Furosemide
Furosemide Prescribing Information
Injection: Furosemide Injection, USP is supplied as a sterile, colorless solution as
- 20 mg/2 mL (10 mg/mL) in a single-dose vial
- 40 mg/4 mL (10 mg/mL) in a single-dose vial
- 100 mg/10 mL (10 mg/mL) in a single-dose vial
- 500 mg/50 mL (10 mg/mL) in a single-dose vial with hanger
- 1,000 mg/100 mL (10 mg/mL) in a single-dose vial with hanger
- Furosemide injection is contraindicated in patients with anuria.
- Furosemide injection is contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to furosemide.
The following adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Fluid, Electrolyte, and Metabolic Abnormalities [see Warnings and Precautions ]
- Ototoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions ]
The following adverse reactions associated with the use of furosemide were identified in clinical studies or postmarketing reports. Because some of these reactions were reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Adverse reactions are categorized below by organ system and listed by decreasing severity.
Furosemide Injection, USP contains furosemide as the active pharmaceutical ingredient. Furosemide is a loop diuretic which is an anthranilic acid derivative. Furosemide chemical name is 4-chloro-
Furosemide is a white to slightly-yellow crystalline powder. It is practically insoluble in water, sparingly soluble in alcohol, freely soluble in dilute alkali solutions and insoluble in dilute acids.
The structural formula is as follows:
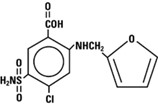
Molecular formula: C12H11CIN2O5S Molecular weight: 330.74
Furosemide Injection, USP 10 mg/mL is a sterile, non-pyrogenic solution, available in single-dose vials for intravenous and intramuscular injection. Each mL contains: Furosemide 10 mg, Sodium Chloride 7.5 mg for isotonicity, Sodium Hydroxide 1.35 mg, Sodium Hydroxide and Hydrochloric Acid, if necessary, to adjust pH between 8.0 and 9.3, Water for Injection q.s.
Furosemide inhibits primarily the reabsorption of sodium and chloride not only in the proximal and distal tubules but also in the loop of Henle. The high degree of efficacy is largely due to this unique site of action. The action on the distal tubule is independent of any inhibitory effect on carbonic anhydrase and aldosterone.
Furosemide was tested for carcinogenicity by oral administration in one strain of mice and one strain of rats. A small but significantly increased incidence of mammary gland carcinomas occurred in female mice at a dose approximately 8 times a human i.v. dose of 80 mg based on BSA and oral bioavailability corrections. There were marginal increases in uncommon tumors in male rats at a dose of 15 mg/kg but not at 30 mg/kg.
Furosemide was devoid of mutagenic activity in various strains of
Furosemide produced no impairment of fertility in male or female rats, at 100 mg/kg/day (the maximum effective diuretic dose in the rat), approximately 7 times a human i.v. dose of 80 mg based on BSA and oral bioavailability corrections.