Ferriprox Prescribing Information
- FERRIPROX can cause agranulocytosis that can lead to serious infections and death. Neutropenia may precede the development of agranulocytosis.[see Warnings and Precautions ()]
5.1 Agranulocytosis and NeutropeniaFatal agranulocytosis can occur with FERRIPROX use. FERRIPROX can also cause neutropenia, which may foreshadow agranulocytosis. Measure the absolute neutrophil count (ANC) before starting FERRIPROX therapy and monitor it weekly while on therapy.
Interrupt FERRIPROX therapy if neutropenia develops (ANC < 1.5 x 109/L).
Interrupt FERRIPROX if infection develops and monitor the ANC frequently.
Advise patients taking FERRIPROX to immediately interrupt therapy and report to their physician if they experience any symptoms indicative of infection.
The incidence of agranulocytosis was 1.7% of patients in pooled clinical trials of 642 patients with thalassemia syndromes and 1.5% of patients in pooled clinical trials of 196 patients with sickle cell disease or other anemias. The mechanism of FERRIPROX-associated agranulocytosis is unknown. Agranulocytosis and neutropenia usually resolve upon discontinuation of FERRIPROX, but there have been reports of agranulocytosis leading to death.
Implement a plan to monitor for and to manage agranulocytosis and neutropenia prior to initiating FERRIPROX treatment.
For agranulocytosis (ANC < 0.5 x 109/L):Consider hospitalization and other management as clinically appropriate.
Do not resume FERRIPROX in patients who have developed agranulocytosis unless potential benefits outweigh potential risks. Do not rechallenge patients who have developed neutropenia with FERRIPROX unless potential benefits outweigh potential risks.
For neutropenia (ANC < 1.5 x 109/L and > 0.5 x 109/L):Instruct the patient to immediately discontinue FERRIPROX and all other medications with a potential to cause neutropenia.
Obtain a complete blood cell (CBC) count, including a white blood cell (WBC) count corrected for the presence of nucleated red blood cells, an absolute neutrophil count (ANC), and a platelet count daily until recovery (ANC ≥ 1.5 x 109/L).
- Measure the absolute neutrophil count (ANC) before starting FERRIPROX therapy and monitor weekly while on therapy. Interrupt FERRIPROX therapy if neutropenia develops.[see Warnings and Precautions ()]
5.1 Agranulocytosis and NeutropeniaFatal agranulocytosis can occur with FERRIPROX use. FERRIPROX can also cause neutropenia, which may foreshadow agranulocytosis. Measure the absolute neutrophil count (ANC) before starting FERRIPROX therapy and monitor it weekly while on therapy.
Interrupt FERRIPROX therapy if neutropenia develops (ANC < 1.5 x 109/L).
Interrupt FERRIPROX if infection develops and monitor the ANC frequently.
Advise patients taking FERRIPROX to immediately interrupt therapy and report to their physician if they experience any symptoms indicative of infection.
The incidence of agranulocytosis was 1.7% of patients in pooled clinical trials of 642 patients with thalassemia syndromes and 1.5% of patients in pooled clinical trials of 196 patients with sickle cell disease or other anemias. The mechanism of FERRIPROX-associated agranulocytosis is unknown. Agranulocytosis and neutropenia usually resolve upon discontinuation of FERRIPROX, but there have been reports of agranulocytosis leading to death.
Implement a plan to monitor for and to manage agranulocytosis and neutropenia prior to initiating FERRIPROX treatment.
For agranulocytosis (ANC < 0.5 x 109/L):Consider hospitalization and other management as clinically appropriate.
Do not resume FERRIPROX in patients who have developed agranulocytosis unless potential benefits outweigh potential risks. Do not rechallenge patients who have developed neutropenia with FERRIPROX unless potential benefits outweigh potential risks.
For neutropenia (ANC < 1.5 x 109/L and > 0.5 x 109/L):Instruct the patient to immediately discontinue FERRIPROX and all other medications with a potential to cause neutropenia.
Obtain a complete blood cell (CBC) count, including a white blood cell (WBC) count corrected for the presence of nucleated red blood cells, an absolute neutrophil count (ANC), and a platelet count daily until recovery (ANC ≥ 1.5 x 109/L).
- Interrupt FERRIPROX if infection develops, and monitor the ANC more frequently.[see Warnings and Precautions ()]
5.1 Agranulocytosis and NeutropeniaFatal agranulocytosis can occur with FERRIPROX use. FERRIPROX can also cause neutropenia, which may foreshadow agranulocytosis. Measure the absolute neutrophil count (ANC) before starting FERRIPROX therapy and monitor it weekly while on therapy.
Interrupt FERRIPROX therapy if neutropenia develops (ANC < 1.5 x 109/L).
Interrupt FERRIPROX if infection develops and monitor the ANC frequently.
Advise patients taking FERRIPROX to immediately interrupt therapy and report to their physician if they experience any symptoms indicative of infection.
The incidence of agranulocytosis was 1.7% of patients in pooled clinical trials of 642 patients with thalassemia syndromes and 1.5% of patients in pooled clinical trials of 196 patients with sickle cell disease or other anemias. The mechanism of FERRIPROX-associated agranulocytosis is unknown. Agranulocytosis and neutropenia usually resolve upon discontinuation of FERRIPROX, but there have been reports of agranulocytosis leading to death.
Implement a plan to monitor for and to manage agranulocytosis and neutropenia prior to initiating FERRIPROX treatment.
For agranulocytosis (ANC < 0.5 x 109/L):Consider hospitalization and other management as clinically appropriate.
Do not resume FERRIPROX in patients who have developed agranulocytosis unless potential benefits outweigh potential risks. Do not rechallenge patients who have developed neutropenia with FERRIPROX unless potential benefits outweigh potential risks.
For neutropenia (ANC < 1.5 x 109/L and > 0.5 x 109/L):Instruct the patient to immediately discontinue FERRIPROX and all other medications with a potential to cause neutropenia.
Obtain a complete blood cell (CBC) count, including a white blood cell (WBC) count corrected for the presence of nucleated red blood cells, an absolute neutrophil count (ANC), and a platelet count daily until recovery (ANC ≥ 1.5 x 109/L).
- Advise patients taking FERRIPROX to report immediately any symptoms indicative of infection.[see Warnings and Precautions ()]
5.1 Agranulocytosis and NeutropeniaFatal agranulocytosis can occur with FERRIPROX use. FERRIPROX can also cause neutropenia, which may foreshadow agranulocytosis. Measure the absolute neutrophil count (ANC) before starting FERRIPROX therapy and monitor it weekly while on therapy.
Interrupt FERRIPROX therapy if neutropenia develops (ANC < 1.5 x 109/L).
Interrupt FERRIPROX if infection develops and monitor the ANC frequently.
Advise patients taking FERRIPROX to immediately interrupt therapy and report to their physician if they experience any symptoms indicative of infection.
The incidence of agranulocytosis was 1.7% of patients in pooled clinical trials of 642 patients with thalassemia syndromes and 1.5% of patients in pooled clinical trials of 196 patients with sickle cell disease or other anemias. The mechanism of FERRIPROX-associated agranulocytosis is unknown. Agranulocytosis and neutropenia usually resolve upon discontinuation of FERRIPROX, but there have been reports of agranulocytosis leading to death.
Implement a plan to monitor for and to manage agranulocytosis and neutropenia prior to initiating FERRIPROX treatment.
For agranulocytosis (ANC < 0.5 x 109/L):Consider hospitalization and other management as clinically appropriate.
Do not resume FERRIPROX in patients who have developed agranulocytosis unless potential benefits outweigh potential risks. Do not rechallenge patients who have developed neutropenia with FERRIPROX unless potential benefits outweigh potential risks.
For neutropenia (ANC < 1.5 x 109/L and > 0.5 x 109/L):Instruct the patient to immediately discontinue FERRIPROX and all other medications with a potential to cause neutropenia.
Obtain a complete blood cell (CBC) count, including a white blood cell (WBC) count corrected for the presence of nucleated red blood cells, an absolute neutrophil count (ANC), and a platelet count daily until recovery (ANC ≥ 1.5 x 109/L).
Tablets: 500 mg film-coated, capsule-shaped, white to off-white tablets with functional scoring, and imprinted with “APO” score “500” on one side and plain on the other.
FERRIPROX is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to deferiprone or to any of the excipients in the formulation. The following reactions have been reported in association with the administration of deferiprone: Henoch-Schönlein purpura; urticaria; and periorbital edema with skin rash
The following additional adverse reactions have been reported in patients receiving FERRIPROX. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or to establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described below and elsewhere in the labeling:
- Agranulocytosis and Neutropenia [see Warnings and Precautions ()]
5.1 Agranulocytosis and NeutropeniaFatal agranulocytosis can occur with FERRIPROX use. FERRIPROX can also cause neutropenia, which may foreshadow agranulocytosis. Measure the absolute neutrophil count (ANC) before starting FERRIPROX therapy and monitor it weekly while on therapy.
Interrupt FERRIPROX therapy if neutropenia develops (ANC < 1.5 x 109/L).
Interrupt FERRIPROX if infection develops and monitor the ANC frequently.
Advise patients taking FERRIPROX to immediately interrupt therapy and report to their physician if they experience any symptoms indicative of infection.
The incidence of agranulocytosis was 1.7% of patients in pooled clinical trials of 642 patients with thalassemia syndromes and 1.5% of patients in pooled clinical trials of 196 patients with sickle cell disease or other anemias. The mechanism of FERRIPROX-associated agranulocytosis is unknown. Agranulocytosis and neutropenia usually resolve upon discontinuation of FERRIPROX, but there have been reports of agranulocytosis leading to death.
Implement a plan to monitor for and to manage agranulocytosis and neutropenia prior to initiating FERRIPROX treatment.
For agranulocytosis (ANC < 0.5 x 109/L):Consider hospitalization and other management as clinically appropriate.
Do not resume FERRIPROX in patients who have developed agranulocytosis unless potential benefits outweigh potential risks. Do not rechallenge patients who have developed neutropenia with FERRIPROX unless potential benefits outweigh potential risks.
For neutropenia (ANC < 1.5 x 109/L and > 0.5 x 109/L):Instruct the patient to immediately discontinue FERRIPROX and all other medications with a potential to cause neutropenia.
Obtain a complete blood cell (CBC) count, including a white blood cell (WBC) count corrected for the presence of nucleated red blood cells, an absolute neutrophil count (ANC), and a platelet count daily until recovery (ANC ≥ 1.5 x 109/L).
- Liver Enzyme Elevations [see Warnings and Precautions ()]
5.2 Liver Enzyme ElevationsIn pooled clinical trials, 7.5% of 642 patients with thalassemia syndromes treated with FERRIPROX developed increased ALT values. Four (0.62%) FERRIPROX-treated subjects discontinued the drug due to increased serum ALT levels and 1 (0.16%) due to an increase in both ALT and AST. In pooled clinical trials, 7.7% of 196 patients with sickle cell disease or other anemias treated with FERRIPROX developed increased ALT values.
Monitor serum ALT values monthly during therapy with FERRIPROX and consider interruption of therapy if there is a persistent increase in the serum transaminase levels.
- Zinc Deficiency [see Warnings and Precautions ()]
5.3 Zinc DeficiencyDecreased plasma zinc concentrations have been observed on FERRIPROX therapy. Monitor plasma zinc, and supplement in the event of a deficiency.
FERRIPROX Tablets (deferiprone) contain 500 mg deferiprone (3-hydroxy-1,2-dimethylpyridin-4-one), a synthetic, orally active, iron-chelating agent. The molecular formula for deferiprone is C7H9NO2 and its molecular weight is 139.15 g/mol. Deferiprone has the following structural formula:
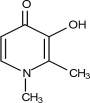
Deferiprone is a white to pinkish-white powder. It is sparingly soluble in deionized water (14.3 mg/mL) and has a melting point range of 272 °C - 278 °C.
FERRIPROX Tablets are white to off-white, capsule-shaped tablets, and imprinted with “APO” score “500” on one side and plain on the other. The tablets can be broken in half along the score line. Each tablet contains 500 mg deferiprone and the following inactive ingredients: Tablet core - microcrystalline cellulose, magnesium stearate, colloidal silicon dioxide; Coating - hypromellose, polyethylene glycol, titanium dioxide.
FERRIPROX® Tablets (deferiprone) are white to off-white capsule-shaped tablets, film-coated, and have a functional score imprinted with “APO” score “500” on one side and are plain on the other. They are provided in HDPE bottles.
500 mg film-coated tablets, 100 tablets NDC 10122-100-10
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].