Heparin Sodium In Dextrose
(Heparin Sodium And Dextrose)Heparin Sodium In Dextrose Prescribing Information
Heparin Sodium in 5% Dextrose Injection is indicated for:
- Prophylaxis and treatment of venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism
- Prophylaxis and treatment of thromboembolic complications associated with atrial fibrillation
- Treatment of acute and chronic consumption coagulopathies (disseminated intravascular coagulation)
- Prevention of clotting in arterial and cardiac surgery
- Prophylaxis and treatment of peripheral arterial embolism
- Anticoagulant use in blood transfusions, extracorporeal circulation, and dialysis procedures.
HEPARIN SODIUM IN 5% DEXTROSE INJECTION is available as:
• Heparin Sodium 20,000 USP units per 500 mL (40 USP units per mL) in 5% Dextrose Injection.
• Heparin Sodium 25,000 USP units per 500 mL (50 USP units per mL) in 5% Dextrose Injection.
• Heparin Sodium 25,000 USP units per 250 mL (100 USP units per mL) in 5% Dextrose Injection.
The use of HEPARIN SODIUM in 5% Dextrose Injection is contraindicated in patients with the following conditions:
- History of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) and heparin-induced thrombocytopenia and thrombosis (HITT) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Known hypersensitivity to heparin or pork products (e.g., anaphylactoid reactions) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)]
- In whom suitable blood coagulation tests – e.g., the whole blood clotting time, partial thromboplastin time, etc., – cannot be performed at appropriate intervals (this contraindication refers to full-dose heparin; there is usually no need to monitor coagulation parameters in patients receiving low-dose heparin) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Uncontrollable active bleeding state except when this is due to disseminated intravascular coagulation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
The following serious adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Hemorrhage [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia and Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia with Thrombosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Thrombocytopenia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Heparin Resistance [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Hypersensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Hyperkalemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Elevations of Serum Aminotransferases [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Drugs that interfere with coagulation, platelet aggregation or drugs that counteract coagulation may induce bleeding. ()
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS- Drugs that interfere with coagulation, platelet aggregation or drugs that counteract coagulation may induce bleeding.
7.1 Oral
AnticoagulantsHeparin sodium may prolong the one-stage prothrombin time. Therefore, when heparin sodium is given with dicumarol or warfarin sodium, a period of at least 5 hours after the last intravenous dose or 24 hours after the last subcutaneous dose should elapse before blood is drawn if a valid prothrombin time is to be obtained.
7.2 Platelet InhibitorsDrugs such as NSAIDS (including acetylsalicylic acid, ibuprofen, indomethacin, and celecoxib), dextran, phenylbutazone, thienopyridines, dipyridamole, hydroxychloroquine, glycoprotein IIv/IIa antagonists (including abciximab, eptifibatide, and tirofiban), and others that interfere with platelet-aggregation reactions (the main hemostatic defense of heparinized patients) may induce bleeding and should be used with caution in patients receiving heparin sodium. To reduce the risk of bleeding, a reduction in the dose of antiplatelet agent or heparin is recommended.
7.3 Other Medications that May Interfere with HeparinDigitalis, tetracyclines, nicotine, antihistamines, or intravenous nitroglycerin may partially counteract the anticoagulant action of heparin sodium. Intravenous nitroglycerin administered to heparinized patients may result in a decrease of the partial thromboplastin time with subsequent rebound effect upon discontinuation of nitroglycerin. Careful monitoring of partial thromboplastin time and adjustment of heparin dosage are recommended during coadministration of heparin and intravenous nitroglycerin. Antithrombin III (human) – The anticoagulant effect of heparin is enhanced by concurrent treatment with antithrombin III (human) in patients with hereditary antithrombin III deficiency. To reduce the risk of bleeding, a reduced dosage of heparin is recommended during treatment with antithrombin III (human).
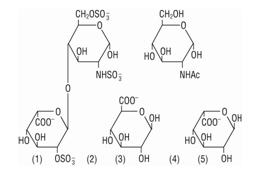
Heparin is a heterogenous group of straight-chain anionic mucopolysaccharides, called glycosaminoglycans having anticoagulant properties. It is composed of polymers of alternating derivations of alpha-L-iduronic acid 2-sulfate (1), 2-deoxy-2-sulfamino- alpha-D-glucose 6-sulfate (2), beta-D-glucuronic acid (3), 2-acetamido-2- deoxy-alpha-D-glucose (4), and alpha-L-iduronic acid (5).
Structure of Heparin Sodium (representative subunits):
Heparin Sodium in 5% Dextrose Injection is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution prepared from Heparin Sodium USP (derived from porcine intestinal mucosa and standardized for use as an anticoagulant) and Hydrous Dextrose USP. It is to be administered by intravenous injection. The potency is determined by a biological assay using a USP reference standard based on units of heparin activity per milligram.
The pH range is 5.6 (4.5 – 7.0) and the osmolarity mOsmol/L (calc.) is 315. The concentration of electrolytes is 38 mEq/L Sodium, 30 mEq/L Phosphate, and 15 mEq/L Citrate.
40 USP units/mL: Each 100 mL of the 20,000 USP units per 500 mL preparation contains: 4,000 USP units of heparin sodium, 5 g Hydrous Dextrose USP, 0.41 g Dibasic Sodium Phosphate, 0.093 g Citric Acid Anhydrous USP, 0.0686 g Sodium Metabisulfite NF (antioxidant), and Water for Injection USP until quantity sufficient.
50 USP units/mL: Each 100 mL of the 25,000 USP units per 500 mL preparation contains: 5,000 USP units of heparin sodium, 5 g Hydrous Dextrose USP, 0.41 g Dibasic Sodium Phosphate, 0.093 g Citric Acid Anhydrous USP, 0.0686 g Sodium Metabisulfite NF (antioxidant), and Water for Injection USP until quantity sufficient.
100 USP units/mL: Each 100 mL of the 25,000 USP units per 250 mL preparation contains: 10,000 USP units of heparin sodium, 5 g Hydrous Dextrose USP, 0.41 g Dibasic Sodium Phosphate, 0.093 g Citric Acid Anhydrous USP, 0.0686 g Sodium Metabisulfite NF (antioxidant), and Water for Injection USP until quantity sufficient.
The plastic container is made from a multilayered film specifically developed for parenteral drugs. It contains no plasticizers and exhibits virtually no leachables. The solution contact layer is a rubberized copolymer of ethylene and propylene. The container is nontoxic and biologically inert. The container-solution unit is a closed system and is not dependent upon entry of external air during administration. The container is overwrapped to provide protection from the physical environment and to provide an additional moisture barrier when necessary.
The plastic container is not made with natural rubber latex, PVC or DEHP.
The closure system has two ports; the one for the administration set has a tamper evident plastic protector.