Lisdexamfetamine Dimesylate Prescribing Information
Overdose of CNS stimulants is characterized by the following sympathomimetic effects:
- Cardiovascular effects including tachyarrhythmias, and hypertension or hypotension. Vasospasm, myocardial infarction, or aortic dissection may precipitate sudden cardiac death. Takotsubo cardiomyopathy may develop.
- CNS effects including psychomotor agitation, confusion, and hallucinations. Serotonin syndrome, seizures, cerebral vascular accidents, and coma may occur.
- Life-threatening hyperthermia (temperatures greater than 104°F) and rhabdomyolysis may develop.
Consider the possibility of multiple drug ingestion. The pharmacokinetic profile of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules should be considered when treating patients with overdose. Lisdexamfetamine and d-amphetamine are not dialyzable. Consider contacting the Poison Help line (1-800-222-1222) or a medical toxicologist for additional overdose management recommendations.
and Addiction
Lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules have a high potential for abuse and misuse which can lead to the development of a substance use disorder, including addiction
Abuse is the intentional non-therapeutic use of a drug, even once, to achieve a desired psychological or physiological effect. Misuse is the intentional use, for therapeutic purposes, of a drug by an individual in a way other than prescribed by a health care provider or for whom it was not prescribed. Drug addiction is a cluster of behavioral, cognitive, and physiological phenomena that may include a strong desire to take the drug, difficulties in controlling drug use (e.g., continuing drug use despite harmful consequences, giving a higher priority to drug use than other activities and obligations), and possible tolerance or physical dependence.
Misuse and abuse of lisdexamfetamine, a prodrug of amphetamine, may cause increased heart rate, respiratory rate, or blood pressure; sweating; dilated pupils; hyperactivity; restlessness; insomnia; decreased appetite; loss of coordination; tremors; flushed skin; vomiting; and/or abdominal pain. Anxiety, psychosis, hostility, aggression, and suicidal or homicidal ideation have also been observed with CNS stimulants abuse and/or misuse. Misuse and abuse of CNS stimulants, including lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules, can result in overdose and death
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-control, cross-over, abuse liability study in 38 patients with a history of drug abuse was conducted with single-doses of 50, 100, or 150 mg of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules, 40 mg of immediate-release d-amphetamine sulphate (a controlled II substance), and 200 mg of diethylpropion hydrochloride (a controlled IV substance). Lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules 100 mg produced significantly less "Drug Liking Effects” as measured by the Drug Rating Questionnaire-Subject score, compared to d-amphetamine 40 mg; and 150 mg of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules demonstrated similar “Drug-Liking Effects” compared to 40 mg of d-amphetamine and 200 mg of diethylpropion.
Intravenous administration of 50 mg lisdexamfetamine dimesylate to individuals with a history of drug abuse produced positive subjective responses on scales measuring "Drug Liking", "Euphoria", "Amphetamine Effects", and "Benzedrine Effects" that were greater than placebo but less than those produced by an equivalent dose (20 mg) of intravenous d-amphetamine.
Indications and Usage 7/2021
Warning and Precaution 7/2021
Lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules are contraindicated in patients with:
- Known hypersensitivity to amphetamine products or other ingredients of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules. Anaphylactic reactions, Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, angioedema, and urticaria have been observed in postmarketing reports [see Adverse Reactions (.)]
6.2 Postmarketing ExperienceThe following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. These events are as follows: cardiomyopathy, mydriasis, diplopia, difficulties with visual accommodation, blurred vision, eosinophilic hepatitis, anaphylactic reaction, hypersensitivity, dyskinesia, dysgeusia, motor and verbal tics, bruxism, depression, dermatillomania, alopecia, aggression, Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, chest pain, angioedema, urticaria, seizures, libido changes, frequent or prolonged erections, constipation, rhabdomyolysis, and intestinal ischemia.
- Patients taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), or within 14 days of stopping MAOIs (including MAOIs such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue), because of an increased risk of hypertensive crisis [see Warnings and Precautions (.) and Drug Interactions (
5.7 Serotonin SyndromeSerotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening reaction, may occur when amphetamines are used in combination with other drugs that affect the serotonergic neurotransmitter systems such as monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), triptans, tricyclic antidepressants, fentanyl, lithium, tramadol, tryptophan, buspirone, and St. John’s Wort
[see Drug Interactions ]. The co-administration with cytochrome P450 2D6 (CYP2D6) inhibitors may also increase the risk with increased exposure to the active metabolite of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules (dextroamphetamine). In these situations, consider an alternative non-serotonergic drug or an alternative drug that does not inhibit CYP2D6[see Drug Interactions ].Serotonin syndrome symptoms may include mental status changes (e.g., agitation, hallucinations, delirium, and coma), autonomic instability (e.g., tachycardia, labile blood pressure, dizziness, diaphoresis, flushing, hyperthermia), neuromuscular symptoms (e.g., tremor, rigidity, myoclonus, hyperreflexia, incoordination), seizures, and/or gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea).
Concomitant use of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules with MAOI drugs is contraindicated
[see Contraindications ].Discontinue treatment with lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules and any concomitant serotonergic agents immediately if symptoms of serotonin syndrome occur, and initiate supportive symptomatic treatment. If concomitant use of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules with other serotonergic drugs or CYP2D6 inhibitors is clinically warranted, initiate lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules with lower doses, monitor patients for the emergence of serotonin syndrome during drug initiation or titration, and inform patients of the increased risk for serotonin syndrome.
)]7.1 Drugs Having Clinically Important Interactions with AmphetaminesTable 5: Drugs having clinically important interactions with amphetamines. MAO Inhibitors (MAOI)Clinical Impact MAOI antidepressants slow amphetamine metabolism, increasing amphetamines effect on the release of norepinephrine and other monoamines from adrenergic nerve endings causing headaches and other signs of hypertensive crisis. Toxic neurological effects and malignant hyperpyrexia can occur, sometimes with fatal results. Intervention Do not administer lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules during or within 14 days following the administration of MAOI [see Contraindications ].Serotonergic DrugsClinical Impact The concomitant use of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules and serotonergic drugs increases the risk of serotonin syndrome. Intervention Initiate with lower doses and monitor patients for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome, particularly during lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules initiation or dosage increase. If serotonin syndrome occurs, discontinue lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules and the concomitant serotonergic drug(s) [see Warnings and Precautions ].CYP2D6 InhibitorsClinical Impact The concomitant use of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules and CYP2D6 inhibitors may increase the exposure of dextroamphetamine, the active metabolite of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules compared to the use of the drug alone and increase the risk of serotonin syndrome. Intervention Initiate with lower doses and monitor patients for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome particularly during lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules initiation and after a dosage increase. If serotonin syndrome occurs, discontinue lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules and the CYP2D6 inhibitor [see Warnings and Precautions and Overdosage ].Alkalinizing AgentsClinical Impact Urinary alkalinizing agents can increase blood levels and potentiate the action of amphetamine. Intervention Co-administration of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules and urinary alkalinizing agents should be avoided. Acidifying AgentsClinical Impact Urinary acidifying agents can lower blood levels and efficacy of amphetamines. Intervention Increase dose based on clinical response. Tricyclic AntidepressantsClinical Impact May enhance the activity of tricyclic or sympathomimetic agents causing striking and sustained increases in the concentration of d-amphetamine in the brain; cardiovascular effects can be potentiated. Intervention Monitor frequently and adjust or use alternative therapy based on clinical response.
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Known hypersensitivity to amphetamine products or other ingredients of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules [see Contraindications (
4 CONTRAINDICATIONSLisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules are contraindicated in patients with:
- Known hypersensitivity to amphetamine products or other ingredients of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules. Anaphylactic reactions, Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, angioedema, and urticaria have been observed in postmarketing reports[see Adverse Reactions ].
- Patients taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), or within 14 days of stopping MAOIs (including MAOIs such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue), because of an increased risk of hypertensive crisis[see Warnings and Precautions and Drug Interactions ].
- Known hypersensitivity to amphetamine products or other ingredients in lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules
- Use with monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitor, or within 14 days of the last MAO inhibitor dose
)] - Known hypersensitivity to amphetamine products or other ingredients of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules. Anaphylactic reactions, Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, angioedema, and urticaria have been observed in postmarketing reports
- Hypertensive Crisis When Used Concomitantly with Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors [see Contraindications (
4 CONTRAINDICATIONSLisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules are contraindicated in patients with:
- Known hypersensitivity to amphetamine products or other ingredients of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules. Anaphylactic reactions, Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, angioedema, and urticaria have been observed in postmarketing reports[see Adverse Reactions ].
- Patients taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), or within 14 days of stopping MAOIs (including MAOIs such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue), because of an increased risk of hypertensive crisis[see Warnings and Precautions and Drug Interactions ].
- Known hypersensitivity to amphetamine products or other ingredients in lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules
- Use with monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitor, or within 14 days of the last MAO inhibitor dose
) and Drug Interactions (7.1 Drugs Having Clinically Important Interactions with AmphetaminesTable 5: Drugs having clinically important interactions with amphetamines. MAO Inhibitors (MAOI)Clinical Impact MAOI antidepressants slow amphetamine metabolism, increasing amphetamines effect on the release of norepinephrine and other monoamines from adrenergic nerve endings causing headaches and other signs of hypertensive crisis. Toxic neurological effects and malignant hyperpyrexia can occur, sometimes with fatal results. Intervention Do not administer lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules during or within 14 days following the administration of MAOI [see Contraindications ].Serotonergic DrugsClinical Impact The concomitant use of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules and serotonergic drugs increases the risk of serotonin syndrome. Intervention Initiate with lower doses and monitor patients for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome, particularly during lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules initiation or dosage increase. If serotonin syndrome occurs, discontinue lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules and the concomitant serotonergic drug(s) [see Warnings and Precautions ].CYP2D6 InhibitorsClinical Impact The concomitant use of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules and CYP2D6 inhibitors may increase the exposure of dextroamphetamine, the active metabolite of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules compared to the use of the drug alone and increase the risk of serotonin syndrome. Intervention Initiate with lower doses and monitor patients for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome particularly during lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules initiation and after a dosage increase. If serotonin syndrome occurs, discontinue lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules and the CYP2D6 inhibitor [see Warnings and Precautions and Overdosage ].Alkalinizing AgentsClinical Impact Urinary alkalinizing agents can increase blood levels and potentiate the action of amphetamine. Intervention Co-administration of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules and urinary alkalinizing agents should be avoided. Acidifying AgentsClinical Impact Urinary acidifying agents can lower blood levels and efficacy of amphetamines. Intervention Increase dose based on clinical response. Tricyclic AntidepressantsClinical Impact May enhance the activity of tricyclic or sympathomimetic agents causing striking and sustained increases in the concentration of d-amphetamine in the brain; cardiovascular effects can be potentiated. Intervention Monitor frequently and adjust or use alternative therapy based on clinical response. )] - Known hypersensitivity to amphetamine products or other ingredients of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules. Anaphylactic reactions, Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, angioedema, and urticaria have been observed in postmarketing reports
- Abuse, Misuse, and Addiction [see
WARNING: ABUSE, MISUSE,
AND ADDICTIONLisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsuleshave a high potential for abuse and misuse, which can lead to the development of a substance use disorder, including addiction. Misuse and abuse of CNS stimulants, includinglisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules, can result in overdose and death[see Overdosage ], and this risk is increased with higher doses or unapproved methods of administration, such as snorting or injection.Before prescribinglisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules, assess each patient’s risk for abuse, misuse, and addiction. Educate patients and their families about these risks, proper storage of the drug, and proper disposal of any unused drug. Throughoutlisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsulestreatment, reassess each patient’s risk of abuse, misuse, and addiction and frequently monitor for signs and symptoms of abuse, misuse, and addiction[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), and Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.2)].WARNING: ABUSE, MISUSE, AND ADDICTIONSee full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.Lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules has a high potential for abuse and misuse, which can lead to the development of a substance use disorder, including addiction.Misuse and abuse of CNS stimulants, includinglisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules, can result in overdose and death :- Before prescribing lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules, assess each patient’s risk for abuse, misuse, and addiction.
- Educate patients and their families about these risks, proper storage of the drug, and proper disposal of any unused drug.
- Throughout treatment, reassess each patient’s risk and frequently monitor for signs and symptoms of abuse, misuse, and addiction.
, Warnings and Precautions (5.1 Abuse, Misuse,
and AddictionLisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules have a high potential for abuse and misuse. The use of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules exposes individuals to the risks of abuse and misuse, which can lead to the development of a substance use disorder, including addiction. Lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules can be diverted for non-medical use into illicit channels or distribution[see Drug Abuse and Dependence ]. Misuse and abuse of CNS stimulants, including lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules, can result in overdose and death[see Overdosage ]. The co-administration with cytochrome P450 2D6 (CYP2D6) inhibitors may also increase the risk with increased exposure to the active metabolite of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules (dextroamphetamine). In these situations, consider an alternative non-serotonergic drug or an alternative drug that does not inhibit CYP2D6[see Drug Interactions ].Serotonin syndrome symptoms may include mental status changes (e.g., agitation, hallucinations, delirium, and coma), autonomic instability (e.g., tachycardia, labile blood pressure, dizziness, diaphoresis, flushing, hyperthermia), neuromuscular symptoms (e.g., tremor, rigidity, myoclonus, hyperreflexia, incoordination), seizures, and/or gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea).
Concomitant use of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules with MAOI drugs is contraindicated
[see Contraindications ].Discontinue treatment with lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules and any concomitant serotonergic agents immediately if symptoms of serotonin syndrome occur, and initiate supportive symptomatic treatment. If concomitant use of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules with other serotonergic drugs or CYP2D6 inhibitors is clinically warranted, initiate lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules with lower doses, monitor patients for the emergence of serotonin syndrome during drug initiation or titration, and inform patients of the increased risk for serotonin syndrome.
)]- Motor and Verbal Tics, and Worsening of Tourette’s Syndrome
[see Warnings andPrecautions (5.8 Motor and Verbal Tics, and Worsening of Tourette’s SyndromeCNS stimulants, including amphetamine, have been associated with the onset or exacerbation of motor and verbal tics. Worsening of Tourette’s syndrome has also been reported[see AdverseReactions ].Before initiating lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules, assess the family history and clinically evaluate patients for tics or Tourette’s syndrome. Regularly monitor lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules-treated patients for the emergence or worsening of tics or Tourette’s syndrome, and discontinue treatment if clinically appropriate.)]
Lisdexamfetamine Dimesylate Capsules, a CNS stimulant, is for once-a-day oral administration. The chemical designation for lisdexamfetamine dimesylate is (2S)-2,6-diamino-
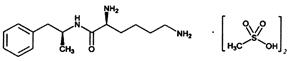
Lisdexamfetamine dimesylate is a white to off-white powder that is soluble in water (792 mg/mL).
Lisdexamfetamine is a prodrug of dextroamphetamine. Amphetamines are non-catecholamine sympathomimetic amines with CNS stimulant activity. The exact mode of therapeutic action in ADHD and BED is not known.