Lidocaine And Prilocaine
Lidocaine And Prilocaine Prescribing Information
Lidocaine and Prilocaine Cream USP, 2.5%/2.5% (a eutectic mixture of lidocaine 2.5% and prilocaine 2.5%) is indicated as a topical anesthetic for use on:
- normal intact skinfor local analgesia.
- Genital mucous membranesfor superficial minor surgery and as pretreatment for infiltration anesthesia.
Lidocaine and Prilocaine Cream, 2.5%/2.5% is not recommended in any clinical situation when penetration or migration beyond the tympanic membrane into the middle ear is possible because of the ototoxic effect observed in animal studies (see
Application of lidocaine and prilocaine cream, 2.5%/2.5% to larger areas or for longer times than those recommended could result in sufficient absorption of lidocaine and prilocaine resulting in serious adverse effects (see
Patients treated with class III anti-arrhythmic drugs (eg, amiodarone, bretylium, sotalol, dofetilide) should be under close surveillance and ECG monitoring considered, because cardiac effects may be additive.
Studies in laboratory animals (guinea pigs) have shown that lidocaine and prilocaine cream, 2.5%/2.5% has an ototoxic effect when instilled into the middle ear. In these same studies, animals exposed to lidocaine and prilocaine cream, 2.5%/2.5% only in the external auditory canal, showed no abnormality. Lidocaine and prilocaine cream, 2.5%/2.5% should not be used in any clinical situation when its penetration or migration beyond the tympanic membrane into the middle ear is possible.
Cases of methemoglobinemia have been reported in association with local anesthetic use. Although all patients are at risk for methemoglobinemia, patients with glucose-6- phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, congenital or idiopathic methemoglobinemia, cardiac or pulmonary compromise, infants under 6 months of age, and concurrent exposure to oxidizing agents or their metabolites more susceptible to developing clinical manifestations of the condition. If local anesthetics must be used in these patients, close monitoring for symptoms and signs of methemoglobinemia is recommended.
Signs of methemoglobinemia may occur immediately or may be delayed some hours after exposure and are characterized by a cyanotic skin discoloration and/or abnormal coloration of the blood. Methemoglobin levels may continue to rise; therefore, immediate treatment is required to avert more serious central nervous system and cardiovascular adverse effects, including seizures, coma, arrhythmias, and death. Discontinue Lidocaine and Prilocaine Cream, 2.5%/2.5% and any other oxidizing agents. Depending on the severity of the signs and symptoms, patients may respond to supportive care, i.e., oxygen therapy, hydration. A more severe clinical presentation may require treatment with methylene blue, exchange transfusion, or hyperbaric oxygen.
A thick layer of Lidocaine and Prilocaine Cream USP, 2.5%/2.5% is applied to intact skin and covered with an occlusive dressing (see
To measure 1 gram of Lidocaine and Prilocaine Cream USP, 2.5%/2.5%, the cream should be gently squeezed out of the tube as a narrow strip that is 1.5 inches (3.8 cm) long and 0.2 inches (5mm) wide. The strip of Lidocaine and Prilocaine Cream USP, 2.5%/2.5% should be contained within the lines of the diagram shown below.

Use the number of strips that equals your dose, like the examples in the table below.
1 gram = 1 strip
2 grams = 2 strips
2.5 grams = 2.5 strips
For adult and pediatric patients, apply ONLY as prescribed by your physician.
If your child is below the age of 3 months or small for their age, please inform your doctor before applying Lidocaine and Prilocaine Cream USP, 2.5%/2.5%, which can be harmful, if applied over too much skin at one time in young children.
When applying Lidocaine and Prilocaine Cream USP, 2.5%/2.5% to the intact skin of young children, it is important that they be carefully observed by an adult in order to prevent the accidental ingestion of or eye contact with Lidocaine and Prilocaine Cream USP, 2.5%/2.5%.
Lidocaine and Prilocaine Cream USP, 2.5%/2.5% must be applied to intact skin at least 1 hour before the start of a routine procedure and for 2 hours before the start of a painful procedure. A protective covering of the cream is not necessary for absorption but may be helpful to keep the cream in place.
If using a protective covering, your doctor will remove it, wipe off the Lidocaine and Prilocaine Cream USP, 2.5%/2.5%, and clean the entire area with an antiseptic solution before the procedure. The duration of effective skin anesthesia will be at least 1 hour after removal of the protective covering.

1. Do not apply near eyes or on open wounds.
2. Keep out of the reach of children
3. If your child becomes very dizzy, excessively sleepy, or develops duskiness of the face or lips after applying Lidocaine and Prilocaine Cream USP, 2.5%/2.5%, remove the cream and contact the child's physician at once.
Lidocaine and prilocaine cream, 2.5%/2.5% is contraindicated in patients with a known history of sensitivity to local anesthetics of the amide type or to any other component of the product.
During or immediately after treatment with lidocaine and prilocaine cream, 2.5%/2.5% on intact skin, the skin at the site of treatment may develop erythema or edema or may be the locus of abnormal sensation. Rare cases of discrete purpuric or petechial reactions at the application site have been reported. Rare cases of hyperpigmentation following the use of lidocaine and prilocaine cream, 2.5%/2.5% have been reported. The relationship to lidocaine and prilocaine cream, 2.5%/2.5% or the underlying procedure has not been established. In clinical studies on intact skin involving over 1,300 lidocaine and prilocaine cream, 2.5%/2.5%-treated subjects, one or more such local reactions were noted in 56% of patients, and were generally mild and transient, resolving spontaneously within 1 or 2 hours. There were no serious reactions that were ascribed to lidocaine and prilocaine cream, 2.5%/2.5%.
Two recent reports describe blistering on the foreskin in neonates about to undergo circumcision. Both neonates received 1.0 g of lidocaine and prilocaine cream, 2.5%/2.5%.
In patients treated with lidocaine and prilocaine cream, 2.5%/2.5% on intact skin, local effects observed in the trials included: paleness (pallor or blanching) 37%, redness (erythema) 30%, alterations in temperature sensations 7%, edema 6%, itching 2% and rash, less than 1%.
In clinical studies on genital mucous membranes involving 378 lidocaine and prilocaine cream, 2.5%/2.5%-treated patients, one or more application site reactions, usually mild and transient, were noted in 41% of patients. The most common application site reactions were redness (21%), burning sensation (17%) and edema (10%).
Lidocaine and prilocaine cream, 2.5%/2.5% should be used with caution in patients receiving Class I antiarrhythmic drugs (such as tocainide and mexiletine) since the toxic effects are additive and potentially synergistic.
Patients who are administered local anesthetics are at increased risk of developing methemoglobinemia when concurrently exposed to the following drugs, which could include other local anesthetics:
| Class | Examples |
|---|---|
| Nitrates/Nitrites | nitric oxide, nitroglycerin, nitroprusside, nitrous oxide |
| Local anesthetics | articaine, benzocaine, bupivacaine, lidocaine, mepivacaine, prilocaine, procaine, ropivacaine, tetracaine |
| Antineoplastic Agents | cyclophosphamide, flutamide, hydroxyurea, ifosfamide, rasburicase |
| Antibiotics | dapsone, nitrofurantoin, para-aminosalicylic acid, sulfonamides |
| Antimalarials | chloroquine, primaquine |
| Anticonvulsants | phenobarbital, phenytoin, sodium valproate |
| Other drugs | acetaminophen, metoclopramide, quinine, sulfasalazine |
Specific interaction studies with lidocaine/prilocaine and class III anti-arrhythmic drugs (eg, amiodarone, bretylium, sotalol, dofetilide) have not been performed, but caution is advised (
Application of lidocaine and prilocaine cream, 2.5%/2.5% to larger areas or for longer times than those recommended could result in sufficient absorption of lidocaine and prilocaine resulting in serious adverse effects (see
Patients treated with class III anti-arrhythmic drugs (eg, amiodarone, bretylium, sotalol, dofetilide) should be under close surveillance and ECG monitoring considered, because cardiac effects may be additive.
Studies in laboratory animals (guinea pigs) have shown that lidocaine and prilocaine cream, 2.5%/2.5% has an ototoxic effect when instilled into the middle ear. In these same studies, animals exposed to lidocaine and prilocaine cream, 2.5%/2.5% only in the external auditory canal, showed no abnormality. Lidocaine and prilocaine cream, 2.5%/2.5% should not be used in any clinical situation when its penetration or migration beyond the tympanic membrane into the middle ear is possible.
Cases of methemoglobinemia have been reported in association with local anesthetic use. Although all patients are at risk for methemoglobinemia, patients with glucose-6- phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, congenital or idiopathic methemoglobinemia, cardiac or pulmonary compromise, infants under 6 months of age, and concurrent exposure to oxidizing agents or their metabolites more susceptible to developing clinical manifestations of the condition. If local anesthetics must be used in these patients, close monitoring for symptoms and signs of methemoglobinemia is recommended.
Signs of methemoglobinemia may occur immediately or may be delayed some hours after exposure and are characterized by a cyanotic skin discoloration and/or abnormal coloration of the blood. Methemoglobin levels may continue to rise; therefore, immediate treatment is required to avert more serious central nervous system and cardiovascular adverse effects, including seizures, coma, arrhythmias, and death. Discontinue Lidocaine and Prilocaine Cream, 2.5%/2.5% and any other oxidizing agents. Depending on the severity of the signs and symptoms, patients may respond to supportive care, i.e., oxygen therapy, hydration. A more severe clinical presentation may require treatment with methylene blue, exchange transfusion, or hyperbaric oxygen.
Should lidocaine and prilocaine cream, 2.5%/2.5% be used concomitantly with other products containing lidocaine and/or prilocaine, cumulative doses from all formulations must be considered.
Lidocaine and Prilocaine Cream USP, 2.5%/2.5% is an emulsion in which the oil phase is a eutectic mixture of lidocaine and prilocaine in a ratio of 1:1 by weight. This eutectic mixture has a melting point below room temperature and therefore both local anesthetics exist as a liquid oil rather than as crystals. It is packaged in 30 gram tubes. Lidocaine is chemically designated as acetamide, 2-(diethylamino)-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl), has an octanol: water partition ratio of 43 at pH 7.4, and has the following structure:
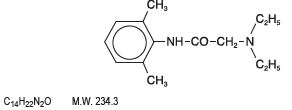
Prilocaine is chemically designated as propanamide, N-(2-methylphenyl)-2-(propylamino), has an octanol: water partition ratio of 25 at pH 7.4, and has the following structure:
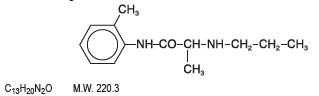
Each gram of Lidocaine and Prilocaine Cream USP, 2.5%/2.5% contains lidocaine 25 mg, prilocaine 25 mg, PEG-60 Hydrogenated Castor oil (as emulsifiers), carbomer homopolymer type B, sodium hydroxide to adjust to a pH approximating 9, and purified water to 1 gram. Lidocaine and Prilocaine Cream USP, 2.5%/2.5% contains no preservative, however it passes the USP antimicrobial effectiveness test due to the pH. The specific gravity of Lidocaine and Prilocaine Cream USP, 2.5%/2.5% is 1.00.