Isosorbide Mononitrate
Isosorbide Mononitrate Prescribing Information
Isosorbide mononitrate extended-release tablets are indicated for the prevention of angina pectoris due to coronary artery disease. The onset of action of oral isosorbide mononitrate is not sufficiently rapid for this product to be useful in aborting an acute anginal episode.
The recommended starting dose of Isosorbide Mononitrate Extended-Release Tablets, USP is 30 mg (given as a single 30 mg tablet or as 1/2 of a 60 mg tablet) or 60 mg (given as a single tablet) once daily. After several days, the dosage may be increased to 120 mg (given as a single 120 mg tablet or as two 60 mg tablets) once daily. Rarely, 240 mg may be required. The daily dose of Isosorbide Mononitrate Extended-Release Tablets, USP should be taken in the morning on arising. Isosorbide Mononitrate Extended-Release Tablets, USP should not be chewed or crushed and should be swallowed together with a half-glassful of fluid.
Isosorbide mononitrate extended-release tablets are contraindicated in patients who have shown hypersensitivity or idiosyncratic reactions to other nitrates or nitrites.
The table below shows the frequencies of the adverse events that occurred in >5% of the subjects in three placebo-controlled North American studies in which patients in the active treatment arm received 30 mg, 60 mg, 120 mg, or 240 mg of isosorbide mononitrate extended-release tablets once daily. In parentheses, the same table shows the frequencies with which these adverse events were associated with the discontinuation of treatment. Overall, 8% of the patients who received 30 mg, 60 mg, 120 mg, or 240 mg of isosorbide mononitrate in the three placebo-controlled North American studies discontinued treatment because of adverse events. Most of these discontinued because of headache. Dizziness was rarely associated with withdrawal from these studies. Since headache appears to be a dose-related adverse effect and tends to disappear with continued treatment, it is recommended that isosorbide mononitrate extended-release tablets treatment be initiated at low doses for several days before being increased to desired levels.
* Some individuals discontinued for multiple reasons. | |||||
† Patients were started on 60 mg and titrated to their final dose. | |||||
Three Controlled North American Studies | |||||
Dose | Placebo | 30 mg | 60 mg | 120 mg † | 240 mg † |
| Patients | 96 | 60 | 102 | 65 | 65 |
| Headache | 15% (0%) | 38% (5%) | 51% (8%) | 42% (5%) | 57% (8%) |
| Dizziness | 4% (0%) | 8% (0%) | 11% (1%) | 9% (2%) | 9% (2%) |
In addition, the three North American trials were pooled with 11 controlled trials conducted in Europe. Among the 14 controlled trials, a total of 711 patients were randomized to isosorbide mononitrate extended-release tablets. When the pooled data were reviewed, headache and dizziness were the only adverse events that were reported by >5% of patients. Other adverse events, each reported by ≤5% of exposed patients, and in many cases of uncertain relation to drug treatment, were:
In addition, the following spontaneous adverse event has been reported during the marketing of isosorbide mononitrate: syncope.
The vasodilating effects of isosorbide mononitrate may be additive with those of other vasodilators. Alcohol, in particular, has been found to exhibit additive effects of this variety.
Marked symptomatic orthostatic hypotension has been reported when calcium channel blockers and organic nitrates were used in combination. Dose adjustments of either class of agents may be necessary.
Isosorbide mononitrate (ISMN), an organic nitrate and the major biologically active metabolite of isosorbide dinitrate (ISDN), is a vasodilator with effects on both arteries and veins.
Isosorbide mononitrate tablets contain either 30 mg, 60 mg or 120 mg of isosorbide mononitrate in an extended-release formulation. In addition, each tablet contains the following inactive ingredients: microcrystalline cellulose, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose, colloidal silicon dioxide, lactose monohydrate and magnesium stearate.
The molecular formula of ISMN is C6H9NO6 and the molecular weight is 191.14. The chemical name for ISMN is 1,4:3,6-dianhydro-,D-glucitol 5-nitrate; the compound has the following structural formula:
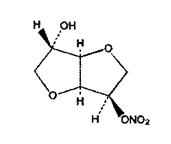
ISMN is a white, crystalline, odorless compound which is stable in air and in solution, has a melting point of about 90°C, and an optical rotation of +140° to 146° (2% in water, 20°C).
Isosorbide mononitrate is freely soluble in water, acetic acid, alcohol, acetone and ethyl acetate; soluble in ether and chloroform, slightly soluble in toluene; practically insoluble in aliphatic hydrocarbons.