two consecutive periods, rule out pregnancy.
Females who use FEMLVY may experience absence of scheduled (withdrawal) bleeding, even if they are not pregnant. In the clinical trial with a 24-day regimen of norethindrone acetate 1 mg/ethinyl estradiol 0.020 mg tablets, 22 to 36% of the women using norethindrone acetate 1 mg/ethinyl estradiol 0.020 mg tablets experienced amenorrhea in at least one of 6 cycles of use
After discontinuation of FEMLYV, amenorrhea or oligomenorrhea may occur, especially if these conditions were pre-existent.
Monitor females with a history of depression and discontinue FEMLYV if depression recurs to a serious degree. Data on the association of COCs with onset of depression or exacerbation of existing depression are limited.
Increase the dosage of thyroid hormone replacement therapy as needed in females taking FEMLYV
Avoid FEMLYV in females with hereditary angioedema. Exogenous estrogens may induce or exacerbate symptoms of hereditary angioedema.
Avoid FEMLYV in females with a history of chloasma gravidarum or increased sensitivity to sun and/or ultraviolet radiation exposure. Chloasma may occur with FEMLYV, especially in females with a history of chloasma gravidarum.
Dosage and Administration, Dosing FEMLYV ( To achieve maximum contraceptive effectiveness, take one ODT every day at about the same time each day. Place one ODT on the tongue, allow to disintegrate and then follow with 8 oz. (240 mL) of water. The tablets can also be swallowed whole with 8 oz. (240 mL) of water. The recommended dosage of FEMLYV is one ODT daily for 28 consecutive days: one green active ODT daily during the first 24 days followed by one white inert ODT daily during the 4 following days (see Table 1). FEMLYV must be taken in the order directed on the blister pack. ODTs should not be skipped or taken at intervals exceeding 24 hours. FEMLYV may be administered without regard to meals [see 12.3]. Instruct the patient to begin taking FEMLYV either on the first day of her menstrual period (Day 1 Start) or on the first Sunday after the onset of her menstrual period (Sunday Start). | XX/2025 |
FEMLYV is indicated for use by females of reproductive potential to prevent pregnancy
The effectiveness of FEMLYV has been established for the prevention of pregnancy in females of reproductive potential based on adequate and well-controlled studies of norethindrone acetate/ethinyl estradiol tablets. The data presented below reflects results from studies of norethindrone acetate/ethinyl estradiol tablets.
In a clinical study, 743 women 18 to 45 years of age were studied to assess the efficacy of norethindrone acetate/ethinyl estradiol tablets, for up to six 28-day cycles providing a total of 3,823 treatment-cycles of exposure. The racial demographic of all enrolled women was: 70% Caucasian, 16% African American, 10% Hispanic, 2% Asian and 2% Other. Women with BMI greater than 35 kg/m2were excluded from the study. The weight range for those women treated was 90 to 260 pounds, with a mean weight of 147 pounds. Among the women in the study, about 40% had not used hormonal contraception immediately prior to enrolling in this study.
A total of 583 women completed 6 cycles of treatment. There were a total of 5 on-treatment pregnancies in 3,565 treatment cycles during which no backup contraception was used. The Pearl Index for norethindrone acetate and ethinyl estradiol tablets was 1.82 (95% confidence interval 0.59 - 4.25).
The efficacy of FEMLYV in females with a body mass index (BMI) of more than 35 kg/m2 has not been evaluated.
• Place one FEMLYV orally disintegrating tablet (ODT) on the tongue, allow to disintegrate and then follow with 8 oz. (240 mL) of water.• The tablets can also be swallowed whole with 8 oz. (240 mL) of water.• Take at the same time daily without regards to meals (,2.1 Dosing FEMLYVTo achieve maximum contraceptive effectiveness, take one ODT every day at about the same time each day.
Place one ODT on the tongue, allow to disintegrate and then follow with 8 oz. (240 mL) of water. The tablets can also be swallowed whole with 8 oz. (240 mL) of water.The recommended dosage of FEMLYV is one ODT daily for 28 consecutive days: one green active ODT daily during the first 24 days followed by one white inert ODT daily during the 4 following days (see Table 1). FEMLYV must be taken in the order directed on the blister pack. ODTs should not be skipped or taken at intervals exceeding 24 hours. FEMLYV may be administered without regard to meals [see 12.3].Instruct the patient to begin taking FEMLYV either on the first day of her menstrual period (Day 1 Start) or on the first Sunday after the onset of her menstrual period (Sunday Start).)12.3 PharmacokineticsAbsorptionNorethindrone acetate appears to be completely and rapidly deacetylated to norethindrone after oral administration The absolute bioavailability was approximately 64% for norethindrone and 43% for ethinyl estradiol following oral administration.
The plasma norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol pharmacokinetics following single-dose administrations of FEMLYV ODT in 36 healthy female subjects are provided in Figures 3and 4, and Table 3.
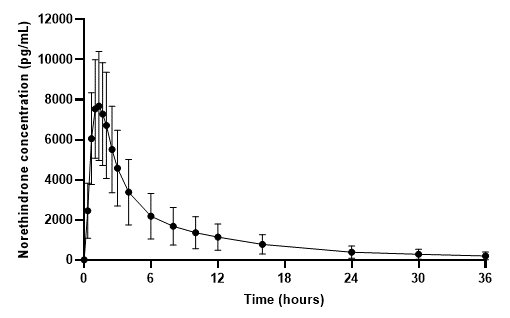
Figure 3. Mean (± Standard Deviation) Plasma Norethindrone Concentration-Time Profile Following Single-Dose Administration of FEMLYV ODT to Healthy Female Volunteers under Fasting Conditions (n = 36) 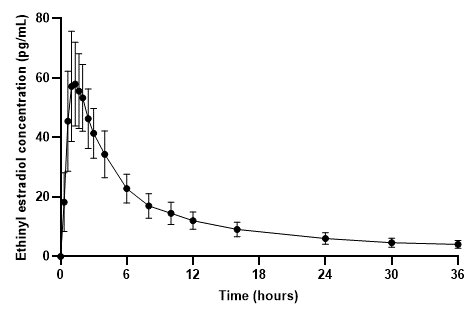
Figure 4. Mean (± Standard Deviation) Plasma Ethinyl Estradiol Concentration- Time Profile Following Single-Dose Administration of FEMLYV ODT to Healthy Female Volunteers under Fasting Conditions (n = 36) Table 3. Summary of Norethindrone (NE) and Ethinyl Estradiol (EE) Pharmacokinetics Following Single-Dose Administration of FEMLYV ODT to Healthy Female Volunteers Under Fasting Conditions (n = 36) Cmax= Maximum plasma concentration tmax= Time of Cmax AUC(0-tldc)= Area under plasma concentration versus time curve from 0 to tldc, the time of last determinable concentration AUC(0-inf)= Area under the plasma concentration versus time curve from time 0 to infinity t½= Terminal phase half-life % CV = Coefficient of Variation (%) aThe median (range) is reported for tmax
bn = 35Analyte
Arithmetic Meana(% CV) by Pharmacokinetic Parameter
Cmax
(pg/mL)tmax
(hr)AUC(0-tldc)
(pg•h/mL)AUC(0-inf)
(pg•h/mL)t½
(hr)NE
8438
(34)
1.33
(0.66–2.50)
50060
(48)
51190
(49)
10.25
(26)
EE
62.8
(25)
1.33
(0.67–2.03)
505.1
(25)
595.6b
(24)
18.02b
(34)
Effect of FoodNo clinically significant differences in pharmacokinetics of norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol were observed following administration of a high-fat meal in healthy premenopausal subjects.
DistributionVolume of distribution of norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol ranges from 2 to 4 L/kg. Plasma protein binding of both steroids is extensive (greater than 95%); norethindrone binds to both albumin and SHBG, whereas ethinyl estradiol binds only to albumin. Although ethinyl estradiol does not bind to SHBG, it induces SHBG synthesis.
MetabolismNorethindrone undergoes extensive biotransformation, primarily via reduction, followed by sulfate and glucuronide conjugation. The majority of metabolites in the circulation are sulfates, with glucuronides accounting for most of the urinary metabolites.
Ethinyl estradiol is also extensively metabolized, both by oxidation and by conjugation with sulfate and glucuronide. Sulfates are the major circulating conjugates of ethinyl estradiol and glucuronides predominate in urine. The primary oxidative metabolite is 2-hydroxy ethinyl estradiol, formed by the CYP3A4 isoform of cytochrome P450. Part of the first-pass metabolism of ethinyl estradiol is believed to occur in gastrointestinal mucosa. Ethinyl estradiol may undergo enterohepatic circulation.
ExcretionNorethindrone and ethinyl estradiol are excreted in both urine and feces, primarily as metabolites. Plasma clearance values for norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol are similar (approximately 0.4 L/hr/kg). Elimination half-lives of norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol following administration of FEMLYV are approximately 10 hours and 18 hours, respectively.

Figure 3 
Figure 4 • Take ODTs in the order directed on the blister pack ()2.1 Dosing FEMLYVTo achieve maximum contraceptive effectiveness, take one ODT every day at about the same time each day.
Place one ODT on the tongue, allow to disintegrate and then follow with 8 oz. (240 mL) of water. The tablets can also be swallowed whole with 8 oz. (240 mL) of water.The recommended dosage of FEMLYV is one ODT daily for 28 consecutive days: one green active ODT daily during the first 24 days followed by one white inert ODT daily during the 4 following days (see Table 1). FEMLYV must be taken in the order directed on the blister pack. ODTs should not be skipped or taken at intervals exceeding 24 hours. FEMLYV may be administered without regard to meals [see 12.3].Instruct the patient to begin taking FEMLYV either on the first day of her menstrual period (Day 1 Start) or on the first Sunday after the onset of her menstrual period (Sunday Start).
Orally disintegrating tablets:
• 1 mg norethindrone acetate and 0.02 mg ethinyl estradiol, green, round ODTs, imprinted with “M” on one side and “312” on the other side• White, round, inert ODTs imprinted with “M” on one side and “313” on the other side
• Pregnancy: Discontinue if pregnancy occurs ()8.1 PregnancyRisk SummaryDiscontinue FEMLYV if pregnancy occurs, because there is no reason to use hormonal contraceptives during pregnancy. Epidemiologic studies and meta-analyses have not found an increased risk of genital or nongenital birth defects (including cardiac anomalies and limb-reduction defects) following exposure to COCs before conception or during early pregnancy.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4 percent and 15 to 20 percent, respectively.
• Lactation: Advise postpartum females that FEMLYV can decrease milk production ()8.2 LactationRisk SummaryContraceptive hormones and/or metabolites are present in human milk. COCs can reduce milk production in breast-feeding females. This reduction can occur at any time but is less likely to occur once breast-feeding is well-established. When possible, advise the nursing female to use other methods of contraception until she discontinues breast-feeding
[see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].The developmental and health benefits of breast-feeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for FEMLYV and any potential adverse effects on the breast-fed child from FEMLYV or from the underlying maternal condition.