Lagevrio Prescribing Information
In order to mitigate the risks of using this unapproved product under the EUA and to optimize the potential benefit of LAGEVRIO, the following steps are required. Use of LAGEVRIO under this EUA is limited to the following (all requirements must be met):
- Treatment of adults with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 who are at high risk for progression to severe COVID-19, including hospitalization or death and for whom alternative COVID-19 treatment options approved or authorized by FDA are not accessible or clinically appropriate [see.]LIMITATIONS OF AUTHORIZED USE
- As the prescribing healthcare provider, review the information contained within the “Fact Sheet for Patients and Caregivers” with your patient or caregiver prior to the patient receiving LAGEVRIO. Healthcare providers must provide the patient/caregiver with an electronic or hard copy of the “Fact Sheet for Patients and Caregivers” prior to the patient receiving LAGEVRIO and must document that the patient/caregiver has been given an electronic or hard copy of the “Fact Sheet for Patients and Caregivers”.
- The prescribing healthcare providers must inform the patient/caregiver that:
- LAGEVRIO is an unapproved drug that is authorized for use under this Emergency Use Authorization.
- Other therapeutics are currently approved for the same use as LAGEVRIO [see].APPROVED AVAILABLE ALTERNATIVES
- There are benefits and risks of taking LAGEVRIO as outlined in the “Fact Sheet for Patients and Caregivers.”
- There is a pregnancy registry.
- Females of childbearing potential should use a reliable method of contraception correctly and consistently, as applicable, for the duration of treatment and for 4 days after the last dose of LAGEVRIO.
- Males of reproductive potential who are sexually active with females of childbearing potential should use a reliable method of contraception correctly and consistently during treatment and for at least 3 months after the last dose.
- The prescribing healthcare provider must assess whether a female of childbearing potential is pregnant or not, if clinically indicated [seeand
5.1 Embryo-Fetal ToxicityBased on findings from animal reproduction studies, LAGEVRIO may cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant individuals. There are no available human data on the use of LAGEVRIO in pregnant individuals to evaluate the risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes; therefore, LAGEVRIO is not recommended for use during pregnancy. When considering LAGEVRIO for a pregnant individual, the prescribing healthcare provider must communicate the known and potential benefits and the potential risks of using LAGEVRIO during pregnancy to the pregnant individual. LAGEVRIO is authorized to be prescribed to a pregnant individual only after the healthcare provider has determined that the benefits would outweigh the risks for that individual patient. If the decision is made to use LAGEVRIO during pregnancy, the prescribing healthcare provider must document that the known and potential benefits and the potential risks of using LAGEVRIO during pregnancy were communicated to the pregnant individual.
Advise individuals of childbearing potential of the potential risk to a fetus and to use an effective method of contraception correctly and consistently, as applicable, during treatment with LAGEVRIO and for 4 days after the final dose
[see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3and Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].Prior to initiating treatment with LAGEVRIO, assess whether an individual of childbearing potential is pregnant or not, if clinically indicated. Pregnancy status does not need to be confirmed in patients who have undergone permanent sterilization, are currently using an intrauterine system or contraceptive implant, or in whom pregnancy is not possible. In all other patients, assess whether the patient is pregnant based on the first day of last menstrual period in individuals who have regular menstrual cycles, is using a reliable method of contraception correctly and consistently or have had a negative pregnancy test. A pregnancy test is recommended if the individual has irregular menstrual cycles, is unsure of the first day of last menstrual period or is not using effective contraception correctly and consistently
[see Box].].8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive PotentialBased on animal studies, LAGEVRIO may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant individual.
Pregnancy TestingPrior to initiating treatment with LAGEVRIO, assess whether an individual of childbearing potential is pregnant or not, if clinically indicated
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].ContraceptionFemales
Advise individuals of childbearing potential to use a reliable method of contraception correctly and consistently, as applicable for the duration of treatment and for 4 days after the last dose of LAGEVRIO
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].Males
While the risk is regarded as low, there is a theoretical risk for LAGEVRIO to affect offspring of treated males based on its mechanism of action. Advise sexually active individuals with partners of childbearing potential to use a reliable method of contraception correctly and consistently during treatment and for at least 3 months after the last dose of LAGEVRIO.
The risk beyond three months after the last dose of LAGEVRIO is unknown.Molnupiravir was equivocal (neither clearly positive nor negative) in one
in vivomutagenicity assay of reticulocytes and RBCs which are used to reflect prior effects on hematopoietic stem cells in bone marrow. Molnupiravir was not mutagenic when assessed inin vivoassays of liver (somatic cells), bone marrow (somatic cells and stem cells), and sperm (male germ cells) from transgenic rats administered molnupiravir for 28 days[see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)]. - Based on findings from animal reproduction studies, LAGEVRIO may cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant individuals. If LAGEVRIO is used during pregnancy, prescribing healthcare providers must communicate to the patient the known and potential benefits and the potential risks of LAGEVRIO use during pregnancy, as outlined in the “Fact Sheet for Patients and Caregivers” [see,
5.1 Embryo-Fetal ToxicityBased on findings from animal reproduction studies, LAGEVRIO may cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant individuals. There are no available human data on the use of LAGEVRIO in pregnant individuals to evaluate the risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes; therefore, LAGEVRIO is not recommended for use during pregnancy. When considering LAGEVRIO for a pregnant individual, the prescribing healthcare provider must communicate the known and potential benefits and the potential risks of using LAGEVRIO during pregnancy to the pregnant individual. LAGEVRIO is authorized to be prescribed to a pregnant individual only after the healthcare provider has determined that the benefits would outweigh the risks for that individual patient. If the decision is made to use LAGEVRIO during pregnancy, the prescribing healthcare provider must document that the known and potential benefits and the potential risks of using LAGEVRIO during pregnancy were communicated to the pregnant individual.
Advise individuals of childbearing potential of the potential risk to a fetus and to use an effective method of contraception correctly and consistently, as applicable, during treatment with LAGEVRIO and for 4 days after the final dose
[see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3and Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].Prior to initiating treatment with LAGEVRIO, assess whether an individual of childbearing potential is pregnant or not, if clinically indicated. Pregnancy status does not need to be confirmed in patients who have undergone permanent sterilization, are currently using an intrauterine system or contraceptive implant, or in whom pregnancy is not possible. In all other patients, assess whether the patient is pregnant based on the first day of last menstrual period in individuals who have regular menstrual cycles, is using a reliable method of contraception correctly and consistently or have had a negative pregnancy test. A pregnancy test is recommended if the individual has irregular menstrual cycles, is unsure of the first day of last menstrual period or is not using effective contraception correctly and consistently
[see Box].,5.3 Bone and Cartilage ToxicityLAGEVRIO is not authorized for use in patients less than 18 years of age because it may affect bone and cartilage growth. Bone and cartilage toxicity was observed in rats after repeated dosing
[see Nonclinical Toxicity (13.2)]. The safety and efficacy of LAGEVRIO have not been established in pediatric patients[see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].,8.1 PregnancyPregnancy RegistryThere is a pregnancy registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in individuals exposed to LAGEVRIO during pregnancy. The prescribing healthcare provider must document that a pregnant individual was made aware of the pregnancy registry at
https://covid-pr.pregistry.comor 1-800-616-3791. Pregnant individuals exposed to LAGEVRIO or their healthcare providers can also report the exposure by contacting Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC, Rahway, NJ USA at 1-877-888-4231.Risk SummaryBased on animal data, LAGEVRIO may cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant individuals. There are no available human data on the use of LAGEVRIO in pregnant individuals to evaluate the risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes; therefore, LAGEVRIO is not recommended during pregnancy
[see Boxand Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. In an animal reproduction study, oral administration of molnupiravir to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis resulted in embryofetal lethality and teratogenicity at 8 times the human NHC (N4-hydroxycytidine) exposures at the recommended human dose (RHD) and reduced fetal growth at ≥ 3 times the human NHC exposure at the RHD. Oral administration of molnupiravir to pregnant rabbits during the period of organogenesis resulted in reduced fetal body weights at 18 times the human NHC exposure at the RHD (seeData). When considering LAGEVRIO for a pregnant individual, the prescribing healthcare provider must communicate the known and potential benefits and the potential risks of using LAGEVRIO during pregnancy to the pregnant individual. LAGEVRIO may only be prescribed to a pregnant individual after the prescribing healthcare provider has determined that the benefits would outweigh the risks for that individual patient. If the decision is made to use LAGEVRIO during pregnancy, the prescribing healthcare provider must document that the known and potential benefits and potential risks of using LAGEVRIO during pregnancy were communicated to the pregnant individual[see Box]. There are maternal and fetal risks associated with untreated COVID-19 in pregnancy(see Clinical Considerations).The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Clinical ConsiderationsDisease-associated maternal and/or embryo/fetal riskCOVID-19 in pregnancy is associated with adverse maternal and fetal outcomes, including preeclampsia, eclampsia, preterm birth, premature rupture of membranes, venous thromboembolic disease, and fetal death.
DataAnimal DataIn an embryofetal development (EFD) study in rats, molnupiravir was administered orally to pregnant rats at 0, 100, 250, or 500 mg/kg/day from gestation days (GDs) 6 to 17. Molnupiravir was also administered orally to pregnant rats at up to 1,000 mg/kg/day from GDs 6 to 17 in a preliminary EFD study. Developmental toxicities included post-implantation losses, malformations of the eye, kidney, and axial skeleton, and rib variations at 1,000 mg/kg/day (8 times the human NHC exposure at the RHD) and decreased fetal body weights and delayed ossification at ≥500 mg/kg/day (3 times the human NHC exposure at the RHD). There were no developmental toxicities at ≤250 mg/kg/day (less than the human NHC exposure at the RHD). Maternal toxicities included decreased food consumption and body weight losses, resulting in the early sacrifice of two of sixteen animals at 1,000 mg/kg/day, and decreased body weight gain at 500 mg/kg/day.
In an EFD study in rabbits, molnupiravir was administered orally to pregnant rabbits at 0, 125, 400, or 750 mg/kg/day from GDs 7 to 19. Developmental toxicity was limited to reduced fetal body weights at 750 mg/kg/day (18 times the human NHC exposures at the RHD). There was no developmental toxicity at ≤400 mg/kg/day (7 times the human NHC exposures at the RHD). Maternal toxicities included reduced food consumption and body weight gains, and abnormal fecal output at 750 mg/kg/day.
In a pre- and post-natal developmental study, molnupiravir was administered orally to female rats at doses up to 500 mg/kg/day (similar to the human NHC exposure at the RHD) from GD6 through lactation day 20. No effects were observed in offspring.
and8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive PotentialBased on animal studies, LAGEVRIO may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant individual.
Pregnancy TestingPrior to initiating treatment with LAGEVRIO, assess whether an individual of childbearing potential is pregnant or not, if clinically indicated
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].ContraceptionFemales
Advise individuals of childbearing potential to use a reliable method of contraception correctly and consistently, as applicable for the duration of treatment and for 4 days after the last dose of LAGEVRIO
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].Males
While the risk is regarded as low, there is a theoretical risk for LAGEVRIO to affect offspring of treated males based on its mechanism of action. Advise sexually active individuals with partners of childbearing potential to use a reliable method of contraception correctly and consistently during treatment and for at least 3 months after the last dose of LAGEVRIO.
The risk beyond three months after the last dose of LAGEVRIO is unknown.Molnupiravir was equivocal (neither clearly positive nor negative) in one
in vivomutagenicity assay of reticulocytes and RBCs which are used to reflect prior effects on hematopoietic stem cells in bone marrow. Molnupiravir was not mutagenic when assessed inin vivoassays of liver (somatic cells), bone marrow (somatic cells and stem cells), and sperm (male germ cells) from transgenic rats administered molnupiravir for 28 days[see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].].13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of FertilityCarcinogenesisMolnupiravir was not carcinogenic in a 6-month oral carcinogenicity study in RasH2 transgenic (Tg.RasH2) mice at any dose tested (30, 100 or 300 mg/kg/day).
MutagenesisMolnupiravir and NHC were positive in the
in vitrobacterial reverse mutation assay (Ames assay) with and without metabolic activation. Molnupiravir was studied in twoin vivorodent mutagenicity models. Thein vivoPig-a mutagenicity assay gave equivocal results. Molnupiravir was negative inin vivoBig Blue® (cII Locus) transgenic rodent mutagenicity assays in somatic and germ cells. Molnupiravir was negative for induction of chromosomal damage inin vitromicronucleus (with and without metabolic activation) andin vivorat micronucleus assays.Based on the totality of the available genotoxicity data and the duration of treatment (5 days), molnupiravir is low risk for genotoxicity.
Impairment of FertilityThere were no effects on fertility, mating performance or early embryonic development when molnupiravir was administered to female or male rats at NHC exposures approximately 2 and 6 times, respectively, the human NHC exposure at the RHD.
- If the decision is made to use LAGEVRIO during pregnancy, the prescriber must document that the known and potential benefits and the potential risks of LAGEVRIO use during pregnancy, as outlined in the “Fact Sheet for Patients and Caregivers,” were discussed with the patient.
- The prescribing healthcare provider must document that a pregnant individual was made aware of the pregnancy registry at https://covid-pr.pregistry.comor 1-800-616-3791.
- The prescribing healthcare provider and/or the provider’s designee is/are responsible for mandatory reporting of all medication errors and serious adverse events potentially related to LAGEVRIO within 7 calendar days from the healthcare provider’s awareness of the event [see].
6.4 Required Reporting for Serious Adverse Events and Medication ErrorsThe prescribing healthcare provider and/or the provider’s designee is/are responsible for mandatory reporting of all serious adverse events *and medication errors potentially related to LAGEVRIO within 7 calendar days from the healthcare provider’s awareness of the event, using FDA Form 3500 (for information on how to access this form, see below). The FDA requires that such reports, using FDA Form 3500, include the following:
- Patient demographics and baseline characteristics (e.g., patient identifier, age or date of birth, gender, weight, ethnicity, and race)
- A statement "LAGEVRIOuse for COVID-19 under Emergency Use Authorization (EUA)” under the“Describe Event, Problem, or Product Use/Medication Error”heading
- Information about the serious adverse event or medication error (e.g., signs and symptoms, test/laboratory data, complications, timing of drug initiation in relation to the occurrence of the event, duration of the event, treatments required to mitigate the event, evidence of event improvement/disappearance after stopping or reducing the dosage, evidence of event reappearance after reintroduction, clinical outcomes).
- Patient’s preexisting medical conditions and use of concomitant products
- Information about the product (e.g., dosage, route of administration, NDC #).
Submit adverse event and medication error reports, using Form 3500, to FDA MedWatch using one of the following methods:
- Complete and submit the report online:www.fda.gov/medwatch/report.htm
- Complete and submit a postage-paid FDA Form 3500 (https://www.fda.gov/media/76299/download) and return by:
- Mail to MedWatch, 5600 Fishers Lane, Rockville, MD 20852-9787, or
- Fax to 1-800-FDA-0178, or
- Call 1-800-FDA-1088 to request a reporting form
In addition, please provide a copy of all FDA MedWatch forms to:
Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC, Rahway, NJ USA
Fax: 215-616-5677
E-mail:dpoc.usa@msd.comThe prescribing healthcare provider and/or the provider’s designee is/are responsible for mandatory responses to requests from FDA for information about adverse events and medication errors following receipt of LAGEVRIO.
*Serious adverse events are defined as:
- Death;
- A life-threatening adverse event;
- Inpatient hospitalization or prolongation of existing hospitalization;
- A persistent or significant incapacity or substantial disruption of the ability to conduct normal life functions;
- A congenital anomaly/birth defect;
- Other important medical event, which may require a medical or surgical intervention to prevent death, a life-threatening event, hospitalization, disability, or congenital anomaly.
For information on clinical studies of LAGEVRIO and other therapies for the treatment of COVID-19, see
The dosage in adult patients is 800 mg (four 200 mg capsules) taken orally every 12 hours for 5 days, with or without food
Molnupiravir is a 5´-isobutyrate prodrug of NHC that is hydrolyzed during or after absorption. NHC, the primary circulating analyte, is taken up by cells and anabolized to NHC-TP. NHC is eliminated by metabolism to uridine and/or cytidine through the same pathways involved in endogenous pyrimidine metabolism. NHC pharmacokinetics are shown in Table 2.
Plasma NHC concentrations in patients (N=5) following administration of molnupiravir via nasogastric or orogastric tube fell within the range of NHC concentrations following oral molnupiravir capsule administration under the same dosing regimen.
| NHC Geometric Mean (%CV) | |
|---|---|
| Values were obtained from a Phase 1 study of healthy subjects, unless otherwise indicated. | |
Pharmacokinetics in Patients | |
| AUC0-12hr(ng*hr/mL)Values were obtained from population PK analysis. | 8260 (41.0) |
| Cmax(ng/mL) | 2330 (36.9) |
| C12hr(ng/mL) | 31.1 (124) |
Pharmacokinetics in Healthy Subjects | |
| AUC0-12hr(ng*hr/mL) | 8330 (17.9) |
| Cmax(ng/mL) | 2970 (16.8) |
| C12hr(ng/mL) | 16.7 (42.8) |
| AUC Accumulation Ratio | 1.09 (11.8) |
Absorption | |
| Tmax(hr)Median [min - max] | 1.50 [1.00 – 2.02] |
| Effect of Food | 35% reduction in Cmax, no effect on AUC |
Distribution | |
| Plasma Protein Binding ( in vitro ) | 0% |
| Apparent Volume of Distribution (L) | 142 |
Elimination | |
| Effective t1/2(hr) | 3.3 |
| Apparent Clearance (L/hr) | 76.9 |
| Fraction of dose excreted in urine over the time interval of 0-12 hours | 3% (81.6%) |
Population PK analysis results indicated that age, sex, race, ethnicity, or disease severity do not meaningfully influence the PK of NHC.
LAGEVRIO has not been studied in pediatric patients.
Renal clearance is not a meaningful route of elimination for NHC. In a population PK analysis, mild or moderate renal impairment did not have a meaningful impact on the PK of NHC. The PK of molnupiravir and NHC has not been evaluated in patients with eGFR less than 30 mL/min/1.73m2or on dialysis.
The PK of molnupiravir and NHC has not been evaluated in patients with moderate and severe hepatic impairment. Preclinical data indicate that hepatic elimination is not expected to be a major route of NHC elimination; therefore, hepatic impairment is unlikely to affect NHC exposure.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has issued an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) to permit the emergency use of the unapproved product LAGEVRIO™ for treatment of adults with mild-to-moderate coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19):
- who are at high risk for progression to severe COVID-19, including hospitalization or death. Refer to CDC websitehttps://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/clinical-care/underlyingconditions.html. Healthcare providers should consider the benefit-risk for an individual patient.for additional details, and for
- whom alternative COVID-19 treatment options approved or authorized by FDA are not accessible or clinically appropriate.
- LAGEVRIO is not authorized for use in patients who are less than 18 years of age[see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- LAGEVRIO is not authorized for initiation of treatment in patients hospitalized due to COVID-19Should a patient require hospitalization after starting treatment with LAGEVRIO, the patient may complete the full 5 day treatment course per the healthcare provider’s discretion.. Benefit of treatment with LAGEVRIO has not been observed in subjects when treatment was initiated after hospitalization due to COVID-19[see Dosing and Administration (2.1)].
- LAGEVRIO is not authorized for use for longer than 5 consecutive days.
- LAGEVRIO is not authorized for pre-exposure or post-exposure prophylaxis for prevention of COVID-19.
LAGEVRIO may only be prescribed for an individual patient by physicians, advanced practice registered nurses, and physician assistants that are licensed or authorized under state law to prescribe drugs in the therapeutic class to which LAGEVRIO belongs (i.e., anti-infectives).
LAGEVRIO is not approved for any use, including for use for the treatment of COVID-19.
Prior to initiating treatment with LAGEVRIO, carefully consider the known and potential risks and benefits
LAGEVRIO is authorized only for the duration of the declaration that circumstances exist justifying the authorization of the emergency use of LAGEVRIO under section 564(b)(1) of the Act, 21 U.S.C. § 360bbb-3(b)(1), unless the authorization is terminated or revoked sooner.
There is currently an outbreak of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by SARS-CoV-2, a novel coronavirus. The Secretary of HHS has:
- Determined that there is a public health emergency, or significant potential for a public health emergency, related to COVID-19SeeU.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Determination of a Public Health Emergency and Declaration that Circumstances Exist Justifying Authorizations Pursuant to Section 564(b) of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, 21 U.S.C. § 360bbb-3. February 4, 2020;https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2020/02/07/2020-02496/determination-of-public-health-emergency.See alsoU.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Amended Determination of a Public Health Emergency or Significant Potential for a Public Health Emergency Pursuant to Section 564(b) of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, 21 U.S.C. § 360bbb-3(b). March 15, 2023 (“Amended Determination”);https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2023/03/20/2023-05609/covid-19-emergency-use-authorization-declaration..
- Declared that circumstances exist justifying the authorization of emergency use of drugs and biological products for the prevention or treatment of COVID-19SeeU.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Declaration that Circumstances Exist Justifying Authorizations Pursuant to Section 564(b) of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, 21 U.S.C. § 360bbb-3, 85 FR 18250 (April 1, 2020);https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2020/04/01/2020-06905/emergency-use-authorization-declaration.See alsoAmended Determination (“The declarations issued pursuant to section 564(b)(1) of the FD&C Act that circumstances exist justifying the authorization of emergency use of certain in vitro diagnostics, personal respiratory protective devices, other medical devices and drugs and biological products, as set forth in those declarations, and that are based on the February 4, 2020 determination, remain in effect until those declarations are terminated in accordance with section 564 of the FD&C Act.”)..
An EUA is a FDA authorization for the emergency use of an unapproved product or unapproved use of an approved product (i.e., drug, biological product, or device) in the United States under certain circumstances including, but not limited to, when the Secretary of HHS declares that there is a public health emergency that affects the national security or the health and security of United States citizens living abroad, and that involves biological agent(s) or a disease or condition that may be attributable to such agent(s). Criteria for issuing an EUA include:
- The biological agent(s) can cause a serious or life-threatening disease or condition;
- Based on the totality of the available scientific evidence (including data from adequate and well-controlled clinical trials, if available), it is reasonable to believe that
- the product may be effective in diagnosing, treating, or preventing the serious or life-threatening disease or condition; and
- the known and potential benefits of the product - when used to diagnose, prevent, or treat such disease or condition - outweigh the known and potential risks of the product, taking into consideration the material threat posed by the biological agent(s);
- There is no adequate, approved, and available alternative to the product for diagnosing, preventing, or treating the serious or life-threatening disease or condition.
Veklury (remdesivir) is FDA-approved for the treatment of COVID-19 in adults and pediatric patients (at least 28 days old and weighing at least 3 kg) who are not hospitalized and have mild-to-moderate COVID-19, and who are at high risk for progression to severe COVID-19, including hospitalization or death. Veklury is administered via intravenous infusion for a total treatment duration of 3 days.
Although Veklury is an approved alternative to LAGEVRIO for the treatment of mild-to-moderate COVID-19 in adults and who are at high risk for progression to severe COVID-19, including hospitalization or death, FDA does not consider Veklury to be an adequate alternative to LAGEVRIO for this authorized use because it may not be feasible or clinically appropriate for certain patients (e.g., it requires a 3-day intravenous treatment duration).
Paxlovid (nirmatrelvir tablets; ritonavir tablets co-packaged for oral use) is FDA-approved for the treatment of mild-to-moderate COVID-19 in adults who are at high risk for progression to severe COVID-19, including hospitalization or death. Paxlovid is administered orally for a total treatment duration of 5 days. Although Paxlovid is an approved alternative to LAGEVRIO for the treatment of mild-to-moderate COVID-19 in adults and who are at high risk for progression to severe COVID-19, including hospitalization or death, FDA does not consider Paxlovid to be an adequate alternative to LAGEVRIO for this authorized use because it may not be clinically appropriate for patients on medications that are primarily metabolized by CYP3A and/or that are strong CYP3A inducers.
For additional information on all products authorized for treatment or prevention of COVID-19, please see
For information on clinical studies of LAGEVRIO and other therapies for the treatment of COVID-19, see www.clinicaltrials.gov.
Clinical data supporting this EUA are based on data from 1,433 randomized subjects in the Phase 3 MOVe-OUT trial (NCT04575597). MOVe-OUT is a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial studying LAGEVRIO for the treatment of non-hospitalized patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 who are at risk for progressing to severe COVID-19 and/or hospitalization. Eligible subjects were 18 years of age and older and had one or more pre-defined risk factors for disease progression: over 60 years of age, diabetes, obesity (BMI ≥30), chronic kidney disease, serious heart conditions, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or active cancer. The study included symptomatic subjects not vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2 and who had laboratory confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection and symptom onset within 5 days of randomization. Subjects were randomized 1:1 to receive 800 mg of LAGEVRIO or placebo orally twice daily for 5 days.
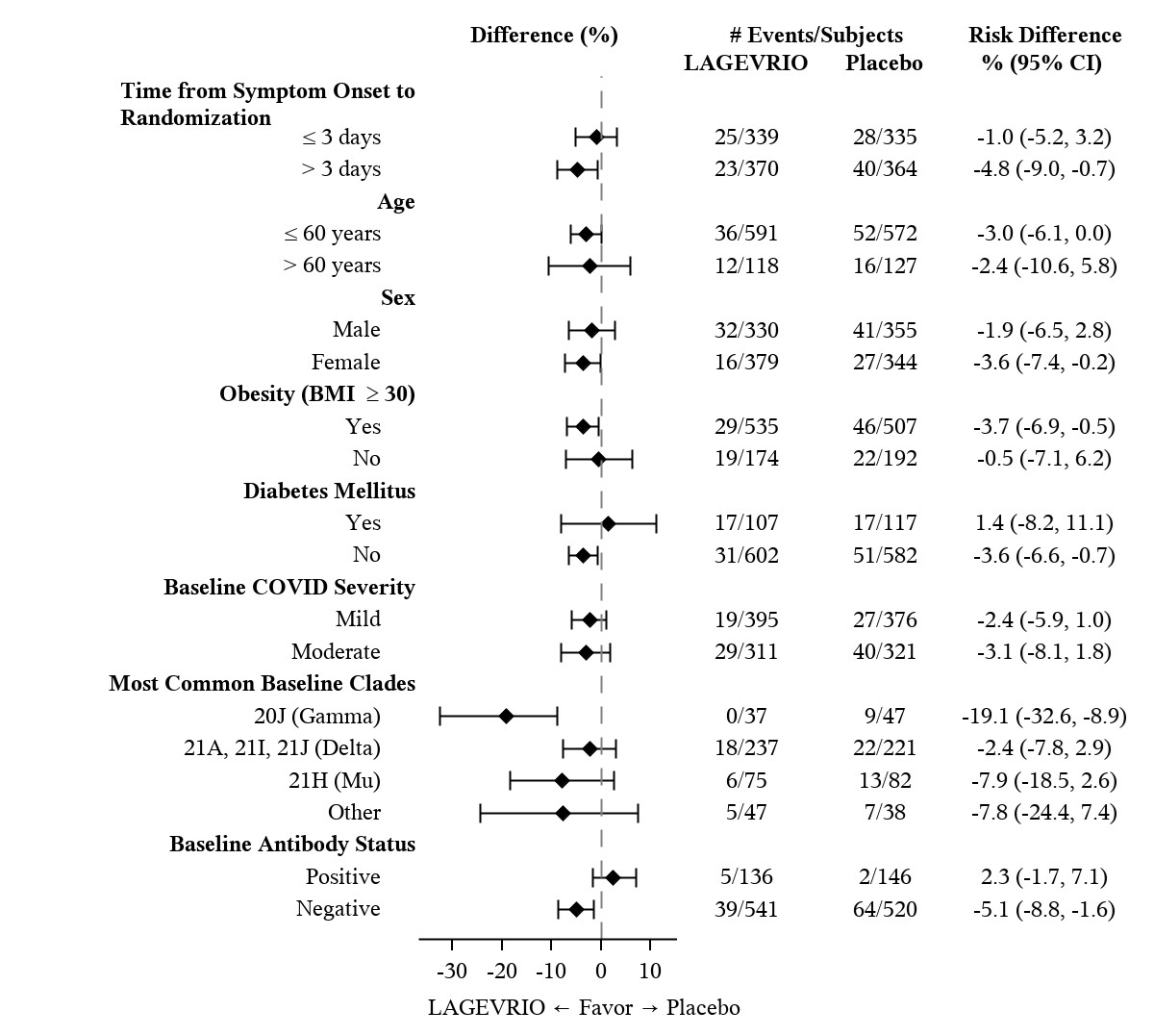
At baseline, in all randomized subjects, the median age was 43 years (range:18 to 90); 17% of subjects were over 60 years of age and 3% were 75 years of age or older; 49% of subjects were male; 57% were White, 5% Black or African American, 3% Asian, 50% Hispanic or Latino. The majority of subjects were enrolled from sites in Latin America (46%) and Europe (33%); 12% were enrolled in Africa, 6% were enrolled in North America and 3% were enrolled in Asia. Forty-eight percent of subjects received LAGEVRIO or placebo within 3 days of COVID-19 symptom onset. The most common risk factors were obesity (74%), over 60 years of age (17%), and diabetes (16%). Among 792 subjects (55% of total randomized population) with available baseline SARS-CoV-2 variant/clade identification results, 58% were infected with Delta (B.1.617.2 and AY lineages), 20% were infected with Mu (B.1.621), 11% were infected with Gamma (P.1), and the remainder were infected with other variants/clades. Overall, baseline demographic and disease characteristics were well balanced between the treatment arms.
Table 3provides the results of the primary endpoint (the percentage of subjects who were hospitalized or died through Day 29 due to any cause). The efficacy results are based on unvaccinated adults who were 18 years of age and older and had one or more pre-defined risk factors for disease progression: over 60 years of age, diabetes, obesity (BMI ≥30), chronic kidney disease, serious heart conditions, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or active cancer. Please refer to Figure 1 for results by certain subgroups. These subgroup analyses are considered exploratory. Data are not available in certain subgroups of subjects who are at high risk for progression to severe COVID-19 as defined by CDC.
| LAGEVRIO (N=709) n (%) | Placebo (N=699) n (%) | Adjusted Risk Difference % (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|
| Adjusted relative risk reduction of LAGEVRIO compared to placebo for all randomized subjects was 30% (95% CI: 1%, 51%). | ||
| Analyses are adjusted by the stratification factor of time of COVID-19 symptom onset (≤3 days vs. >3 [4-5] days). | ||
All-cause hospitalization ≥24 hours for acute care or death through Day 29 | ||
| 48 (6.8%) | 68 (9.7%) | -3.0% (-5.9%, -0.1%) |
All-cause mortality through Day 29 | ||
| 1 (0.1%) | 9 (1.3%) | |
| The corresponding confidence interval is based on Miettinen & Nurminen method. |
| The modified intent-to-treat population is the efficacy analysis population. |
| Baseline serum samples were evaluated with the Roche Elecsys anti-N assay to test for the presence of antibodies (IgM, IgG and IgA) against the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein. |
| The findings of these subgroup analyses are considered exploratory. |
 |

Completion of the full 5-day treatment course and continued isolation in accordance with public health recommendations are important to maximize viral clearance and minimize transmission of SARS-CoV-2
As a prescribing healthcare practitioner, you must communicate to the patient and/or caregiver information consistent with the “ FACT SHEET FOR PATIENTS AND CAREGIVERS” and document that information was provided. A copy of this Fact Sheet should be provided to the patient and/or caregiver prior to receiving LAGEVRIO
Inform patients that hypersensitivity reactions have been reported, even following a single dose of LAGEVRIO, and to discontinue the drug and to inform their healthcare provider at the first sign of a skin rash, hives or other skin reactions, a rapid heartbeat, difficulty in swallowing or breathing, any swelling suggesting angioedema (for example, swelling of the lips, tongue, face, tightness of the throat, hoarseness), or other symptoms of an allergic reaction
Advise patients that LAGEVRIO is not recommended for use in pregnancy because it may cause fetal harm. Advise individuals of childbearing potential to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy
Advise individuals of childbearing potential to use effective contraception correctly and consistently while taking LAGEVRIO and for 4 days after the last dose.
While the risk is regarded as low, there is a theoretical risk for LAGEVRIO to affect offspring of treated males based on its mechanism of action. Advise sexually active individuals with partners of childbearing potential to use a reliable method of contraception correctly and consistently while taking LAGEVRIO and for at least 3 months after the last dose of LAGEVRIO. The risk beyond 3 months after the last dose of LAGEVRIO is unknown
LAGEVRIO is not authorized for use in patients less than 18 year of age as it may affect bone growth and cartilage formation
There is a pregnancy registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in individuals exposed to LAGEVRIO during pregnancy. Encourage participation and advise patients about how they may enroll in the pregnancy registry at
Breastfeeding is not recommended while taking LAGEVRIO and for 4 days after the last dose of LAGEVRIO. Advise lactating individuals to consider interrupting breastfeeding and to consider pumping and discarding breast milk during treatment and for 4 days after the last dose of LAGEVRIO
Inform patients to take LAGEVRIO with or without food. Advise patients to swallow LAGEVRIO capsules whole, and to not open, break, or crush the capsules. Instruct patients that if they miss a dose of LAGEVRIO and it is within 10 hours of the time it is usually taken, the patient should take it as soon as possible and resume the normal dosing schedule. If the patient misses a dose by more than 10 hours, the patient should not take the missed dose and instead take the next dose at the regularly scheduled time. Advise the patient to not double the dose to make up for a missed dose
LAGEVRIO capsule contents can be mixed with water and given via NG/OG, G and GJ tubes. Inform patients to follow the instructions as described in the fact sheet for patients and caregivers
Alert the patient of the importance of completing the full 5-day treatment course and to continuing isolation in accordance with public health recommendations to maximize viral clearance and minimize transmission of SARS-CoV-2
LAGEVRIO is not authorized for use for longer than 5 consecutive days because the safety and efficacy have not been established.
If the patient misses a dose of LAGEVRIO within 10 hours of the time it is usually taken, the patient should take it as soon as possible and resume the normal dosing schedule. If the patient misses a dose by more than 10 hours, the patient should not take the missed dose and instead take the next dose at the regularly scheduled time. The patient should not double the dose to make up for a missed dose.
Should a patient require hospitalization after starting treatment with LAGEVRIO, the patient may complete the full 5 day treatment course per the healthcare provider’s discretion.
Capsules: 200 mg, Swedish Orange opaque size 0 capsules. The capsules have the corporate logo and “82” printed in white ink.
There is a pregnancy registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in individuals exposed to LAGEVRIO during pregnancy. The prescribing healthcare provider must document that a pregnant individual was made aware of the pregnancy registry at
Based on animal data, LAGEVRIO may cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant individuals. There are no available human data on the use of LAGEVRIO in pregnant individuals to evaluate the risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes; therefore, LAGEVRIO is not recommended during pregnancy
In order to mitigate the risks of using this unapproved product under the EUA and to optimize the potential benefit of LAGEVRIO, the following steps are required. Use of LAGEVRIO under this EUA is limited to the following (all requirements must be met):
- Treatment of adults with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 who are at high risk for progression to severe COVID-19, including hospitalization or death and for whom alternative COVID-19 treatment options approved or authorized by FDA are not accessible or clinically appropriate[see Limitations of Authorized Use (1)].
- As the prescribing healthcare provider, review the information contained within the “Fact Sheet for Patients and Caregivers” with your patient or caregiver prior to the patient receiving LAGEVRIO. Healthcare providers must provide the patient/caregiver with an electronic or hard copy of the “Fact Sheet for Patients and Caregivers” prior to the patient receiving LAGEVRIO and must document that the patient/caregiver has been given an electronic or hard copy of the “Fact Sheet for Patients and Caregivers”.
- The prescribing healthcare providers must inform the patient/caregiver that:
- LAGEVRIO is an unapproved drug that is authorized for use under this Emergency Use Authorization.
- Other therapeutics are currently approved for the same use as LAGEVRIO[seeEmergency Use Authorization (1) - Information Regarding Available Alternatives for the EUA Authorized Use].
- There are benefits and risks of taking LAGEVRIO as outlined in the “Fact Sheet for Patients and Caregivers.”
- There is a pregnancy registry.
- Females of childbearing potential should use a reliable method of contraception correctly and consistently, as applicable, for the duration of treatment and for 4 days after the last dose of LAGEVRIO.
- Males of reproductive potential who are sexually active with females of childbearing potential should use a reliable method of contraception correctly and consistently during treatment and for at least 3 months after the last dose.
- The prescribing healthcare provider must assess whether a female of childbearing potential is pregnant or not, if clinically indicated[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)and Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
- Based on findings from animal reproduction studies, LAGEVRIO may cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant individuals. If LAGEVRIO is used during pregnancy, prescribing healthcare providers must communicate to the patient the known and potential benefits and the potential risks of LAGEVRIO use during pregnancy, as outlined in the “Fact Sheet for Patients and Caregivers”[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.3), Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)and Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
- If the decision is made to use LAGEVRIO during pregnancy, the prescriber must document that the known and potential benefits and the potential risks of LAGEVRIO use during pregnancy, as outlined in the “Fact Sheet for Patients and Caregivers,” were discussed with the patient.
- The prescribing healthcare provider must document that a pregnant individual was made aware of the pregnancy registry athttps://covid-pr.pregistry.comor 1-800-616-3791.
- The prescribing healthcare provider and/or the provider’s designee is/are responsible for mandatory reporting of all medication errors and serious adverse events potentially related to LAGEVRIO within 7 calendar days from the healthcare provider’s awareness of the event[see Adverse Reactions (6.4)].
For information on clinical studies of LAGEVRIO and other therapies for the treatment of COVID-19, see
Based on findings from animal reproduction studies, LAGEVRIO may cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant individuals. There are no available human data on the use of LAGEVRIO in pregnant individuals to evaluate the risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes; therefore, LAGEVRIO is not recommended for use during pregnancy. When considering LAGEVRIO for a pregnant individual, the prescribing healthcare provider must communicate the known and potential benefits and the potential risks of using LAGEVRIO during pregnancy to the pregnant individual. LAGEVRIO is authorized to be prescribed to a pregnant individual only after the healthcare provider has determined that the benefits would outweigh the risks for that individual patient. If the decision is made to use LAGEVRIO during pregnancy, the prescribing healthcare provider must document that the known and potential benefits and the potential risks of using LAGEVRIO during pregnancy were communicated to the pregnant individual.
Advise individuals of childbearing potential of the potential risk to a fetus and to use an effective method of contraception correctly and consistently, as applicable, during treatment with LAGEVRIO and for 4 days after the final dose
Prior to initiating treatment with LAGEVRIO, assess whether an individual of childbearing potential is pregnant or not, if clinically indicated. Pregnancy status does not need to be confirmed in patients who have undergone permanent sterilization, are currently using an intrauterine system or contraceptive implant, or in whom pregnancy is not possible. In all other patients, assess whether the patient is pregnant based on the first day of last menstrual period in individuals who have regular menstrual cycles, is using a reliable method of contraception correctly and consistently or have had a negative pregnancy test. A pregnancy test is recommended if the individual has irregular menstrual cycles, is unsure of the first day of last menstrual period or is not using effective contraception correctly and consistently
In order to mitigate the risks of using this unapproved product under the EUA and to optimize the potential benefit of LAGEVRIO, the following steps are required. Use of LAGEVRIO under this EUA is limited to the following (all requirements must be met):
- Treatment of adults with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 who are at high risk for progression to severe COVID-19, including hospitalization or death and for whom alternative COVID-19 treatment options approved or authorized by FDA are not accessible or clinically appropriate[see Limitations of Authorized Use (1)].
- As the prescribing healthcare provider, review the information contained within the “Fact Sheet for Patients and Caregivers” with your patient or caregiver prior to the patient receiving LAGEVRIO. Healthcare providers must provide the patient/caregiver with an electronic or hard copy of the “Fact Sheet for Patients and Caregivers” prior to the patient receiving LAGEVRIO and must document that the patient/caregiver has been given an electronic or hard copy of the “Fact Sheet for Patients and Caregivers”.
- The prescribing healthcare providers must inform the patient/caregiver that:
- LAGEVRIO is an unapproved drug that is authorized for use under this Emergency Use Authorization.
- Other therapeutics are currently approved for the same use as LAGEVRIO[seeEmergency Use Authorization (1) - Information Regarding Available Alternatives for the EUA Authorized Use].
- There are benefits and risks of taking LAGEVRIO as outlined in the “Fact Sheet for Patients and Caregivers.”
- There is a pregnancy registry.
- Females of childbearing potential should use a reliable method of contraception correctly and consistently, as applicable, for the duration of treatment and for 4 days after the last dose of LAGEVRIO.
- Males of reproductive potential who are sexually active with females of childbearing potential should use a reliable method of contraception correctly and consistently during treatment and for at least 3 months after the last dose.
- The prescribing healthcare provider must assess whether a female of childbearing potential is pregnant or not, if clinically indicated[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)and Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
- Based on findings from animal reproduction studies, LAGEVRIO may cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant individuals. If LAGEVRIO is used during pregnancy, prescribing healthcare providers must communicate to the patient the known and potential benefits and the potential risks of LAGEVRIO use during pregnancy, as outlined in the “Fact Sheet for Patients and Caregivers”[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.3), Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)and Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
- If the decision is made to use LAGEVRIO during pregnancy, the prescriber must document that the known and potential benefits and the potential risks of LAGEVRIO use during pregnancy, as outlined in the “Fact Sheet for Patients and Caregivers,” were discussed with the patient.
- The prescribing healthcare provider must document that a pregnant individual was made aware of the pregnancy registry athttps://covid-pr.pregistry.comor 1-800-616-3791.
- The prescribing healthcare provider and/or the provider’s designee is/are responsible for mandatory reporting of all medication errors and serious adverse events potentially related to LAGEVRIO within 7 calendar days from the healthcare provider’s awareness of the event[see Adverse Reactions (6.4)].
For information on clinical studies of LAGEVRIO and other therapies for the treatment of COVID-19, see
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
COVID-19 in pregnancy is associated with adverse maternal and fetal outcomes, including preeclampsia, eclampsia, preterm birth, premature rupture of membranes, venous thromboembolic disease, and fetal death.
In an embryofetal development (EFD) study in rats, molnupiravir was administered orally to pregnant rats at 0, 100, 250, or 500 mg/kg/day from gestation days (GDs) 6 to 17. Molnupiravir was also administered orally to pregnant rats at up to 1,000 mg/kg/day from GDs 6 to 17 in a preliminary EFD study. Developmental toxicities included post-implantation losses, malformations of the eye, kidney, and axial skeleton, and rib variations at 1,000 mg/kg/day (8 times the human NHC exposure at the RHD) and decreased fetal body weights and delayed ossification at ≥500 mg/kg/day (3 times the human NHC exposure at the RHD). There were no developmental toxicities at ≤250 mg/kg/day (less than the human NHC exposure at the RHD). Maternal toxicities included decreased food consumption and body weight losses, resulting in the early sacrifice of two of sixteen animals at 1,000 mg/kg/day, and decreased body weight gain at 500 mg/kg/day.
In an EFD study in rabbits, molnupiravir was administered orally to pregnant rabbits at 0, 125, 400, or 750 mg/kg/day from GDs 7 to 19. Developmental toxicity was limited to reduced fetal body weights at 750 mg/kg/day (18 times the human NHC exposures at the RHD). There was no developmental toxicity at ≤400 mg/kg/day (7 times the human NHC exposures at the RHD). Maternal toxicities included reduced food consumption and body weight gains, and abnormal fecal output at 750 mg/kg/day.
In a pre- and post-natal developmental study, molnupiravir was administered orally to female rats at doses up to 500 mg/kg/day (similar to the human NHC exposure at the RHD) from GD6 through lactation day 20. No effects were observed in offspring.
No contraindications have been identified based on the limited available data on the emergency use of LAGEVRIO authorized under this EUA.
There are limited clinical data available for LAGEVRIO. Serious and unexpected adverse events may occur that have not been previously reported with LAGEVRIO use.