Flumazenil
Flumazenil Prescribing Information
Flumazenil Injection, USP is indicated for the reversal of conscious sedation induced with benzodiazepines (see
Flumazenil Injection, USP is indicated for the complete or partial reversal of the sedative effects of benzodiazepines in cases where general anesthesia has been induced and/or maintained with benzodiazepines, where sedation has been produced with benzodiazepines for diagnostic and therapeutic procedures, and for the management of benzodiazepine overdose.
Flumazenil Injection, USP is indicated for the reversal of conscious sedation induced with benzodiazepines (see
The safety and effectiveness of flumazenil have been established in pediatric patients 1 year of age and older. Use of flumazenil in this age group is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies of flumazenil in adults with additional data from uncontrolled pediatric studies including one open-label trial.
The use of flumazenil to reverse the effects of benzodiazepines used for conscious sedation was evaluated in one uncontrolled clinical trial involving 107 pediatric patients between the ages of 1 and 17 years. At the doses used, flumazenil’s safety was established in this population. Patients received up to 5 injections of 0.01 mg/kg flumazenil up to a maximum total dose of 1 mg at a rate not exceeding 0.2 mg/min.
Of 60 patients who were fully alert at 10 minutes, 7 experienced resedation. Resedation occurred between 19 and 50 minutes after the start of flumazenil administration. None of the patients experienced a return to the baseline level of sedation. All 7 patients were between the ages of 1 and 5 years. The types and frequency of adverse events noted in these pediatric patients were similar to those previously documented in clinical trials with flumazenil to reverse conscious sedation in adults. No patient experienced a serious adverse event attributable to flumazenil.
The safety and efficacy of flumazenil in the reversal of conscious sedation in pediatric patients below the age of 1 year have not been established (see
The safety and efficacy of flumazenil have not been established in pediatric patients for reversal of the sedative effects of benzodiazepines used for induction of general anesthesia, for the management of overdose, or for the resuscitation of the newborn, as no well-controlled clinical studies have been performed to determine the risks, benefits and dosages to be used. However, published anecdotal reports discussing the use of flumazenil in pediatric patients for these indications have reported similar safety profiles and dosing guidelines to those described for the reversal of conscious sedation.
The risks identified in the adult population with flumazenil use also apply to pediatric patients. Therefore, consult the
Flumazenil Injection, USP is supplied in sealed dosage forms and poses no known risk to the healthcare provider. Routine care should be taken to avoid aerosol generation when preparing syringes for injection, and spilled medication should be rinsed from the skin with cool water.
Flumazenil Injection, USP is contraindicated:
• in patients with a known hypersensitivity to flumazenil or benzodiazepines.
• in patients who have been given a benzodiazepine for control of a potentially life-threatening condition (e.g., control of intracranial pressure or status epilepticus).
• in patients who are showing signs of serious cyclic antidepressant overdose (see
THE USE OF FLUMAZENIL HAS BEEN ASSOCIATED WITH THE OCCURRENCE OF SEIZURES. THESE ARE MOST FREQUENT IN PATIENTS WHO HAVE BEEN ON BENZODIAZEPINES FOR LONG-TERM SEDATION OR IN OVERDOSE CASES WHERE PATIENTS ARE SHOWING SIGNS OF SERIOUS CYCLIC ANTIDEPRESSANT OVERDOSE. PRACTITIONERS SHOULD INDIVIDUALIZE THE DOSAGE OF FLUMAZENIL AND BE PREPARED TO MANAGE SEIZURES. |
The following events have been reported during postapproval use of flumazenil.
Withdrawal symptoms may occur following rapid injection of flumazenil in patients with long-term exposure to benzodiazepines.
Flumazenil Injection, USP is a benzodiazepine receptor antagonist. Chemically, flumazenil is ethyl 8-fluoro-5,6-dihydro-5-methyl-6-oxo-4H-imidazo [1,5-a] (1,4) benzodiazepine-3-carboxylate. Flumazenil has an imidazobenzodiazepine structure and the following structural formula:
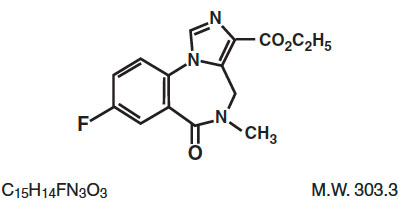
Flumazenil is a white to off-white crystalline compound with an octanol:buffer partition coefficient of 14 to 1 at pH 7.4. It is insoluble in water but slightly soluble in acidic aqueous solutions. Flumazenil Injection, USP is available as a sterile parenteral dosage form for intravenous administration. Each mL contains 0.1 mg of flumazenil compounded with 1.8 mg of methylparaben, 0.2 mg of propylparaben, 0.9% sodium chloride, 0.01% edetate disodium, and 0.01% acetic acid; the pH is adjusted to approximately 3.8 to 4.3 with hydrochloric acid and/or, if necessary, sodium hydroxide.
The pharmacokinetics of flumazenil have been evaluated in 29 pediatric patients ranging in age from 1 to 17 years who had undergone minor surgical procedures. The average doses administered were 0.53 mg (0.044 mg/kg) in patients aged 1 to 5 years, 0.63 mg (0.020 mg/kg) in patients aged 6 to 12 years, and 0.8 mg (0.014 mg/kg) in patients aged 13 to 17 years. Compared to adults, the half-life was somewhat shorter and more variable in these patients, averaging 40 minutes and generally ranging from 20 to 75 minutes. Clearance and volume of distribution, normalized for body weight, were in the same range as those seen in adults, although more variability was seen in the pediatric patients.