Fluocinonide - Fluocinonide ointment (Fluocinonide)
Fluocinonide - Fluocinonide ointment prescribing information
Fluocinonide Ointment is indicated for the relief of the inflammatory and pruritic manifestations of corticosteroid-responsive dermatoses.
Fluocinonide Ointment is generally applied to the affected area as a thin film from two to four times daily depending on the severity of the condition.
Occlusive dressings may be used for the management of psoriasis or recalcitrant conditions.
If an infection develops, the use of the occlusive dressings should be discontinued and appropriate antimicrobial therapy instituted.
Topical corticosteroids are contraindicated in those patients with a history of hypersensitivity to any of the components of the preparation.
The following local adverse reactions are reported infrequently with topical corticosteroids, but may occur more frequently with the use of occlusive dressings. These reactions are listed in an approximate decreasing order of occurrence:
| Burning | Perioral dermatitis |
| Itching | Allergic contact dermatitis |
| Irritation | Maceration of the skin |
| Dryness | Secondary infection |
| Folliculitis | Skin atrophy |
| Hypertrichosis | Striae |
| Acneiform eruptions | Miliaria |
| Hypopigmentation |
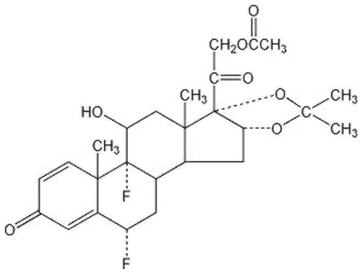
Fluocinonide Ointment, 0.05% is intended for topical administration. The active component is the corticosteroid fluocinonide, which is the 21-acetate ester of fluocinolone acetonide and has the chemical name pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione,21-(acetyloxy)-6,9-difluoro-11-hydroxy-16,17-[(1-methylethylidene)bis(oxy)]-,(6α,11β,16α)-. It has the following chemical structure:
Fluocinonide Ointment contains fluocinonide 0.5 mg/g in a specially formulated ointment base consisting of glyceryl monostearate, white petrolatum, propylene carbonate, propylene glycol and white wax. It provides the occlusive and emollient effects desirable in an ointment.
In this formulation, the active ingredient is totally in solution.
Topical corticosteroids share anti-inflammatory, anti-pruritic and vasoconstrictive actions.
The mechanism of anti-inflammatory activity of the topical corticosteroids is unclear. Various laboratory methods, including vasoconstrictor assays, are used to compare and predict potencies and/or clinical efficacies of the topical corticosteroids. There is some evidence to suggest that a recognizable correlation exists between vasoconstrictor potency and therapeutic efficacy in man.