Hydrochlorothiazide
Hydrochlorothiazide Prescribing Information
Hydrochlorothiazide tablets are indicated as adjunctive therapy in edema associated with congestive heart failure, hepatic cirrhosis, and corticosteroid and estrogen therapy.
Hydrochlorothiazide tablets have also been found useful in edema due to various forms of renal dysfunction such as nephrotic syndrome, acute glomerulonephritis, and chronic renal failure.
Hydrochlorothiazide tablets are indicated in the management of hypertension either as the sole therapeutic agent or to enhance the effectiveness of other antihypertensive drugs in the more severe forms of hypertension.
Therapy should be individualized according to patient response. Use the smallest dosage necessary to achieve the required response
Hypersensitivity to this product or to other sulfonamide-derived drugs.
The following adverse reactions have been reported and, within each category, are listed in order of decreasing severity.
Hydrochlorothiazide is a diuretic and antihypertensive. It is the 3,4-dihydro derivative of chlorothiazide. It is chemically designated as 6-chloro-3,4-dihydro-
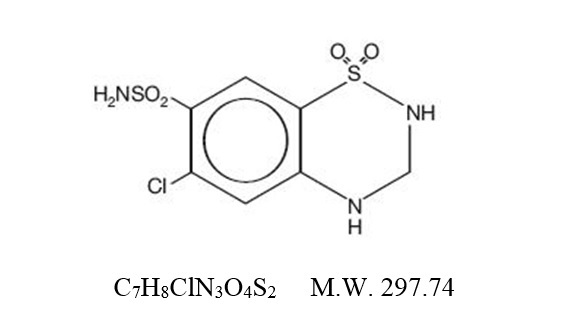
Hydrochlorothiazide, USP is a white, or practically white, crystalline powder which is slightly soluble in water, freely soluble in sodium hydroxide solution, in
The mechanism of the antihypertensive effect of thiazides is unknown. Hydrochlorothiazide does not usually affect normal blood pressure.
Hydrochlorothiazide affects the distal renal tubular mechanism of electrolyte reabsorption. At maximal therapeutic dosage all thiazides are approximately equal in their diuretic efficacy.
Hydrochlorothiazide increases excretion of sodium and chloride in approximately equivalent amounts. Natriuresis may be accompanied by some loss of potassium and bicarbonate.
After oral use diuresis begins within 2 hours, peaks in about 4 hours and lasts about 6 to 12 hours.