Ivra Prescribing Information
- Severe bone marrow suppression with resulting infection or bleeding may occur. Controlled trials comparing intravenous melphalan to oral melphalan have shown more myelosuppression with the intravenous formulation. Monitor hematologic laboratory parameters[see Warnings and Precautions ()]
5.1 Bone Marrow SuppressionIVRA causes bone marrow suppression in most patients.
Obtain complete blood counts with differential at the start of therapy and prior to each subsequent dose of IVRA. Withhold treatment for grade 3 thrombocytopenia and/ or leukopenia until blood counts have returned to grade 2
[see Dosage and Administration ]. Consider dose adjustment on the basis of blood counts at the nadir and day of treatment..
- Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, have occurred in approximately 2% of patients who received the intravenous formulation of melphalan. Discontinue treatment withIVRAfor serious hypersensitivity reactions[see Warnings and Precautions (5.4 Hypersensitivity
Acute hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis were reported in 2.4% of 425 patients receiving melphalan injection for myeloma. These reactions were characterized by urticaria, pruritus, edema, skin rashes, and in some patients, tachycardia, bronchospasm, dyspnea, and hypotension. These patients appeared to respond to antihistamine and corticosteroid therapy. If a hypersensitivity reaction occurs, intravenous or oral melphalan should not be readministered since hypersensitivity reactions have also been reported with oral melphalan. Cardiac arrest has also been reported in association with such reports.
Discontinue treatment with IVRA for serious hypersensitivity reactions.
)].
- Melphalan produces chromosomal aberrationsin vitroandin vivo.IVRAshould be considered potentially leukemogenic in humans[see Warnings and Precautions()].5.5 Secondary Malignancies
Melphalan has been shown to cause chromatid or chromosome damage in humans. Secondary malignancies, including acute nonlymphocytic leukemia, myeloproliferative syndrome, and carcinoma, have been reported in patients with cancer treated with alkylating agents (including melphalan). Some patients also received other chemotherapeutic agents or radiation therapy. The potential benefits from melphalan therapy must be weighed on an individual basis against the possible risk of the induction of a second malignancy.
IVRA is indicated for the palliative treatment of patients with multiple myeloma for whom oral therapy is not appropriate.
Injection: 90 mg/mL melphalan as a clear colorless to yellow solution in a multiple-dose vial for dilution.
IVRA is contraindicated in patients with a history of severe hypersensitivity to melphalan. Reactions have included anaphylaxis
Acute hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis were reported in 2.4% of 425 patients receiving melphalan injection for myeloma. These reactions were characterized by urticaria, pruritus, edema, skin rashes, and in some patients, tachycardia, bronchospasm, dyspnea, and hypotension. These patients appeared to respond to antihistamine and corticosteroid therapy. If a hypersensitivity reaction occurs, intravenous or oral melphalan should not be readministered since hypersensitivity reactions have also been reported with oral melphalan. Cardiac arrest has also been reported in association with such reports.
Discontinue treatment with IVRA for serious hypersensitivity reactions.
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Bone Marrow Suppression [see Warnings and Precautions()]
5.1 Bone Marrow SuppressionIVRA causes bone marrow suppression in most patients.
Obtain complete blood counts with differential at the start of therapy and prior to each subsequent dose of IVRA. Withhold treatment for grade 3 thrombocytopenia and/ or leukopenia until blood counts have returned to grade 2
[see Dosage and Administration ]. Consider dose adjustment on the basis of blood counts at the nadir and day of treatment. - Gastrointestinal Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions()]5.2 Gastrointestinal Toxicity
Gastrointestinal disturbances such as nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, and oral ulceration can occur with melphalan treatment.
Severe mucositis, stomatitis, colitis, diarrhea, and hemorrhage of the gastrointestinal tract occur at high doses (greater than 100 mg/m26 times the recommended approved dose).
Use prophylactic antiemetics [see Dosage and Administration ]. Provide supportive care for nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and mucositis.
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions()]5.3 Hepatotoxicity
Hepatic disorders ranging from abnormal liver function tests to clinical manifestations such as hepatitis and jaundice have been reported during treatment with melphalan. Hepatic veno-occlusive disease has been reported. Monitor liver enzymes as clinically indicated.
- Hypersensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions()]5.4 Hypersensitivity
Acute hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis were reported in 2.4% of 425 patients receiving melphalan injection for myeloma. These reactions were characterized by urticaria, pruritus, edema, skin rashes, and in some patients, tachycardia, bronchospasm, dyspnea, and hypotension. These patients appeared to respond to antihistamine and corticosteroid therapy. If a hypersensitivity reaction occurs, intravenous or oral melphalan should not be readministered since hypersensitivity reactions have also been reported with oral melphalan. Cardiac arrest has also been reported in association with such reports.
Discontinue treatment with IVRA for serious hypersensitivity reactions.
- Secondary Malignancies [see Warnings and Precautions()]5.5 Secondary Malignancies
Melphalan has been shown to cause chromatid or chromosome damage in humans. Secondary malignancies, including acute nonlymphocytic leukemia, myeloproliferative syndrome, and carcinoma, have been reported in patients with cancer treated with alkylating agents (including melphalan). Some patients also received other chemotherapeutic agents or radiation therapy. The potential benefits from melphalan therapy must be weighed on an individual basis against the possible risk of the induction of a second malignancy.
IVRA contains melphalan which is an alkylating drug. The chemical name of melphalan hydrochloride is 4-[bis(2-chloroethyl)amino]-L-phenylalanine hydrochloride. The molecular formula is C13H18Cl2N2O2 • HCl and the molecular weight is 341.67. The structural formula is:
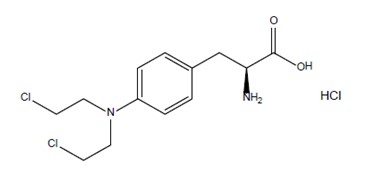
Melphalan hydrochloride is a white to off-white powder, with a melting range of 199°C to 201°C. It is practically insoluble in water, but freely soluble in 1N HCl and methanol.
IVRA is supplied as a sterile, clear colorless to yellow solution in a multiple-dose vial for intravenous use. Each mL contains 90 mg melphalan free base equivalent to 100.75 mg melphalan hydrochloride, 170 mg propylene glycol, 5 mg monothioglycerol, 0.5 mg (1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid dihydrate), and 0.025 mL water for injection in polyethylene glycol 400. May contain hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide for pH adjustment. The pH of the drug product solution after dilution with 0.9% sodium chloride ranges from 2.4 - 3.5. Each mL contains 90 mg melphalan free base equivalent to 100.75 mg melphalan hydrochloride.