Jynarque prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Jynarque patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Recommended dosage (2.1 )
Initial Dosage Titration Step Target Dosage 1st Dose 45 mg 1st Dose 60 mg 1st Dose 90 mg 2nd Dose
(8 hours later)15 mg 2nd Dose
(8 hours later)30 mg 2nd Dose
(8 hours later)30 mg Total Daily Dose 60 mg Total Daily Dose 90 mg Total Daily Dose 120 mg
Recommended Dosage
The initial dosage for JYNARQUE is 60 mg orally per day as 45 mg taken on waking and 15 mg taken 8 hours later. Titrate to 60 mg plus 30 mg then to 90 mg plus 30 mg per day if tolerated with at least weekly intervals between titrations. Patients may down-titrate based on tolerability. Encourage patients to drink enough water to avoid thirst or dehydration.
Monitoring
To mitigate the risk of significant or irreversible liver injury, perform blood testing for ALT, AST and bilirubin prior to initiation of JYNARQUE, at 2 and 4 weeks after initiation, monthly for 18 months and every 3 months thereafter . Monitor for concurrent symptoms that may indicate liver injury [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
Missed Doses
If a dose of JYNARQUE is not taken at the scheduled time, take the next dose at its scheduled time.
Co-Administration with CYP3A Inhibitors
CYP3A Inhibitors
Concomitant use of strong CYP3A inhibitors is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ] .
In patients taking concomitant moderate CYP3A inhibitors, reduce the dose of JYNARQUE per Table 1. Consider further reductions if patients cannot tolerate the reduced dose [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Drug Interactions (7.1) ] . Interrupt JYNARQUE temporarily for short term therapy with moderate CYP3A inhibitors if the recommended reduced doses are not available.
| Standard Morning and Afternoon Dose (mg) | Dose (mg) with Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors |
|---|---|
| 90 mg and 30 mg | 45 mg and 15 mg |
| 60 mg and 30 mg | 30 mg and 15 mg |
| 45 mg and 15 mg | 15 mg and 15 mg |

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Jynarque prescribing information
WARNING: RISK OF SERIOUS LIVER INJURY
JYNARQUE (tolvaptan) can cause serious and potentially fatal liver injury. Acute liver failure requiring liver transplantation has been reported [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
Measure ALT, AST and bilirubin before initiating treatment, at 2 weeks and 4 weeks after initiation, then monthly for the first 18 months and every 3 months thereafter [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] . Prompt action in response to laboratory abnormalities, signs, or symptoms indicative of hepatic injury can mitigate, but not eliminate, the risk of serious hepatotoxicity.
Because of the risks of serious liver injury, JYNARQUE is available only through a restricted distribution program under a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) called the Tolvaptan for ADPKD Shared System REMS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] .
| Warnings and Precautions Tolvaptan for ADPKD Shared System REMS (5.2 ) | 3/2025 |
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
JYNARQUE is indicated to slow kidney function decline in adults at risk of rapidly progressing autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD).
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Recommended dosage (2.1 )
Initial Dosage Titration Step Target Dosage 1st Dose 45 mg 1st Dose 60 mg 1st Dose 90 mg 2nd Dose (8 hours later) 15 mg 2nd Dose (8 hours later) 30 mg 2nd Dose (8 hours later) 30 mg Total Daily Dose 60 mg Total Daily Dose 90 mg Total Daily Dose 120 mg
Recommended Dosage
The initial dosage for JYNARQUE is 60 mg orally per day as 45 mg taken on waking and 15 mg taken 8 hours later. Titrate to 60 mg plus 30 mg then to 90 mg plus 30 mg per day if tolerated with at least weekly intervals between titrations. Patients may down-titrate based on tolerability. Encourage patients to drink enough water to avoid thirst or dehydration.
Monitoring
To mitigate the risk of significant or irreversible liver injury, perform blood testing for ALT, AST and bilirubin prior to initiation of JYNARQUE, at 2 and 4 weeks after initiation, monthly for 18 months and every 3 months thereafter . Monitor for concurrent symptoms that may indicate liver injury [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
Missed Doses
If a dose of JYNARQUE is not taken at the scheduled time, take the next dose at its scheduled time.
Co-Administration with CYP3A Inhibitors
CYP3A Inhibitors
Concomitant use of strong CYP3A inhibitors is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ] .
In patients taking concomitant moderate CYP3A inhibitors, reduce the dose of JYNARQUE per Table 1. Consider further reductions if patients cannot tolerate the reduced dose [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Drug Interactions (7.1) ] . Interrupt JYNARQUE temporarily for short term therapy with moderate CYP3A inhibitors if the recommended reduced doses are not available.
| Standard Morning and Afternoon Dose (mg) | Dose (mg) with Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors |
|---|---|
| 90 mg and 30 mg | 45 mg and 15 mg |
| 60 mg and 30 mg | 30 mg and 15 mg |
| 45 mg and 15 mg | 15 mg and 15 mg |
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
JYNARQUE (tolvaptan) is supplied as non-scored, blue, shallow-convex, immediate release tablets, debossed with "OTSUKA" and the tablet strength (mg) on one side as follows:
| Strength | Shape |
|---|---|
| 15 mg | triangular |
| 30 mg | round |
| 45 mg | square |
| 60 mg | rectangular |
| 90 mg | pentagonal |
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Available data with JYNARQUE use in pregnant women are insufficient to determine if there is a drug associated risk of adverse developmental outcomes. In embryo-fetal development studies, pregnant rats and rabbits received oral tolvaptan during organogenesis. At maternally non-toxic doses, tolvaptan did not cause any developmental toxicity in rats or in rabbits at exposures approximately 4- and 1-times, respectively, the human exposure at the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 90/30 mg. However, effects on embryo-fetal development occurred in both species at maternally toxic doses. In rats, reduced fetal weights and delayed fetal ossification occurred at 17 times the human exposure. In rabbits, increased abortions, embryo-fetal death, fetal microphthalmia, open eyelids, cleft palate, brachymelia and skeletal malformations occurred at approximately 3 times the human exposure (see Data ). Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to the fetus.
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in the U.S. general population is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20% of clinically recognized pregnancies, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
Oral administration of tolvaptan during the period of organogenesis in Sprague-Dawley rats produced no evidence of teratogenesis at doses up to 100 mg/kg/day. Lower body weights and delayed ossification were seen at 1000 mg/kg, which is approximately 17 times the human exposure at the 90/30 mg dose (AUC 24h 6570 h∙ng/mL). The fetal effects are likely secondary to maternal toxicity (decreased food intake and low body weights). In a prenatal and postnatal study in rats, tolvaptan had no effect on physical development, reflex function, learning ability or reproductive performance at doses up to 1000 mg/kg/day.
In New Zealand White rabbits, placental transfer was demonstrated with C max values in the yolk sac fluid approximating 22.7% of the value in maternal rabbit serum. In embryo-fetal studies, teratogenicity (microphthalmia, embryo-fetal mortality, cleft palate, brachymelia and fused phalanx) was evident in rabbits at 1000 mg/kg (approximately 3 times the exposure at the 90/30 mg dose). Body weights and food consumption were lower in dams at all doses, equivalent to 0.6 to 3 times the human exposure at the 90/30 mg dose.
Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of tolvaptan in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Tolvaptan is present in rat milk. When a drug is present in animal milk, it is possible that the drug will be present in human milk, but relative levels may vary (see Data ) . Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions, including liver toxicity, electrolyte abnormalities (e.g., hypernatremia), hypotension, and volume depletion in breastfed infants, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with JYNARQUE.
Data
In lactating rats administration of radiolabeled tolvaptan, lacteal radioactivity concentrations reached the highest level at 8 hours after administration and then decreased gradually with time with a half-life of 27.3 hours. The level of activity in milk ranged from 1.5- to 15.8-fold those in blood over the period of 72 hours post-dose. In a prenatal and postnatal study in rats, maternal toxicity was noted at 100 mg/kg/day or higher (≥4.4 times the human exposure at the 90/30 mg dose). Increased perinatal death and decreased body weight of the offspring were observed during the lactation period and after weaning at approximately 17.3 times the human exposure at the 90/30 mg dose.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of JYNARQUE in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of tolvaptan did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 years old and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
Use in Patients with Hepatic Impairment
Because of the risk of serious liver injury, use is contraindicated in patients with a history, signs or symptoms of significant liver impairment or injury. This contraindication does not apply to uncomplicated polycystic liver disease which was present in 60% and 66% of patients in TEMPO 3:4 and REPRISE, respectively. No specific exclusion for hepatic impairment was implemented in TEMPO 3:4. However, REPRISE excluded patients with ADPKD who had hepatic impairment or liver function abnormalities other than that expected for ADPKD with typical cystic liver disease [see Contraindications (4) ].
Use in Patients with Renal Impairment
Efficacy studies included patients with normal and reduced renal function [see Clinical Studies (14) ] . TEMPO 3:4 required patients to have an estimated creatinine clearance ≥ 60 mL/min, while REPRISE included patients with eGFR CKD-Epi 25 to 65 mL/min/1.73m 2 .
CONTRAINDICATIONS
JYNARQUE is contraindicated in patients:
- With a history, signs or symptoms of significant liver impairment or injury. This contraindication does not apply to uncomplicated polycystic liver disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- Taking strong CYP3A inhibitors
- With uncorrected abnormal blood sodium concentrations [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
- Unable to sense or respond to thirst [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
- Hypovolemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
- Hypersensitivity (e.g., anaphylaxis, rash) to tolvaptan or any component of the product [see Adverse Reactions (6) ]
- Uncorrected urinary outflow obstruction
- Anuria
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Hypernatremia, dehydration and hypovolemia: May require intervention (5.3 )
Serious Liver Injury
JYNARQUE can cause serious and potentially fatal liver injury. Acute liver failure requiring liver transplantation has been reported in the post-marketing ADPKD experience. Discontinuation in response to laboratory abnormalities or signs or symptoms of liver injury (such as fatigue, anorexia, nausea, right upper abdominal discomfort, vomiting, fever, rash, pruritus, icterus, dark urine or jaundice) can reduce the risk of severe hepatotoxicity.
In a 3-year placebo-controlled trial and its open-label extension (in which patients' liver tests were monitored every 4 months), evidence of serious hepatocellular injury (elevations of hepatic transaminases of at least 3 times the upper limit of normal [ULN] combined with elevated bilirubin at least 2 times the ULN) occurred in 0.2% (3/1487) of tolvaptan-treated patients compared to none of the placebo-treated patients.
To reduce the risk of significant or irreversible liver injury, assess ALT, AST and bilirubin prior to initiation of JYNARQUE, at 2 weeks and 4 weeks after initiation, then monthly for 18 months and every 3 months thereafter.
At the onset of signs or symptoms consistent with hepatic injury or if ALT, AST, or bilirubin increase to >2 times ULN, immediately discontinue JYNARQUE, obtain repeat tests as soon as possible (within 48 to 72 hours), and continue testing as appropriate. If laboratory abnormalities stabilize or resolve, JYNARQUE may be reinitiated with increased frequency of monitoring as long as ALT and AST remain below 3 times the ULN.
Do not restart JYNARQUE in patients who experience signs or symptoms consistent with hepatic injury or whose ALT or AST ever exceeds 3 times the ULN during treatment with tolvaptan, unless there is another explanation for liver injury and the injury has resolved.
In patients with a stable, low baseline AST or ALT, an increase above 2 times baseline, even if less than 2 times the ULN, may indicate early liver injury. Such elevations may warrant treatment suspension and prompt (48 to 72 hours) re-evaluation of liver test trends prior to reinitiating therapy with more frequent monitoring.
Tolvaptan for ADPKD Shared System REMS
JYNARQUE is available only through a restricted distribution program under a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) called the Tolvaptan for ADPKD Shared System REMS, because of the risks of liver injury [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
Notable requirements of the Tolvaptan for ADPKD Shared System REMS include the following:
- Prescribers must be certified by enrolling in the REMS program.
- Prescribers must inform patients receiving JYNARQUE about the risk of hepatotoxicity associated with its use and how to recognize the signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity and the appropriate actions to take if it occurs.
- Patients must enroll in the REMS program and comply with ongoing monitoring requirements.
- Pharmacies must be certified by enrolling in the REMS program and must only dispense to patients who are authorized to receive JYNARQUE.
Further information, including a list of qualified pharmacies/distributors, is available at www.TolvaptanADPKDSharedREMS.com or by telephone at 1-866-244-9446.
Hypernatremia, Dehydration and Hypovolemia
JYNARQUE increases free water clearance and, as a result, may cause dehydration, hypovolemia and hypernatremia. Therefore, ensure abnormalities in sodium concentrations are corrected prior to initiation of therapy.
Instruct patients to drink water when thirsty, and throughout the day and night if awake. Monitor for weight loss, tachycardia and hypotension because they may signal dehydration.
In the two double-blind, placebo-controlled trials of patients with ADPKD, hypernatremia (defined as any serum sodium concentration >150 mEq/L) was observed in 4.0% versus 0.6% and 1.4% versus 0% of tolvaptan-treated versus placebo-treated patients, respectively. The rate of dehydration and hypovolemia in the two studies was 2.1% versus 0.7% and 2.3% versus 0.4% for tolvaptan-treated versus placebo-treated patients, respectively.
During JYNARQUE therapy, if serum sodium increases above normal range or the patient becomes hypovolemic or dehydrated and fluid intake cannot be increased, then suspend JYNARQUE until serum sodium, hydration status and volume status is within the normal range.
Co-Administration with Inhibitors of CYP3A
Concomitant use of JYNARQUE with drugs that are moderate or strong CYP3A inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole, lopinavir/ritonavir, indinavir/ritonavir, ritonavir, and conivaptan) increases tolvaptan exposure [see Drug Interactions (7.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . Use with strong CYP3A inhibitors is contraindicated; dose reduction of JYNARQUE is recommended for patients while taking moderate CYP3A inhibitors [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and Contraindications (4) ].
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in more detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Serious Liver Injury [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- Hypernatremia, Dehydration and Hypovolemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
- Drug Interactions with Inhibitors of CYP3A [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice. JYNARQUE has been studied in over 3000 patients with ADPKD. Long-term, placebo-controlled safety information of JYNARQUE in ADPKD is principally derived from two trials where 1,413 subjects received tolvaptan and 1,098 received placebo for at least 12 months across both studies.
TEMPO 3:4: A Phase 3, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Randomized Trial in Early, Rapidly-Progressing ADPKD
The TEMPO 3:4 (NCT00428948) trial employed a two-arm, 2:1 randomization to tolvaptan or placebo, titrated to a maximally-tolerated total daily dose of 60 to 120 mg. A total of 961 subjects with rapidly progressing ADPKD were randomized to JYNARQUE. Of these, 742 (77%) subjects who were treated with JYNARQUE remained on treatment for at least 3 years. The average daily dose in these subjects was 96 mg daily.
Adverse events that led to discontinuation were reported for 15.4% (148/961) of subjects in the JYNARQUE group and 5.0% (24/483) of subjects in the placebo group. Aquaretic effects were the most common reasons for discontinuation of JYNARQUE. These included pollakiuria, polyuria, or nocturia in 63 (6.6%) subjects treated with JYNARQUE compared to 1 subject (0.2%) treated with placebo.
Table 2 lists the adverse reactions that occurred in at least 3% of ADPKD subjects treated with JYNARQUE and at least 1.5% more than on placebo.
| Adverse Reaction | Tolvaptan (N=961) | Placebo (N=483) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Subjects | Proportion (%) 100× (Number of subjects with an adverse event/N) | Annualized Rate 100× (Number of subjects with an adverse event/Total subject years of drug exposure) | Number of Subjects | Proportion (%) | Annualized Rate | |
| Increased urination Increased urination includes micturition urgency, nocturia, pollakiuria, polyuria | 668 | 69.5 | 28.6 | 135 | 28.0 | 10.3 |
| Thirst Thirst includes polydipsia and thirst | 612 | 63.7 | 26.2 | 113 | 23.4 | 8.7 |
| Dry mouth | 154 | 16.0 | 6.6 | 60 | 12.4 | 4.6 |
| Fatigue | 131 | 13.6 | 5.6 | 47 | 9.7 | 3.6 |
| Diarrhea | 128 | 13.3 | 5.5 | 53 | 11.0 | 4.1 |
| Dizziness | 109 | 11.3 | 4.7 | 42 | 8.7 | 3.2 |
| Dyspepsia | 76 | 7.9 | 3.3 | 16 | 3.3 | 1.2 |
| Decreased appetite | 69 | 7.2 | 3.0 | 5 | 1.0 | 0.4 |
| Abdominal distension | 47 | 4.9 | 2.0 | 16 | 3.3 | 1.2 |
| Dry skin | 47 | 4.9 | 2.0 | 8 | 1.7 | 0.6 |
| Rash | 40 | 4.2 | 1.7 | 9 | 1.9 | 0.7 |
| Hyperuricemia | 37 | 3.9 | 1.6 | 9 | 1.9 | 0.7 |
| Palpitations | 34 | 3.5 | 1.5 | 6 | 1.2 | 0.5 |
REPRISE: A Phase 3, Randomized-Withdrawal, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind, Trial in Late Stage 2 to Early Stage 4 ADPKD
The REPRISE (NCT02160145) trial employed a 5-week single-blind titration and run-in period for JYNARQUE prior to the randomized double-blind period. During the JYNARQUE titration and run-in period, 126 (8.4%) of the 1496 subjects discontinued the study, 52 (3.5%) were due to aquaretic effects and 10 (0.7%) were due to liver test findings. Because of this run-in design, the adverse reaction rates observed during the randomized period are not described.
Liver Injury
In the two double-blind, placebo-controlled trials, ALT elevations >3 times ULN were observed at an increased frequency with JYNARQUE compared with placebo (4.9% [80/1637] versus 1.1% [13/1166], respectively) within the first 18 months after initiating treatment and increases usually resolved within 1 to 4 months after discontinuing the drug.
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of tolvaptan. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Hepatobiliary Disorders: Liver failure requiring transplant
Immune System Disorders: Anaphylaxis
DRUG INTERACTIONS
CYP3A Inhibitors and Inducers
CYP3A Inhibitors
Tolvaptan's AUC was 5.4 times as large and Cmax was 3.5 times as large after co-administration of tolvaptan and 200 mg ketoconazole [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . Larger doses of the strong CYP3A inhibitor would be expected to produce larger increases in tolvaptan exposure. Concomitant use of tolvaptan with strong CYP3A inhibitors is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4) ].
Dose reduction of JYNARQUE is recommended for patients while taking moderate CYP3A inhibitors [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) ]. Patients should avoid grapefruit juice beverages while taking JYNARQUE.
Strong CYP3A Inducers
Co-administration of JYNARQUE with strong CYP3A inducers reduces exposure to JYNARQUE [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ]. Avoid concomitant use of JYNARQUE with strong CYP3A inducers [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) ].
V 2 -Receptor Agonist
As a V 2 -receptor antagonist, tolvaptan will interfere with the V 2 -agonist activity of desmopressin (dDAVP). Avoid concomitant use of JYNARQUE with a V 2 -agonist.
DESCRIPTION
JYNARQUE contains tolvaptan, a selective vasopressin V2-receptor antagonist in immediate release tablets for oral administration available in 15 mg, 30 mg, 45 mg, 60 mg and 90 mg strengths. Tolvaptan is (±)-4'-[(7-chloro-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-5-hydroxy-1 H -1-benzazepin-1-yl) carbonyl]- o -tolu- m -toluidide. The empirical formula is C 26 H 25 ClN 2 O 3 . Molecular weight is 448.94. The chemical structure is:
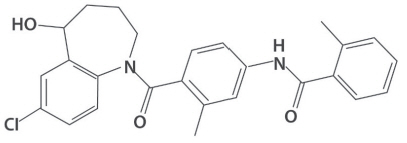
Inactive ingredients include corn starch, hydroxypropyl cellulose, lactose monohydrate, low-substituted hydroxypropyl cellulose, magnesium stearate and microcrystalline cellulose and FD&C Blue No. 2 Aluminum Lake as colorant.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Tolvaptan is a selective vasopressin V 2 -receptor antagonist with an affinity for the V 2 -receptor that is 1.8 times that of native arginine vasopressin (AVP). Tolvaptan affinity for the V 2 -receptor is 29 times that for the V 1a -receptor. Decreased binding of vasopressin to the V 2 -receptor in the kidney lowers adenylate cyclase activity resulting in a decrease in intracellular adenosine 3′, 5′-cyclic monophosphate (cAMP) concentrations. Decreased cAMP concentrations prevent aquaporin 2 containing vesicles from fusing with the plasma membrane, which in turn causes an increase in urine water excretion, an increase in free water clearance (aquaresis) and a decrease in urine osmolality. In human ADPKD cyst epithelial cells, tolvaptan inhibited AVP-stimulated in vitro cyst growth and chloride-dependent fluid secretion into cysts. In animal models, decreased cAMP concentrations were associated with decreases in the rate of growth of total kidney volume and the rate of formation and enlargement of kidney cysts. Tolvaptan metabolites have no or weak antagonist activity for human V 2 -receptors compared with tolvaptan.
Pharmacodynamics
In healthy subjects or patients with eGFRs as low as 10 mL/min/1.73m 2 receiving a single dose of tolvaptan, the onset of the aquaretic effects occurs within 1 to 2 hours post-dose. In healthy subjects, single doses of 60 mg and 90 mg produce a peak effect of about a 9 mL/min increase in urine excretion rate is observed between 4 and 8 hours post-dose. Higher doses of tolvaptan do not increase the peak effect in urine excretion rate but sustain the effect for a longer period of time.
Urine excretion rate returns to baseline within 24 hours following the maximum recommended 90 mg dose of tolvaptan.
Changes in free water clearance mirror the changes in urine excretion rate. Increased free water clearance causes an increase in serum sodium concentration unless fluid intake is increased to match urine output.
Increases in urine excretion rate and free water clearance are positively correlated with baseline glomerular filtration rate with increases in both values observed in patients with creatinine clearance as low as 15 mL/min.
With the recommended split-dose regimens, tolvaptan inhibits vasopressin from binding to the V 2 -receptor in the kidney for the entire day, as indicated by increased urine output and decreased urine osmolality. Following a 90/30 mg split-dose regimen in patients with eGFR >60 mL/min/1.73 m 2 , the change in mean daily urine volume was about 4 L for a mean total daily volume of about 7 L. In patients with eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m 2 , the mean change in daily urine volume was about 2 L for a total daily urine volume of about 5 L.
Plasma concentrations of native AVP may increase (avg. 2 to 9 pg/mL) with tolvaptan treatment and return to baseline levels when treatment is stopped.
During tolvaptan treatment, small changes in renal function are expected and the changes are independent of baseline renal function. Glomerular filtration rate is decreased about 6% to 10% and uric acid clearance is decreased about 20% to 25%. Percent changes in renal plasma flow are highly correlated to percent changes in GFR. These changes are reversed upon discontinuation of tolvaptan.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
No prolongation of the QT interval was observed with tolvaptan following multiple doses of 300 mg/day for 5 days.
Pharmacokinetics
In healthy subjects, the pharmacokinetics of tolvaptan after single doses of up to 480 mg and multiple doses up to 300 mg once daily have been studied. In ADPKD patients, single doses up to 120 mg and multiple split-doses up to 90/30 mg have been studied.
Absorption
In healthy subjects, peak concentrations of tolvaptan are observed between 2 and 4 hours post-dose. Peak concentrations increase less than dose proportionally with doses greater than 240 mg.
The absolute bioavailability of tolvaptan decreases with increasing doses. The absolute bioavailability of tolvaptan following an oral dose of 30 mg is 56% (range 42% to 80%).
Co-administration of 90 mg JYNARQUE with a high-fat meal (~1000 calories, of which 50% are from fat) doubles peak concentrations but has no effect on the AUC of tolvaptan; tolvaptan may be administered with or without food.
Distribution
Tolvaptan binds to both albumin and α1-acid glycoprotein and the overall protein binding is >98%; binding is not affected by disease state. The volume of distribution of tolvaptan is about 3 L/kg. The pharmacokinetic properties of tolvaptan are stereospecific, with a steady-state ratio of the S-(-) to the R-(+) enantiomer of about 3. When administered as multiple once-daily 300 mg doses to healthy subjects or as split-dose regimens to patients with ADPKD, tolvaptan's accumulation factor is <1.2. There is marked inter-subject variation in peak and average exposure to tolvaptan with a percent coefficient of variation ranging between 30% and 60%.
Metabolism and Elimination
Tolvaptan is metabolized almost exclusively by CYP3A. Fourteen metabolites have been identified in plasma, urine and feces; all but one were also metabolized by CYP3A and none are pharmacodynamically active. After oral administration of radiolabeled tolvaptan, tolvaptan was a minor component in plasma representing 3% of total plasma radioactivity; the oxobutyric acid metabolite was present at 52.5% of total plasma radioactivity with all other metabolites present at lower concentrations than tolvaptan. The oxobutyric acid metabolite shows a plasma half-life of ~180 h. About 40% of radioactivity was recovered in urine (<1% as unchanged tolvaptan) and 59% in feces (19% as unchanged tolvaptan). Following intravenous infusion, tolvaptan half-life is approximately 3 hours. Following single oral doses to healthy subjects, the estimated half-life of tolvaptan increases from 3 hours for a 15 mg dose to approximately 12 hours for 120 mg and higher doses due to more prolonged absorption of tolvaptan at higher doses; apparent clearance is approximately 4 mL/min/kg and does not appear to change with increasing dose.
Specific Populations
Age, Gender and Race
Age, gender and race have no effect on tolvaptan pharmacokinetics.
Hepatic Impairment
In studies involving patients with hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class A-C), but without ADPKD; moderate (class A, B) or severe (class C) hepatic impairment decreases the clearance and increases the volume of distribution of tolvaptan.
Renal Impairment
In subjects with creatinine clearances ranging from 10 to 124 mL/min administered a single dose of 60 mg tolvaptan, the AUC and C max of plasma tolvaptan was increased 90% and 10%, respectively, for subjects with clearances of <30 mL/min compared to subjects with clearances >60 mL/min [see Use in Special Populations (8.7) ].
In ADPKD patients with estimated creatinine clearance >60 mL/min, pharmacokinetics were similar to healthy subjects.
Drug Interaction Studies
Impact of Other Drugs on Tolvaptan
Strong CYP3A Inhibitors
Tolvaptan's Cmax and AUC were, respectively, 3.5 times and 5.4 times as high following ketoconazole 200 mg given one day prior to and concomitantly with 30 mg tolvaptan.
Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors
Fluconazole: Fluconazole 400 mg given one day prior and 200 mg given concomitantly produced an 80% and 200% increase in tolvaptan C max and AUC, respectively.
Grapefruit Juice: When 60 mg tolvaptan was taken with 240 mL regular strength grapefruit juice, tolvaptan C max and AUC increased 90% and 60%, respectively.
CYP3A Inducers
Rifampin: Rifampin 600 mg once daily for 7 days followed by a single 240 mg dose of tolvaptan decreased both tolvaptan C max and AUC about 85%.
Other Drugs
Co-administration of lovastatin, digoxin, furosemide, and hydrochlorothiazide with tolvaptan has no clinically relevant impact on the exposure to tolvaptan.
Impact of Tolvaptan on Other Drugs
CYP3A Substrates
Co-administration of lovastatin and tolvaptan increases the AUC of lovastatin and its active metabolite lovastatin-β hydroxy acid by 40% and 30%, respectively. These are non-clinically significant increases in exposure.
P-gp Substrates
Digoxin: Digoxin 0.25 mg was administered once daily for 12 days. Tolvaptan 60 mg, was co-administered once daily on Days 8 to 12. Digoxin C max and AUC were increased 30% and 20%, respectively.
Transporter Substrates
Tolvaptan is a substrate of P-gp and an inhibitor of P-gp and BCRP. The oxobutyric acid metabolite of tolvaptan is an inhibitor of OATP1B1 and OAT3. Co-administration of tolvaptan with rosuvastatin (BCRP substrate) did not have a clinically significant effect on rosuvastatin exposure. Rosuvastatin C max and AUC t increased 54% and 69%, respectively.
Administration of rosuvastatin (OATP1B1 substrate) or furosemide (OAT3 substrate) to healthy subjects with elevated oxobutyric acid metabolite plasma concentrations did not meaningfully alter the pharmacokinetics of rosuvastatin or furosemide.
Other Drugs
Co-administration of tolvaptan did not meaningfully alter the pharmacokinetics of warfarin, furosemide, hydrochlorothiazide, or amiodarone (or its active metabolite, desethylamiodarone).
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
The carcinogenic potential of JYNARQUE was assessed in 2-year carcinogenicity studies in mice and rats. Tolvaptan was not tumorigenic in male or female rats at doses up to 1000 mg/kg/day (1.9 to 5.1 times the human exposure at the 90/30 mg dose), in male mice at doses up to 60 mg/kg/day (0.4 times the human exposure at the 90/30 mg dose) and to female mice at doses up to 100 mg/kg/day (0.7 times the human exposure at the 90/30 mg dose).
Mutagenesis
Tolvaptan was not clastogenic in the in vitro chromosomal aberration test in Chinese hamster lung fibroblast cells or the in vivo rat micronucleus assay and was not mutagenic in the in vitro bacterial reverse mutation assay.
Impairment of fertility
In a fertility study in which male and female rats were administered tolvaptan orally at 100, 300 or 1000 mg/kg/day, altered estrous cycles due to prolongation of diestrus were observed in dams given 300 and 1000 mg/kg/day (9.7- and 17.3 times the human exposure at the 90/30 mg dose). Tolvaptan had no effect on copulation or fertility indices. There were also no effects on the incidences of early or late resorption, dead fetuses, pre- or post-implantation loss, external anomalies, or fetal body weights.
CLINICAL STUDIES
JYNARQUE was shown to slow the rate of decline in renal function in adult patients at risk of rapidly progressing ADPKD in two trials: TEMPO 3:4 in patients at earlier stages of disease and REPRISE in patients at later stages. The findings from these trials, when taken together, suggest that JYNARQUE slows the loss of renal function progressively through the course of the disease.
TEMPO 3:4: A Phase 3, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Randomized Trial in Early, Rapidly-Progressing ADPKD
In TEMPO 3:4 (NCT00428948), 1445 adult patients (age >18 years) with early (estimated creatinine clearance [eCrCl] ≥60 mL/min), rapidly-progressing (total kidney volume [TKV] ≥750 mL and age <51 years) ADPKD (diagnosed by modified Ravine criteria) were randomized 2:1 to treatment with tolvaptan or placebo. Patients were treated for up to 3 years; patients who discontinued medication prematurely were only required to attend clinic visits to assess renal function for up to 42 days after treatment withdrawal and to attend telephone visits at all scheduled visits for up to 36 months. Patients who completed treatment at the 3-year visit had treatment interrupted for 2 to 6 weeks to assess renal function post treatment. Patients received treatment twice a day (first dose on waking, second dose approximately 9 hours later). Patients were initiated on 45 mg/15 mg, and up-titrated weekly to 60 mg/30 mg and then to 90 mg/30 mg as tolerated. Patients were to maintain the highest tolerated dose for 3 years, but could interrupt, decrease and/or increase as clinical circumstances warranted within the range of titrated doses. All patients were encouraged to drink adequate water to avoid thirst or dehydration and before bedtime.
The primary endpoint was the intergroup difference for rate of change of TKV normalized as a percentage. The key secondary composite endpoint (ADPKD progression) was time to multiple clinical progression events of: 1) worsening kidney function (defined as a persistent 25% reduction in reciprocal serum creatinine during treatment from end of titration to last on-drug visit); 2) medically significant kidney pain (defined as requiring prescribed leave, last-resort analgesics, narcotic and anti-nociceptive, radiologic or surgical interventions); 3) worsening hypertension (defined as a persistent increase in blood pressure category or an increased anti-hypertensive prescription); 4) worsening albuminuria (defined as a persistent increase in albumin/creatinine ratio category).
At baseline, average estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was 82 mL/min/1.73 m 2 (CKD-Epidemiology formula) and mean TKV was 1692 mL (height adjusted 972 mL/m). Approximately 35% had an eGFR of 90 mL/min/1.73 m 2 or greater, 48% had an eGFR between 60 to 89 mL/min/1.73 m 2 , 14% had an eGFR of 45 to 60 mL/min/1.73 m 2 , and 3% had an eGFR of <45 mL/min/1.73 m 2 . The subjects' mean age was 39 years, 48% were female, 84% were Caucasian, 13% were Asian, and 1.7% were Black or African-American. Approximately 80% had hypertension and approximately 71% were taking an agent that acts on the renin-angiotensin system. Of the 770 subjects who submitted to genetic analysis in TEMPO 3:4's open-label extension, 749 (97%) had an identifiable mutation in the PKD1 (656 or 88%), or PKD2 (93 or 12%) gene.
The trial met its prespecified primary endpoint of 3-year change in TKV (p<0.0001). The difference in TKV between treatment groups mostly developed within the first year, the earliest assessment, with little further difference in years two and three. In Years 4 and 5 during the TEMPO 3:4 extension trial, both groups received JYNARQUE and the difference between the groups in TKV was not maintained. Tolvaptan has little effect on kidney size beyond what accrues during the first year of treatment.
The relative rate of ADPKD-related events was decreased by 13.5% in tolvaptan-treated patients, (44 vs. 50 events per 100 person-years; hazard ratio, 0.87; 95% CI, 0.78 to 0.97; p=0.0095). As shown in the table below, the result of the key secondary composite endpoint was driven by effects on worsening kidney function and kidney pain events. In contrast, there was no effect of tolvaptan on either progression of hypertension or albuminuria. Few subjects in either arm required a radiologic or surgical intervention for kidney pain. Most kidney pain events reflected use of a medication to treat pain such as use of paracetamol, tricyclic antidepressants, narcotics and other non-narcotic agents.
| Event | Tolvaptan | Placebo | Hazard Ratio, 95% CI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Number of Events (Events per 100 person-years) | Number of Subjects with an Event (percentage) | Total Number of Events (Events per 100 person-years) | Number of Subjects with an Event (percentage) | ||
| Composite | 1049 (43.9) | 572 (59.5) | 665 (50.0) | 341 (70.6) | 0.87 (0.78,0.97) |
| Worsening Kidney Function | 44 (1.9) | 42 (4.6) | 64 (4.8) | 61 (12.8) | 0.39 (0.26,0.57) |
| Kidney Pain | 113 (4.7) | 95 (9.9) | 97 (7.3) | 78 (16.2) | 0.64 (0.47,0.89) |
| Onset or Progression of Hypertension | 734 (30.7) | 426 (44.3) | 426 (32.1) | 244 (50.5) | 0.94 (0.81,1.09) |
| Worsening Albuminuria | 195 (8.2) | 195 (20.3) | 103 (7.8) | 101 (20.9) | 1.04 (0.84,1.28) |
The third endpoint (kidney function slope) was assessed as slope of eGFR during treatment (from end of titration to last on-drug visit). The estimated difference in the annual rate of change in those who contributed to the analysis was 1.0 mL/min/1.73m 2 /year with a 95% confidence interval of (0.6, 1.4). Of the subjects enrolled in the trial, 5% of subjects in the tolvaptan arm and 2% in the placebo arm either had missing baseline data or discontinued from treatment prior to the end of the titration visit and hence were excluded from the analysis. In the extension trial, eGFR differences produced by the third year of the TEMPO 3:4 trial were maintained over the next 2 years of JYNARQUE treatment.
The efficacy profile was generally consistent across subgroups of interest for this indication; few Black or African-American patients were enrolled in the trial.
REPRISE: A Phase 3, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Randomized Withdrawal Trial in Later-Stage ADPKD
REPRISE (NCT02160145) was a double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized withdrawal trial in adult patients (age 18 to 65 years) with chronic kidney disease (CKD) with an eGFR between 25 and 65 mL/min/1.73m 2 if younger than age 56 years, or eGFR between 25 and 44 mL/min/1.73m 2 , plus eGFR decline >2.0 mL/min/1.73m 2 /year if between age 56 to 65 years. Subjects were to be treated for 12 months; after completion of treatment, patients entered a 3-week follow-up period to assess renal function. The primary endpoint was the treatment difference in the change of eGFR from pre-treatment baseline to post-treatment follow-up, annualized by dividing by each subject's treatment duration.
Prior to randomization, patients were required to complete sequential single-blind run-in periods during which they received placebo for 1 week, followed by tolvaptan titration for 2 weeks, and then treatment with tolvaptan at the highest tolerated dose achieved during titration for 3 weeks. During the titration period, tolvaptan was up-titrated every 3 to 4 days from a daily oral dose of 30 mg/15 mg to 45 mg/15 mg, 60 mg/30 mg and up to a maximum dose of 90 mg/30 mg. Only patients who could tolerate the two highest doses of tolvaptan (60 mg/30 mg or 90 mg/30 mg) for the subsequent 3 weeks were randomized 1:1 to treatment with tolvaptan or placebo.
Patients were maintained on their highest tolerated dose for a period of 12 months but could interrupt, decrease and/or increase as clinical circumstances warranted within the range of titrated doses. All patients were encouraged to start drinking an adequate amount of water at screening and continuing through the end of the trial to avoid thirst or dehydration.
A total of 1519 subjects were enrolled in the study. Of these, 1370 subjects successfully completed the pre-randomization period and were randomized and treated during the 12-month double-blind period. Because 57 subjects did not complete the off-treatment follow-up period, 1313 subjects were included in the primary efficacy analysis.
For subjects randomized, the baseline, average estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was 41 mL/min/1.73 m 2 (CKD-Epidemiology formula) and historical TKV, available in 318 (23%) of subjects, averaged 2026 mL. Approximately 5%, 75% and 20% had an eGFR 60 mL/min/1.73 m 2 or greater, between 30 to 59 mL/min/1.73 m 2 , and between 25 and 29 mL/min/1.73 m 2 , respectively. The subjects' mean age was 47 years, 50% were female, 92% were Caucasian, 4% Black or African-American and 3% were Asian, 93% had hypertension, and 87% of subjects were taking antihypertensive agents affecting the angiotensin converting enzyme or receptor. Of the 115 (8%) of subjects who had prior genetic tests, only 54 (47%) knew their results with 48 (89%) of these having PKD1 and 6 (11%) having PKD2 mutations.
In the randomized period, the change of eGFR from pretreatment baseline to post-treatment follow-up was −2.3 mL/min/1.73 m 2 /year with tolvaptan as compared with −3.6 mL/min/1.73 m 2 /year with placebo, corresponding to a treatment effect of 1.3 mL/min/1.73 m 2 /year (p <0.0001). The key secondary endpoint (eGFR slope in ml/min/1.73 m 2 /year assessed using a linear mixed effect model of annualized eGFR (CKD-EPI)) showed a difference between treatment groups of 1.0 ml/min/ m 2 /year that was also statistically significant (p <0.0001).
The efficacy profile was generally consistent across subgroups of interest for this indication; few Black or African-American patients were enrolled in the trial.
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
All JYNARQUE (tolvaptan) tablets are non-scored, blue, shallow-convex, debossed with "OTSUKA" and the tablet strength (mg) on one side and supplied as follows:
15 mg tablets are triangular, 30 mg tablets are round, 45 mg tablets are square, 60 mg tablets are rectangular, and 90 mg tablets are pentagonal.
| Morning and Afternoon Doses | NDC | |
|---|---|---|
| 7‑Day Blister Card (Containing 14 Tablets) | 28‑Day Carton (4 Blister Cards Containing a Total of 56 Tablets) | |
| 15 mg and 15 mg | 59148-079-07 | 59148-079-28 |
| 30 mg and 15 mg | 59148-080-07 | 59148-080-28 |
| 45 mg and 15 mg | 59148-087-07 | 59148-087-28 |
| 60 mg and 30 mg | 59148-088-07 | 59148-088-28 |
| 90 mg and 30 mg | 59148-089-07 | 59148-089-28 |
| 30 Count Bottles | NDC |
|---|---|
| 15 mg | 59148-082-13 |
| 30 mg | 59148-083-13 |
Storage and Handling
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F), excursions permitted between 15°C and 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP controlled Room Temperature].
Mechanism of Action
Tolvaptan is a selective vasopressin V 2 -receptor antagonist with an affinity for the V 2 -receptor that is 1.8 times that of native arginine vasopressin (AVP). Tolvaptan affinity for the V 2 -receptor is 29 times that for the V 1a -receptor. Decreased binding of vasopressin to the V 2 -receptor in the kidney lowers adenylate cyclase activity resulting in a decrease in intracellular adenosine 3′, 5′-cyclic monophosphate (cAMP) concentrations. Decreased cAMP concentrations prevent aquaporin 2 containing vesicles from fusing with the plasma membrane, which in turn causes an increase in urine water excretion, an increase in free water clearance (aquaresis) and a decrease in urine osmolality. In human ADPKD cyst epithelial cells, tolvaptan inhibited AVP-stimulated in vitro cyst growth and chloride-dependent fluid secretion into cysts. In animal models, decreased cAMP concentrations were associated with decreases in the rate of growth of total kidney volume and the rate of formation and enlargement of kidney cysts. Tolvaptan metabolites have no or weak antagonist activity for human V 2 -receptors compared with tolvaptan.