Levetiracetam - Levetiracetam In Sodium Chloride injection prescribing information
Warnings and Precautions (5.5 ) 3/2024
INDICATIONS & USAGE
Levetiracetam in Sodium Chloride Injection is indicated for adjunct therapy in adults (≥16 years of age) with the following seizure types when oral administration is temporarily not feasible:
Partial-Onset Seizures
Levetiracetam in Sodium Chloride Injection is indicated as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial-onset seizures in adults with epilepsy.
Myoclonic Seizures in Patients with Juvenile Myoclonic Epilepsy
Levetiracetam in Sodium Chloride Injection is indicated as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of myoclonic seizures in adults with juvenile myoclonic epilepsy.
Primary Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizures
Levetiracetam in Sodium Chloride Injection is indicated as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures in adults with idiopathic generalized epilepsy.
Limitations of Use
Levetiracetam in Sodium Chloride Injection is an antiepileptic drug indicated for adult patients (16 years and older) when oral administration is temporarily not feasible.
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
- For intravenous infusion only (2.1 )
- Do not dilute prior to its use (2.1 )
- Administer dose-specific bag intravenously over 15-minutes (2.1 )
Initial Exposure to Levetiracetam
- Partial-Onset Seizures: Initial dose is 500 mg twice daily. Increase by 500 mg twice daily every 2 weeks to a maximum recommended dose of 1500 mg twice daily (2.2 ).
- Myoclonic Seizures in Patients with Juvenile Myoclonic Epilepsy: Initial dose is 500 mg twice daily. Increase by 500 mg twice daily every 2 weeks to the recommended dose of 1500 mg twice daily. (2.2 ).
- Primary Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizures: Initial dose is 500 mg twice daily. Increase by 500 mg twice daily every 2 weeks to the recommended dose of 1500 mg twice daily. (2.2 ).
Switching from or to oral Levetiracetam : The total daily dosage/frequency of levetiracetam injection should be equivalent to those of oral levetiracetam (2.3 , 2.4 ).
Renal Impairment: Dose adjustment necessary based on creatinine clearance (2.5 ).
General Information – Administration
Levetiracetam in Sodium Chloride Injection is for intravenous infusion only. It is available in the following concentrations: three single-dose 100 mL bags, each containing a different total dosage of levetiracetam (500 mg [5 mg/mL], 1000 mg [10 mg/mL], or 1500 mg [15 mg/mL]).
A single-dose bag should be administered intravenously over a 15-minute IV infusion period.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration whenever solution and container permit. Levetiracetam in Sodium Chloride Injection should not be further diluted prior to use. Any unused portion of the Levetiracetam in Sodium Chloride Injection contents should be discarded.
Initial Exposure to Levetiracetam
Levetiracetam can be initiated with either intravenous or oral administration. Partial-Onset Seizures In clinical trials of oral levetiracetam, daily doses of 1000 mg, 2000 mg, and 3000 mg, given as twice-daily dosing, were shown to be effective. Although in some studies there was a tendency toward greater response with higher dose [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ], a consistent increase in response with increased dose has not been shown.
Treatment should be initiated with a daily dose of 1000 mg/day, given as twice-daily dosing (500 mg twice daily). Additional dosing increments may be given (1000 mg/day additional every 2 weeks) to a maximum recommended daily dose of 3000 mg. Doses greater than 3000 mg/day have been used in open-label studies with levetiracetam tablets for periods of 6 months and longer. There is no evidence that doses greater than 3000 mg/day confer additional benefit.
Myoclonic Seizures in Patients with Juvenile Myoclonic Epilepsy Treatment should be initiated with a dose of 1000 mg/day, given as twice-daily dosing (500 mg twice daily). Dosage should be increased by 1000 mg/day every 2 weeks to the recommended daily dose of 3000 mg. The effectiveness of doses lower than 3000 mg/day has not been studied.
Primary Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizures
Treatment should be initiated with a dose of 1000 mg/day, given as twice-daily dosing (500 mg twice daily). Dosage should be increased by 1000 mg/day every 2 weeks to the recommended daily dose of 3000 mg. The effectiveness of doses lower than 3000 mg/day has not been adequately studied.
Switching to Intravenous Dosing
When switching from oral levetiracetam, the initial total daily intravenous dosage of levetiracetam should be equivalent to the total daily dosage and frequency of oral levetiracetam.
Switching to Oral Dosing
At the end of the intravenous treatment period, the patient may be switched to levetiracetam oral administration at the equivalent daily dosage and frequency of the intravenous administration.
Adult Patients with Impaired Renal Function
Levetiracetam dosing must be individualized according to the patient's renal function status. Recommended doses and adjustment for dose for adults are shown in Table 1. To use this dosing table, an estimate of the patient's creatinine clearance (CLcr) in mL/min is needed.
Table 1: Dosing Adjustment Regimen for Adult Patients with Impaired Renal Function
| Group | Creatinine Clearance (mL/min) | Dosage (mg) | Frequency |
| Normal | greater than 80 | 500 to 1,500 | Every 12 hours |
| Mild | 50 to 80 | 500 to 1,000 | Every 12 hours |
| Moderate | 30 to 50 | 250 to 750 | Every 12 hours |
| Severe | less than 30 | 250 to 500 | Every 12 hours |
| ESRD patients using dialysis | ---- | 500 to 1,000 | 1 Every 24 hours |
1 Following dialysis, a 250 mg to 500 mg supplemental dose is recommended.
Compatibility with other Antiepileptic Drugs
Levetiracetam in Sodium Chloride Injection is found to be physically compatible and chemically stable for at least 24 hours when mixed with lorazepam, diazepam, and valproate sodium and stored at controlled room temperature 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F). There are no data to support the physical compatibility of levetiracetam injection with antiepileptic drugs that are not listed above.
Discontinuation of Levetiracetam
Avoid abrupt withdrawal from levetiracetam in order to reduce the risk of increased seizure frequency and status epilepticus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ].
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS
Injection: Levetiracetam in Sodium Chloride Injection is a clear, colorless solution packaged in a single-dose bag and available in three strengths:
- 500 mg/100 mL (5 mg/mL): 500 mg levetiracetam in 0.82 % sodium chloride
- 1000 mg/100 mL (10 mg/mL): 1000 mg levetiracetam in 0.75 % sodium chloride
- 1500 mg/100 mL (15 mg/mL): 1500 mg levetiracetam in 0.54% sodium chloride
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Exposure Registry There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to antiepileptic drugs (AEDs), including levetiracetam, during pregnancy. Encourage women who are taking levetiracetam injection during pregnancy to enroll in the North American Antiepileptic Drug (NAAED) pregnancy registry by calling 1-888-233-2334 or visiting http://www.aedpregnancyregistry.org/.
Risk Summary Prolonged experience with levetiracetam in pregnant women has not identified a drug-associated risk of major birth defects or miscarriage, based on published literature, which includes data from pregnancy registries and reflects experience over two decades [see Human Data]. In animal studies, levetiracetam produced developmental toxicity (increased embryofetal and offspring mortality, increased incidences of fetal structural abnormalities, decreased embryofetal and offspring growth, neurobehavioral alterations in offspring) at doses similar to human therapeutic doses [see Animal Data].
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively. The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown.
Clinical Considerations Levetiracetam blood levels may decrease during pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9) ]. Physiological changes during pregnancy may affect levetiracetam concentration. Decrease in levetiracetam plasma concentrations has been observed during pregnancy. This decrease is more pronounced during the third trimester. Dose adjustments may be necessary to maintain clinical response. Data Human Data While available studies cannot definitively establish the absence of risk, data from the published literature and pregnancy registries have not established an association with levetiracetam use during pregnancy and major birth defects or miscarriage. Animal Data When levetiracetam (0, 400, 1200, or 3600 mg/kg/day) was administered orally to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis, reduced fetal weights and increased incidence of fetal skeletal variations were observed at the highest dose tested. There was no evidence of maternal toxicity. The no-effect dose for adverse effects on embryofetal development in rats (1200 mg/kg/day) is approximately 4 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 3000 mg on a body surface area (mg/m 2 ) basis.
Oral administration of levetiracetam (0, 200, 600, or 1800 mg/kg/day) to pregnant rabbits during the period of organogenesis resulted in increased embryofetal mortality and incidence of fetal skeletal variations at the mid and high dose and decreased fetal weights and increased incidence of fetal malformations at the high dose, which was associated with maternal toxicity. The no-effect dose for adverse effects on embryofetal development in rabbits (200 mg/kg/day) is approximately equivalent to the MRHD on a mg/m 2 basis.
Oral administration of levetiracetam (0, 70, 350, or 1800 mg/kg/day) to female rats throughout pregnancy and lactation led to an increased incidence of fetal skeletal variations, reduced fetal body weight, and decreased growth in offspring at the mid and high doses and increased pup mortality and neurobehavioral alterations in offspring at the highest dose tested. There was no evidence of maternal toxicity. The no-effect dose for adverse effects on pre-and postnatal development in rats (70 mg/kg/day) is less than the MRHD on a mg/m 2 basis.
Oral administration of levetiracetam to rats during the latter part of gestation and throughout lactation produced no adverse developmental or maternal effects at doses of up to 1800 mg/kg/day (6 times the MRHD on a mg/m 2 basis).
Lactation
Risk Summary Levetiracetam is excreted in human milk. There are no data on the effects of levetiracetam on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. The development and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for levetiracetam and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from levetiracetam or from the underlying maternal condition.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of levetiracetam injection in patients below the age of 16 years have not been established.
Geriatric Use
There were 347 subjects in clinical studies of levetiracetam that were 65 years old and over. No overall differences in safety were observed between these subjects and younger subjects. There were insufficient numbers of elderly subjects in controlled trials of epilepsy to adequately assess the effectiveness of levetiracetam in these patients.
Levetiracetam is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of adverse reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
Renal Impairment
Clearance of levetiracetam is decreased in patients with renal impairment and is correlated with creatinine clearance [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ]. Dosage adjustment is recommended for patients with impaired renal function and supplemental doses should be given to patients after dialysis [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) ].
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Levetiracetam in Sodium Chloride Injection is contraindicated in patients with a hypersensitivity to levetiracetam. Reactions have included anaphylaxis and angioedema [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ].
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Psychiatric Reactions: Behavioral abnormalities including psychotic symptoms, suicidal ideation, irritability, and aggressive behavior have been observed. Monitor patients for psychiatric signs and symptoms (5.1 )
- Somnolence and Fatigue: Monitor patients for these symptoms and advise patients not to drive or operate machinery until they have gained sufficient experience on levetiracetam (5.2 )
- Serious Dermatological Reactions: Discontinue Levetiracetam at the first sign of rash unless clearly not drug related. (5.4 )
- Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS)/Multiorgan Hypersensitivity: Discontinue if no alternative etiology (5.5 )
- Coordination Difficulties: Monitor for ataxia, abnormal gait, and incoordination. (5.6 )
- Withdrawal Seizures: Levetiracetam must be gradually withdrawn (5.7 )
Psychiatric Reactions
In some patients levetiracetam causes behavioral abnormalities. The incidences of behavioral abnormalities in the myoclonic and primary generalized tonic-clonic seizure studies were comparable to those of the adult partial-onset seizure studies. A total of 13.3% of adult levetiracetam-treated patients compared to 6.2% of placebo patients experienced non-psychotic behavioral symptoms (reported as aggression, agitation, anger, anxiety, apathy, depersonalization, depression, emotional lability, hostility, irritability, and nervousness). A total of 1.7% of adult levetiracetam-treated patients discontinued treatment due to behavioral adverse events, compared to 0.2% of placebo patients. The treatment dose was reduced in 0.8% of adult levetiracetam-treated patients and in 0.5% of placebo patients. One percent of adult levetiracetam-treated patients experienced psychotic symptoms compared to 0.2% of placebo patients.
Two (0.3%) adult levetiracetam-treated patients were hospitalized and their treatment was discontinued due to psychosis. Both events, reported as psychosis, developed within the first week of treatment and resolved within 1 to 2 weeks following treatment discontinuation. The above psychiatric signs and symptoms should be monitored.
Somnolence and Fatigue
In some patients, levetiracetam causes somnolence and fatigue. The incidences of somnolence and fatigue provided below are from controlled adult partial-onset seizure studies. In general, the incidences of somnolence and fatigue in the myoclonic and primary generalized tonic-clonic studies were comparable to those of the adult partial-onset seizure studies. In controlled trials of adult patients with epilepsy experiencing partial-onset seizures, 14.8% of levetiracetam-treated patients reported somnolence, compared to 8.4% of placebo patients. There was no clear dose response up to 3000 mg/day. In a study where there was no titration, about 45% of patients receiving 4000 mg/day reported somnolence. The somnolence was considered serious in 0.3% of the treated patients, compared to 0% in the placebo group. About 3% of levetiracetam-treated patients discontinued treatment due to somnolence, compared to 0.7% of placebo patients. In 1.4% of treated patients and in 0.9% of placebo patients the dose was reduced, while 0.3% of the treated patients were hospitalized due to somnolence. In controlled trials of adult patients with epilepsy experiencing partial-onset seizures, 14.7% of levetiracetam-treated patients reported asthenia, compared to 9.1% of placebo patients. Treatment was discontinued due to asthenia in 0.8% of treated patients as compared to 0.5% of placebo patients. In 0.5% of treated patients and in 0.2% of placebo patients the dose was reduced due to asthenia. Somnolence and asthenia occurred most frequently within the first 4 weeks of treatment. Patients should be monitored for these signs and symptoms and advised not to drive or operate machinery until they have gained sufficient experience on levetiracetam to gauge whether it adversely affects their ability to drive or operate machinery.
Anaphylaxis and Angioedema
Levetiracetam can cause anaphylaxis or angioedema after the first dose or at any time during treatment. Signs and symptoms in cases reported in the postmarketing setting with levetiracetam have included hypotension, hives, rash, respiratory distress, and swelling of the face, lip, mouth, eye, tongue, throat, and feet. In some reported cases, reactions were life-threatening and required emergency treatment. If a patient develops signs or symptoms of anaphylaxis or angioedema, levetiracetam should be discontinued and the patient should seek immediate medical attention. Levetiracetam should be discontinued permanently if a clear alternative etiology for the reaction cannot be established [see Contraindications (4) ].
Serious Dermatological Reactions
Serious dermatological reactions, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), have been reported in patients treated with levetiracetam. The median time of onset is reported to be 14 to 17 days, but cases have been reported at least four months after initiation of treatment. Recurrence of the serious skin reactions following rechallenge with levetiracetam has also been reported. Levetiracetam should be discontinued at the first sign of a rash, unless the rash is clearly not drug-related. If signs or symptoms suggest SJS/TEN, use of this drug should not be resumed and alternative therapy should be considered.
Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS)/Multiorgan Hypersensitivity
Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS), also known as multiorgan hypersensitivity, has been reported in patients taking antiepileptic drugs, including levetiracetam. These events can be fatal or life-threatening, particularly if diagnosis and treatment do not occur as early as possible. DRESS typically, although not exclusively, presents with fever, rash, lymphadenopathy, and/or facial swelling, in association with other organ system involvement, such as hepatitis, nephritis, hematological abnormalities, myocarditis, or myositis, sometimes resembling an acute viral infection. Eosinophilia is often present. Because this disorder is variable in its expression, other organ systems not noted here may be involved. It is important to note that early manifestations of hypersensitivity, such as fever or lymphadenopathy, may be present even though rash is not evident. If such signs or symptoms are present, the patient should be evaluated immediately. Levetiracetam should be discontinued if an alternative etiology for the signs or symptoms cannot be established [see Contraindications (4) ] .
Coordination Difficulties
Coordination difficulties were only observed in the adult partial-onset seizure studies. A total of 3.4% of adult levetiracetam-treated patients experienced coordination difficulties, (reported as either ataxia, abnormal gait, or incoordination) compared to 1.6% of placebo patients. A total of 0.4% of patients in controlled trials discontinued levetiracetam treatment due to ataxia, compared to 0% of placebo patients. In 0.7% of treated patients and in 0.2% of placebo patients the dose was reduced due to coordination difficulties, while one of the treated patients was hospitalized due to worsening of pre-existing ataxia. These events occurred most frequently within the first 4 weeks of treatment. Patients should be monitored for these signs and symptoms and advised not to drive or operate machinery until they have gained sufficient experience on levetiracetam to gauge whether it adversely affects their ability to drive or operate machinery.
Withdrawal Seizures
As with most antiepileptic drugs, levetiracetam should be withdrawn gradually because of the risk of increased seizure frequency and status epilepticus. But if withdrawal is needed because of a serious adverse reaction, rapid discontinuation can be considered.
Hematologic Abnormalities
Levetiracetam can cause hematologic abnormalities. Hematologic abnormalities occurred in clinical trials and included decreases in white blood cell (WBC), neutrophil, and red blood cells counts (RBC); decreases in hemoglobin and hematocrit; and increases in eosinophil counts. Cases of agranulocytosis, pancytopenia, and thrombocytopenia have been reported in the postmarketing setting. A complete blood count is recommended in patients experiencing significant weakness, pyrexia, recurrent infections, or coagulation disorders.
Partial-Onset Seizures In controlled clinical studies using an oral formulation of levetiracetam in adult patients with partial-onset seizures, minor but statistically significant decreases compared to placebo in total mean RBC (0.03 × 10 6 /mm 3 ), mean hemoglobin (0.09 g/dL), and mean hematocrit (0.38%), were seen in levetiracetam-treated patients. A total of 3.2% of levetiracetam-treated and 1.8% of placebo-treated patients had at least one possibly significant (≤2.8 × 10 9 /L) decreased WBC, and 2.4% of levetiracetam-treated and 1.4% of placebo-treated patients had at least one possibly significant (≤1.0 × 10 9 /L) decreased neutrophil count. Of the levetiracetam-treated patients with a low neutrophil count, all but one rose towards or to baseline with continued treatment. No patient was discontinued secondary to low neutrophil counts. Juvenile Myoclonic Epilepsy Although there were no obvious hematologic abnormalities observed in patients with JME, the limited number of patients makes any conclusion tentative. The data from the partial seizure patients should be considered to be relevant for JME patients.
Seizure Control During Pregnancy
Physiological changes may gradually decrease plasma levels of levetiracetam throughout pregnancy. This decrease is more pronounced during the third trimester. It is recommended that patients be monitored carefully during pregnancy. Close monitoring should continue through the postpartum period especially if the dose was changed during pregnancy.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed in more details in other sections of labeling:
- Psychiatric Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- Somnolence and Fatigue [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
- Anaphylaxis and Angioedema [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
- Serious Dermatological Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ]
- Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS)/Multiorgan Hypersensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ]
- Coordination Difficulties [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ]
- Withdrawal Seizures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ]
- Hematologic Abnormalities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) ]
- Seizure Control During Pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9) ]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice. The adverse reactions that result from levetiracetam injection use include all of those reported for levetiracetam tablets and oral solution. Equivalent doses of intravenous (IV) levetiracetam and oral levetiracetam result in equivalent C max , C min , and total systemic exposure to levetiracetam when the IV levetiracetam is administered as a 15-minute infusion. Partial-Onset Seizures In controlled clinical studies using levetiracetam tablets in adults with partial-onset seizures [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ], the most common adverse reactions in adult patients receiving levetiracetam in combination with other AEDs, for events with rates greater than placebo, were somnolence, asthenia, infection and dizziness. Of the most common adverse reactions in adults experiencing partial-onset seizures, asthenia, somnolence and dizziness occurred predominantly during the first 4 weeks of treatment with levetiracetam. Table 2 lists adverse reactions that occurred in at least 1% of adult epilepsy patients receiving levetiracetam tablets in placebo-controlled studies and were numerically more common than in patients treated with placebo. In these studies, either levetiracetam or placebo was added to concurrent AED therapy. Adverse reactions were usually mild to moderate in intensity. Table 2: Adverse Reactions• In Placebo-Controlled, Adjunctive Studies In Adults Experiencing Partial-Onset Seizures
| Adverse Reaction | Levetiracetam (N=769) % | Placebo (N=439) % |
| Asthenia | 15 | 9 |
| Somnolence | 15 | 8 |
| Headache | 14 | 13 |
| Infection | 13 | 8 |
| Dizziness | 9 | 4 |
| Pain | 7 | 6 |
| Pharyngitis | 6 | 4 |
| Depression | 4 | 2 |
| Nervousness | 4 | 2 |
| Rhinitis | 4 | 3 |
| Anorexia | 3 | 2 |
| Ataxia | 3 | 1 |
| Vertigo | 3 | 1 |
| Amnesia | 2 | 1 |
| Anxiety | 2 | 1 |
| Cough Increased | 2 | 1 |
| Diplopia | 2 | 1 |
| Emotional Lability | 2 | 0 |
| Hostility | 2 | 1 |
| Paresthesia | 2 | 1 |
| Sinusitis | 2 | 1 |
•Adverse reactions occurred in at least 1% of levetiracetam-treated patients and occurred more frequently than placebo-treated patients
In controlled adult clinical studies using levetiracetam tablets, 15% of patients receiving levetiracetam and 12% receiving placebo either discontinued or had a dose reduction as a result of an adverse reaction. Table 3 lists the most common (>1%) adverse reactions that resulted in discontinuation or dose reduction and that occurred more frequently in levetiracetam-treated patients than in placebo-treated patients.
Table 3: Adverse Reactions that Resulted in Discontinuation or Dose Reduction in Placebo-Controlled Studies in Adults Experiencing Partial-Onset Seizures
| Adverse Reaction | Levetiracetam (N=769) % | Placebo (N=439) % |
| Somnolence | 4 | 2 |
| Dizziness | 1 | 0 |
Myoclonic Seizures Although the pattern of adverse reactions in this study seems somewhat different from that seen in patients with partial seizures, this is likely due to the much smaller number of patients in this study compared to partial seizure studies. The adverse reaction pattern for patients with JME is expected to be essentially the same as for patients with partial seizures. In the controlled clinical study using levetiracetam tablets in patients with myoclonic seizures, the most common adverse reactions in patients using levetiracetam in combination with other AEDs, for events with rates greater than placebo, were somnolence, neck pain, and pharyngitis. Table 4 lists adverse reactions that occurred in at least 5% of juvenile myoclonic epilepsy patients experiencing myoclonic seizures treated with levetiracetam tablets and were numerically more common than in patients treated with placebo. In this study, either levetiracetam or placebo was added to concurrent AED therapy. Adverse reactions were usually mild to moderate in intensity.
Table 4: Adverse Reactions• in a Placebo-Controlled, Adjunctive Study in Patients 12 Years of Age and Older with Myoclonic Seizures
| Adverse Reaction | Levetiracetam (N=60) % | Placebo (N=60) % |
| Somnolence | 12 | 2 |
| Neck pain | 8 | 2 |
| Pharyngitis | 7 | 0 |
| Depression | 5 | 2 |
| Influenza | 5 | 2 |
| Vertigo | 5 | 3 |
• Adverse reactions occurred in at least 5% of levetiracetam-treated patients and occurred more frequently than placebo-treated patients
In the placebo-controlled study using levetiracetam tablets in patients with JME, 8% of patients receiving levetiracetam and 2% receiving placebo either discontinued or had a dose reduction as a result of an adverse reaction. The adverse reactions that led to discontinuation or dose reduction and that occurred more frequently in levetiracetam-treated patients than in placebo-treated patients are presented in Table 5.
Table 5: Adverse Reactions that Resulted in Discontinuation or Dose Reduction in Patients with Juvenile Myoclonic Epilepsy
| Adverse Reaction | Levetiracetam (N=60) % | Placebo (N=60) % |
| Anxiety | 3 | 2 |
| Depressed mood | 2 | 0 |
| Depression | 2 | 0 |
| Diplopia | 2 | 0 |
| Hypersomnia | 2 | 0 |
| Insomnia | 2 | 0 |
| Irritability | 2 | 0 |
| Nervousness | 2 | 0 |
| Somnolence | 2 | 0 |
Primary Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizures
Although the pattern of adverse reactions in this study seems somewhat different from that seen in patients with partial seizures, this is likely due to the much smaller number of patients in this study compared to partial seizure studies. The adverse reaction pattern for patients with primary generalized tonic-clonic (PGTC) seizures is expected to be essentially the same as for patients with partial seizures. In the controlled clinical study that included patients with PGTC seizures, the most common adverse reaction in patients receiving levetiracetam oral formulation in combination with other AEDs, for events with rates greater than placebo was nasopharyngitis. Table 6 lists adverse reactions that occurred in at least 5% of idiopathic generalized epilepsy patients experiencing PGTC seizures treated with levetiracetam and were numerically more common than in patients treated with placebo. In this study, either levetiracetam or placebo was added to concurrent AED therapy.
Table 6: Adverse Reactions• in a Placebo-Controlled, Adjunctive Study in Patients with PGTC Seizures
| Adverse Reaction | Levetiracetam (N=79) % | Placebo (N=84) % |
| Nasopharyngitis | 14 | 5 |
| Fatigue | 10 | 8 |
| Diarrhea | 8 | 7 |
| Irritability | 6 | 2 |
| Mood swings | 5 | 1 |
• Adverse reactions occurred in at least 5% of levetiracetam-treated patients and occurred more frequently than placebo-treated patients
In the placebo-controlled study, 5% of patients receiving levetiracetam and 8% receiving placebo either discontinued or had a dose reduction during the treatment period as a result of an adverse reaction. This study was too small to adequately characterize the adverse reactions that could be expected to result in discontinuation of treatment in this population. It is expected that the adverse reactions that would lead to discontinuation in this population would be similar to those resulting in discontinuation in other epilepsy trials (see Tables 3 and 5). In addition, the following adverse reactions were seen in other controlled adult studies of levetiracetam: balance disorder, disturbance in attention, eczema, memory impairment, myalgia, and blurred vision. Comparison of Gender, Age and Race The overall adverse reaction profile of levetiracetam was similar between females and males. There are insufficient data to support a statement regarding the distribution of adverse reactions by age and race.
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of levetiracetam. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. In addition to the adverse reactions listed above [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ], the following adverse reactions have been reported in patients receiving marketed levetiracetam worldwide. The listing is alphabetized: abnormal liver function test, acute kidney injury, agranulocytosis, anaphylaxis, angioedema, choreoathetosis, drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), dyskinesia, erythema multiforme, hepatic failure, hepatitis, hyponatremia, muscular weakness, obsessive-compulsive disorders (OCD), pancreatitis, pancytopenia (with bone marrow suppression identified in some of these cases), panic attack, thrombocytopenia, weight loss, and worsening of seizures including in patients with SCN8A mutations. Alopecia has been reported with levetiracetam use; recovery was observed in majority of cases where levetiracetam was discontinued.
DESCRIPTION
Levetiracetam in Sodium Chloride Injection is an antiepileptic drug available as a clear, colorless, sterile solution for intravenous administration. The chemical name of levetiracetam, a single enantiomer, is (-)-(S)-α-ethyl-2-oxo-1-pyrrolidine acetamide, its molecular formula is C 8 H 14 N 2 O 2 and its molecular weight is 170.21. Levetiracetam is chemically unrelated to existing antiepileptic drugs (AEDs). It has the following structural formula:
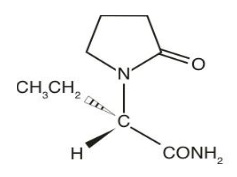
Levetiracetam, USP is a white to off-white crystalline powder with a faint odor and a bitter taste. It is very soluble in water (104.0 g/100 mL). It is freely soluble in chloroform (65.3 g/100 mL) and in methanol (53.6 g/100 mL), soluble in ethanol (16.5 g/100 mL), sparingly soluble in acetonitrile (5.7 g/100 mL) and practically insoluble in n-hexane. (Solubility limits are expressed as g/100 mL solvent.) Levetiracetam in Sodium Chloride Injection is a clear, colorless, sterile solution that is available in a single-dose dual port bag with an aluminum over wrap. The container closure is not made with natural rubber latex.
500 mg/100 mL: One 100 mL bag contains 500 mg of levetiracetam, USP (5 mg/mL), water for injection, 820 mg sodium chloride, 5.5 mg of glacial acetic acid and buffered at approximately pH 5.5 with glacial acetic acid and 164 mg sodium acetate trihydrate. 1000 mg/100 mL: One 100 mL bag contains 1000 mg of levetiracetam, USP (10 mg/mL), water for injection, 750 mg sodium chloride, 6.5 mg of glacial acetic acid and buffered at approximately pH 5.5 with glacial acetic acid and 164 mg sodium acetate trihydrate. 1500 mg/100 mL: One 100 mL bag contains 1500 mg of levetiracetam, USP (15 mg/mL), water for injection, 540 mg sodium chloride, 7.5 mg of glacial acetic acid and buffered at approximately pH 5.5 with glacial acetic acid and 164 mg sodium acetate trihydrate.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
The precise mechanism(s) by which levetiracetam exerts its antiepileptic effect is unknown. A saturable and stereoselective neuronal binding site in rat brain tissue has been described for levetiracetam. Experimental data indicate that this binding site is the synaptic vesicle protein SV2A, thought to be involved in the regulation of vesicle exocytosis. Although the molecular significance of levetiracetam binding to synaptic vesicle protein SV2A is not understood, levetiracetam and related analogs showed a rank order of affinity for SV2A which correlated with the potency of their antiseizure activity in audiogenic seizure-prone mice. These findings suggest that the interaction of levetiracetam with the SV2A protein may contribute to the antiepileptic mechanism of action of the drug.
Pharmacodynamics
Effects on QTc Interval The effect of levetiracetam on QTc prolongation was evaluated in a randomized, double-blind, positive-controlled (moxifloxacin 400 mg) and placebo-controlled crossover study of levetiracetam (1000 mg or 5000 mg) in 52 healthy subjects. The upper bound of the 90% confidence interval for the largest placebo-adjusted, baseline-corrected QTc was below 10 milliseconds. Therefore, there was no evidence of significant QTc prolongation in this study.
Pharmacokinetics
Equivalent doses of intravenous (IV) levetiracetam and oral levetiracetam result in equivalent C max , C min , and total systemic exposure to levetiracetam when the IV levetiracetam is administered as a 15 minute infusion.
Overview Levetiracetam is rapidly and almost completely absorbed after oral administration. Levetiracetam injection and tablets are bioequivalent. The pharmacokinetics of levetiracetam are linear and time-invariant, with low intra-and inter-subject variability. Levetiracetam is not significantly protein-bound (<10% bound) and its volume of distribution is close to the volume of intracellular and extracellular water. Sixty-six percent (66%) of the dose is renally excreted unchanged. The major metabolic pathway of levetiracetam (24% of dose) is an enzymatic hydrolysis of the acetamide group. It is not liver cytochrome P450 dependent. The metabolites have no known pharmacological activity and are renally excreted. Plasma half-life of levetiracetam across studies is approximately 6-8 hours. It is increased in the elderly (primarily due to impaired renal clearance) and in subjects with renal impairment.
Distribution The equivalence of levetiracetam injection and the oral formulation was demonstrated in a bioavailability study of 17 healthy volunteers. In this study, levetiracetam 1500 mg was diluted in 100 mL 0.9% sterile saline solution and was infused over 15 minutes. The selected infusion rate provided plasma concentrations of levetiracetam at the end of the infusion period similar to those achieved at T max after an equivalent oral dose. It is demonstrated that levetiracetam 1500 mg intravenous infusion is equivalent to levetiracetam 3 x 500 mg oral tablets. The time independent pharmacokinetic profile of levetiracetam was demonstrated following 1500 mg intravenous infusion for 4 days with BID dosing. The AUC( 0-12 ) at steady-state was equivalent to AUC inf following an equivalent single dose. Levetiracetam and its major metabolite are less than 10% bound to plasma proteins; clinically significant interactions with other drugs through competition for protein binding sites are therefore unlikely.
Metabolism Levetiracetam is not extensively metabolized in humans. The major metabolic pathway is the enzymatic hydrolysis of the acetamide group, which produces the carboxylic acid metabolite, ucb L057 (24% of dose) and is not dependent on any liver cytochrome P450 isoenzymes. The major metabolite is inactive in animal seizure models. Two minor metabolites were identified as the product of hydroxylation of the 2-oxo-pyrrolidine ring (2% of dose) and opening of the 2-oxo-pyrrolidine ring in position 5 (1% of dose). There is no enantiomeric interconversion of levetiracetam or its major metabolite.
Elimination
Levetiracetam plasma half-life in adults is 7 ± 1 hour and is unaffected by either dose, route of administration or repeated administration. Levetiracetam is eliminated from the systemic circulation by renal excretion as unchanged drug which represents 66% of administered dose. The total body clearance is 0.96 mL/min/kg and the renal clearance is 0.6 mL/min/kg. The mechanism of excretion is glomerular filtration with subsequent partial tubular reabsorption. The metabolite ucb L057 is excreted by glomerular filtration and active tubular secretion with a renal clearance of 4 mL/min/kg. Levetiracetam elimination is correlated to creatinine clearance. Levetiracetam clearance is reduced in patients with renal impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6) ] .
Specific Populations
Elderly Pharmacokinetics of levetiracetam were evaluated in 16 elderly subjects (age 61-88 years) with creatinine clearance ranging from 30 to 74 mL/min. Following oral administration of twice-daily dosing for 10 days, total body clearance decreased by 38% and the half-life was 2.5 hours longer in the elderly compared to healthy adults. This is most likely due to the decrease in renal function in these subjects.
Pregnancy Levetiracetam levels may decrease during pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1) ].
Gender Levetiracetam C max and AUC were 20% higher in women (N=11) compared to men (N=12). However, clearances adjusted for body weight were comparable.
Race Formal pharmacokinetic studies of the effects of race have not been conducted. Cross study comparisons involving Caucasians (N=12) and Asians (N=12), however, show that pharmacokinetics of levetiracetam were comparable between the two races. Because levetiracetam is primarily renally excreted and there are no important racial differences in creatinine clearance, pharmacokinetic differences due to race are not expected. Renal Impairment The disposition of levetiracetam was studied in adult subjects with varying degrees of renal function. Total body clearance of levetiracetam is reduced in patients with impaired renal function by 40% in the mild group (CLcr = 50-80 mL/min), 50% in the moderate group (CLcr = 30-50 mL/min) and 60% in the severe renal impairment group (CLcr <30 mL/min). Clearance of levetiracetam is correlated with creatinine clearance. In anuric (end stage renal disease) patients, the total body clearance decreased 70% compared to normal subjects (CLcr >80mL/min). Approximately 50% of the pool of levetiracetam in the body is removed during a standard 4 hour hemodialysis procedure [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) ]. Hepatic Impairment In subjects with mild (Child-Pugh A) to moderate (Child-Pugh B) hepatic impairment, the pharmacokinetics of levetiracetam were unchanged. In patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C), total body clearance was 50% that of normal subjects, but decreased renal clearance accounted for most of the decrease. No dose adjustment is needed for patients with hepatic impairment. Drug Interactions In vitro data on metabolic interactions indicate that levetiracetam is unlikely to produce, or be subject to, pharmacokinetic interactions. Levetiracetam and its major metabolite, at concentrations well above C max levels achieved within the therapeutic dose range, are neither inhibitors of nor high affinity substrates for human liver cytochrome P450 isoforms, epoxide hydrolase or UDP-glucuronidation enzymes. In addition, levetiracetam does not affect the in vitro glucuronidation of valproic acid. Potential pharmacokinetic interactions of or with levetiracetam were assessed in clinical pharmacokinetic studies (phenytoin, valproate, warfarin, digoxin, oral contraceptive, probenecid) and through pharmacokinetic screening in the placebo-controlled clinical studies in epilepsy patients. Phenytoin Levetiracetam (3000 mg daily) had no effect on the pharmacokinetic disposition of phenytoin in patients with refractory epilepsy. Pharmacokinetics of levetiracetam were also not affected by phenytoin. Valproate Levetiracetam (1500 mg twice daily) did not alter the pharmacokinetics of valproate in healthy volunteers. Valproate 500 mg twice daily did not modify the rate or extent of levetiracetam absorption or its plasma clearance or urinary excretion. There also was no effect on exposure to and the excretion of the primary metabolite, ucb L057. Other Antiepileptic Drugs Potential drug interactions between levetiracetam and other AEDs (carbamazepine, gabapentin, lamotrigine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, primidone and valproate) were also assessed by evaluating the serum concentrations of levetiracetam and these AEDs during placebo-controlled clinical studies. These data indicate that levetiracetam does not influence the plasma concentration of other AEDs and that these AEDs do not influence the pharmacokinetics of levetiracetam. Oral Contraceptives Levetiracetam (500 mg twice daily) did not influence the pharmacokinetics of an oral contraceptive containing 0.03 mg ethinyl estradiol and 0.15 mg levonorgestrel, or of the luteinizing hormone and progesterone levels, indicating that impairment of contraceptive efficacy is unlikely. Coadministration of this oral contraceptive did not influence the pharmacokinetics of levetiracetam. Digoxin Levetiracetam (1000 mg twice daily) did not influence the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics (ECG) of digoxin given as a 0.25 mg dose every day. Coadministration of digoxin did not influence the pharmacokinetics of levetiracetam. Warfarin Levetiracetam (1000 mg twice daily) did not influence the pharmacokinetics of R and S warfarin. Prothrombin time was not affected by levetiracetam. Coadministration of warfarin did not affect the pharmacokinetics of levetiracetam. Probenecid Probenecid, a renal tubular secretion blocking agent, administered at a dose of 500 mg four times a day, did not change the pharmacokinetics of levetiracetam 1000 mg twice daily. C ss max of the metabolite, ucb L057, was approximately doubled in the presence of probenecid while the fraction of drug excreted unchanged in the urine remained the same. Renal clearance of ucb L057 in the presence of probenecid decreased 60%, probably related to competitive inhibition of tubular secretion of ucb L057. The effect of levetiracetam on probenecid was not studied.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment Of Fertility
Carcinogenesis Rats were dosed with levetiracetam in the diet for 104 weeks at doses of 50, 300 and 1800 mg/kg/day. Plasma exposure (AUC) at the highest dose was approximately 6 times that in humans at the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 3000 mg. There was no evidence of carcinogenicity. In mice, oral administration of levetiracetam for 80 weeks (doses up to 960 mg/kg/day) or 2 years (doses up to 4000 mg/kg/day, lowered to 3000 mg/kg/day after 45 weeks due to intolerability) was not associated with an increase in tumors. The highest dose tested in mice for 2 years (3000 mg/kg/day) is approximately 5 times the MRHD on a body surface area (mg/m 2 ) basis.
Mutagenesis
Levetiracetam was negative in in vitro (Ames, chromosomal aberration in mammalian cells) and in vivo (mouse micronucleus) assays. The major human metabolite of levetiracetam (ucb L057) was negative in in vitro (Ames, mouse lymphoma) assays. Impairment of Fertility No adverse effects on male or female fertility or reproductive performance were observed in rats at oral doses up to 1800 mg/kg/day, which were associated with plasma exposures (AUC) up to approximately 6 times that in humans at the MRHD.
CLINICAL STUDIES
All clinical studies supporting the efficacy of levetiracetam utilized oral formulations. The finding of efficacy of levetiracetam injection is based on the results of studies using an oral formulation of levetiracetam, and on the demonstration of comparable bioavailability of the oral and parenteral formulations [see Pharmacokinetics (12.3) ].
Partial-Onset Seizures
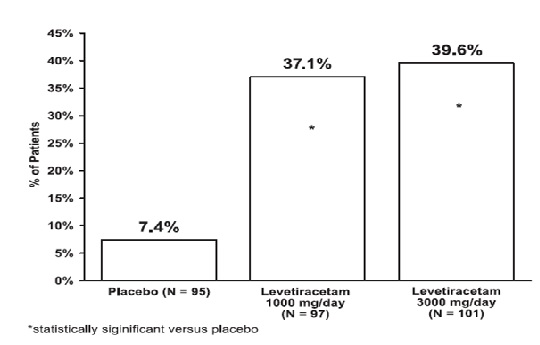
The effectiveness of levetiracetam as adjunctive therapy (added to other antiepileptic drugs) in adults was established in three multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical studies in patients who had refractory partial-onset seizures with or without secondary generalization. The tablet formulation was used in all these studies. In these studies, 904 patients were randomized to placebo, 1000 mg, 2000 mg, or 3000 mg/day. Patients enrolled in Study 1 or Study 2 had refractory partial-onset seizures for at least two years and had taken two or more classical AEDs. Patients enrolled in Study 3 had refractory partial-onset seizures for at least 1 year and had taken one classical AED. At the time of the study, patients were taking a stable dose regimen of at least one and could take a maximum of two AEDs. During the baseline period, patients had to have experienced at least two partial-onset seizures during each 4-week period. Study 1 Study 1 was a double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study conducted at 41 sites in the United States comparing levetiracetam 1000 mg/day (N=97), levetiracetam 3000 mg/day (N=101), and placebo (N=95) given in equally divided doses twice daily. After a prospective baseline period of 12 weeks, patients were randomized to one of the three treatment groups described above. The 18-week treatment period consisted of a 6-week titration period, followed by a 12-week fixed dose evaluation period, during which concomitant AED regimens were held constant. The primary measure of effectiveness was a between group comparison of the percent reduction in weekly partial seizure frequency relative to placebo over the entire randomized treatment period (titration + evaluation period). Secondary outcome variables included the responder rate (incidence of patients with ≥50% reduction from baseline in partial-onset seizure frequency). The results of the analysis of Study 1 are displayed in Table 7.
Table 7: Reduction in Mean Over Placebo in Weekly Frequency of Partial-Onset Seizures in Study 1
| Placebo (N=95) | Levetiracetam 1000 mg/day (N=97) | Levetiracetam 3000 mg/day (N=101) | |
| Percent reduction in partial seizure frequency over placebo | - | 26.1% • | 30.1% • |
•Statistically significant versus placebo
The percentage of patients (y-axis) who achieved ≥50% reduction in weekly seizure rates from baseline in partial-onset seizure frequency over the entire randomized treatment period (titration + evaluation period) within the three treatment groups (x-axis) is presented in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Responder Rate (≥50% Reduction from Baseline) in Study 1
Study 2 Study 2 was a double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study conducted at 62 centers in Europe comparing levetiracetam 1000 mg/day (N=106), levetiracetam 2000 mg/day (N=105), and placebo (N=111) given in equally divided doses twice daily.
The first period of the study (Period A) was designed to be analyzed as a parallel-group study. After a prospective baseline period of up to 12 weeks, patients were randomized to one of the three treatment groups described above. The 16-week treatment period consisted of the 4-week titration period followed by a 12-week fixed dose evaluation period, during which concomitant AED regimens were held constant. The primary measure of effectiveness was a between group comparison of the percent reduction in weekly partial seizure frequency relative to placebo over the entire randomized treatment period (titration + evaluation period). Secondary outcome variables included the responder rate (incidence of patients with ≥50% reduction from baseline in partial-onset seizure frequency). The results of the analysis of Period A are displayed in Table 8.
Table 8: Reduction in Mean Over Placebo in Weekly Frequency of Partial-Onset Seizures in Study 2: Period A
| Placebo (N=111) | Levetiracetam 1000 mg/day (N=106) | Levetiracetam 2000 mg/day (N=105) | |
| Percent reduction in partial seizure frequency over placebo | - | 17.1% • | 21.4% • |
•Statistically significant versus placebo The percentage of patients (y-axis) who achieved ≥50% reduction in weekly seizure rates from baseline in partial-onset seizure frequency over the entire randomized treatment period (titration + evaluation period) within the three treatment groups (x-axis) is presented in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Responder Rate (≥50% Reduction from Baseline) in Study 2: Period A
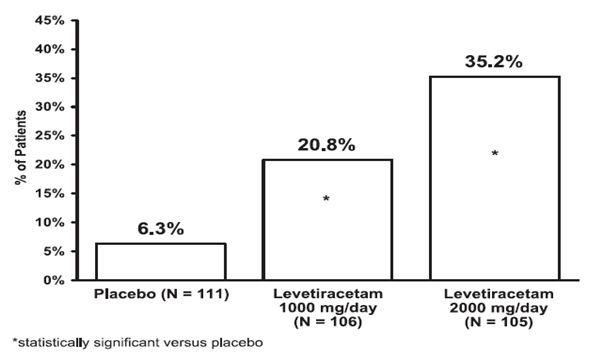
The comparison of levetiracetam 2000 mg/day to levetiracetam 1000 mg/day for responder rate was statistically significant (P=0.02). Analysis of the trial as a cross-over yielded similar results.
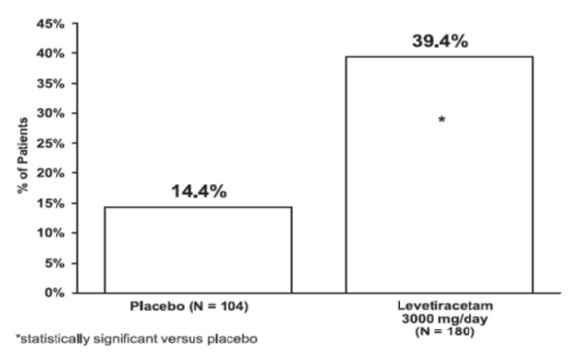
Study 3 Study 3 was a double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study conducted at 47 centers in Europe comparing levetiracetam 3000 mg/day (N=180) and placebo (N=104) in patients with refractory partial-onset seizures, with or without secondary generalization, receiving only one concomitant AED. Study drug was given in two divided doses. After a prospective baseline period of 12 weeks, patients were randomized to one of two treatment groups described above. The 16-week treatment period consisted of a 4-week titration period, followed by a 12-week fixed dose evaluation period, during which concomitant AED doses were held constant. The primary measure of effectiveness was a between group comparison of the percent reduction in weekly seizure frequency relative to placebo over the entire randomized treatment period (titration + evaluation period). Secondary outcome variables included the responder rate (incidence of patients with ≥50% reduction from baseline in partial-onset seizure frequency). Table 9 displays the results of the analysis of Study 3.
Table 9: Reduction in Mean Over Placebo in Weekly Frequency of Partial-Onset Seizures in Study 3
| Placebo (N=104) | Levetiracetam 3000 mg/day (N=180) | |
| Percent reduction in partial seizure frequency over placebo | - | 23.0% • |
•Statistically significant versus placebo
The percentage of patients (y-axis) who achieved ≥50% reduction in weekly seizure rates from baseline in partial-onset seizure frequency over the entire randomized treatment period (titration + evaluation period) within the two treatment groups (x-axis) is presented in Figure 3.
Figure 3: Responder Rate (≥50% Reduction from Baseline) in Study 3
Myoclonic Seizures in Patients with Juvenile Myoclonic Epilepsy
The effectiveness of levetiracetam as adjunctive therapy in patients with juvenile myoclonic epilepsy (JME) experiencing myoclonic seizures was established in one multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study, conducted at 37 sites in 14 countries. Of the 120 patients enrolled, 113 had a diagnosis of confirmed or suspected JME. Eligible patients on a stable dose of 1 antiepileptic drug (AED) experiencing one or more myoclonic seizures per day for at least 8 days during the prospective 8-week baseline period were randomized to either levetiracetam or placebo (levetiracetam N=60, placebo N=60). Patients were titrated over 4 weeks to a target dose of 3000 mg/day and treated at a stable dose of 3000 mg/day over 12 weeks (evaluation period). Study drug was given in 2 divided doses. The primary measure of effectiveness was the proportion of patients with at least 50% reduction in the number of days per week with one or more myoclonic seizures during the treatment period (titration + evaluation periods) as compared to baseline. Table 10 displays the results for the 113 patients with JME in this study. Of 120 patients enrolled, 113 had a diagnosis of confirmed or suspected JME. The results are displayed in Table 10.
Table 10: Responder Rate (≥50% Reduction from Baseline) in Myoclonic Seizure Days Per Week For Patients With JME
| Placebo (N=59) | Levetiracetam (N=54) | |
| Percentage of responders | 23.7% | 60.4% • |
•Statistically significant versus placebo
Primary Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizures
The effectiveness of levetiracetam as adjunctive therapy in patients with idiopathic generalized epilepsy experiencing primary generalized tonic-clonic (PGTC) seizures was established in one multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study, conducted at 50 sites in 8 countries. Eligible patients on a stable dose of 1 or 2 antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) experiencing at least 3 PGTC seizures during the 8-week combined baseline period (at least one PGTC seizure during the 4 weeks prior to the prospective baseline period and at least one PGTC seizure during the 4-week prospective baseline period) were randomized to either levetiracetam or placebo. The 8-week combined baseline period is referred to as “baseline” in the remainder of this section. The population included 164 patients (levetiracetam N=80, placebo N=84) with idiopathic generalized epilepsy (predominately juvenile myoclonic epilepsy, juvenile absence epilepsy, childhood absence epilepsy, or epilepsy with Grand Mal seizures on awakening) experiencing primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures. Each of these syndromes of idiopathic generalized epilepsy was well represented in this patient population. Patients were titrated over 4 weeks to a target dose of 3000 mg/day for adults or a pediatric target dose of 60 mg/kg/day and treated at a stable dose of 3000 mg/day (or 60 mg/kg/day for children) over 20 weeks (evaluation period). Study drug was given in 2 equally divided doses per day. The primary measure of effectiveness was the percent reduction from baseline in weekly PGTC seizure frequency for levetiracetam and placebo treatment groups over the treatment period (titration + evaluation periods). There was a statistically significant decrease from baseline in PGTC frequency in the levetiracetam-treated patients compared to the placebo-treated patients.
Table 11: Median Percent Reduction from Baseline in PGTC Seizure Frequency per Week
| Placebo (N=84) | Levetiracetam (N=78) | |
| Percentage reduction in PGTC seizure frequency | 44.6% | 77.6% • |
•Statistically significant versus placebo
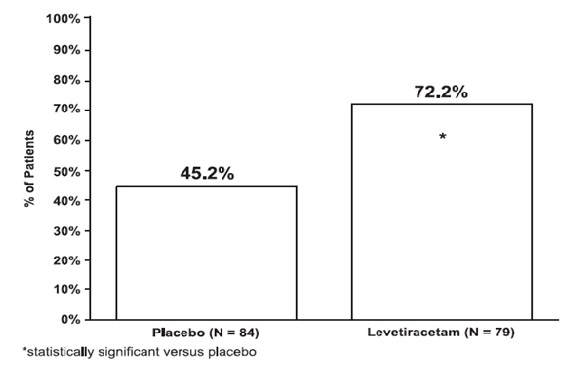
The percentage of patients (y-axis) who achieved ≥50% reduction in weekly seizure rates from baseline in PGTC seizure frequency over the entire randomized treatment period (titration + evaluation period) within the two treatment groups (x-axis) is presented in Figure 4. Figure 4: Responder Rate (≥50% Reduction from Baseline) in PGTC Seizure Frequency per Week
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
Levetiracetam in Sodium Chloride Injection is a clear, colorless, sterile solution that is available in a single-dose 100 mL dual port bag with an aluminum over wrap. The container closure is not made with natural rubber latex. It is available in the following presentations:
| Strength | Package | NDC Number |
| 500 mg/100 mL (5 mg/mL) | 1 single-dose bag | 65145-173-01 |
| 1000 mg/100 mL (10 mg/mL) | 1 single-dose bag | 65145-174-01 |
| 1500 mg/100 mL (15 mg/mL) | 1 single-dose bag | 65145-175-01 |
Storage
Store at 20º to 25ºC (68º to 77ºF); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Mechanism of Action
The precise mechanism(s) by which levetiracetam exerts its antiepileptic effect is unknown. A saturable and stereoselective neuronal binding site in rat brain tissue has been described for levetiracetam. Experimental data indicate that this binding site is the synaptic vesicle protein SV2A, thought to be involved in the regulation of vesicle exocytosis. Although the molecular significance of levetiracetam binding to synaptic vesicle protein SV2A is not understood, levetiracetam and related analogs showed a rank order of affinity for SV2A which correlated with the potency of their antiseizure activity in audiogenic seizure-prone mice. These findings suggest that the interaction of levetiracetam with the SV2A protein may contribute to the antiepileptic mechanism of action of the drug.