Lofexidine Hydrochloride
Lofexidine Hydrochloride Prescribing Information
Lofexidine tablets are indicated for mitigation of opioid withdrawal symptoms to facilitate abrupt opioid discontinuation in adults.
Lofexidine tablets are available as round, peach-colored, film-coated tablets, imprinted with "LFX" on one side and "18" on the other side. Each tablet contains 0.18 mg lofexidine (equivalent to 0.2 mg of lofexidine hydrochloride).
None.
The following serious adverse reactions are described elsewhere in labeling:
- Hypotension, Bradycardia, and Syncope [see]
5.1 Risk of Hypotension, Bradycardia, and SyncopeLofexidine tablets can cause a decrease in blood pressure, a decrease in pulse, and syncope
[see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. Monitor vital signs before dosing. Monitor symptoms related to bradycardia and orthostasis.Patients being given Lofexidine tablets in an outpatient setting should be capable of and instructed on self-monitoring for hypotension, orthostasis, bradycardia, and associated symptoms. If clinically significant or symptomatic hypotension and/or bradycardia occur, the next dose of Lofexidine tablets should be reduced in amount, delayed, or skipped.
Inform patients that Lofexidine tablets may cause hypotension and that patients moving from a supine to an upright position may be at increased risk for hypotension and orthostatic effects. Instruct patients to stay hydrated, on how to recognize symptoms of low blood pressure, and on how to reduce the risk of serious consequences should hypotension occur (e.g., sit or lie down, carefully rise from a sitting or lying position). Instruct outpatients to withhold Lofexidine tablets doses when experiencing symptoms of hypotension or bradycardia and to contact their healthcare provider for guidance on how to adjust dosing.
Avoid using Lofexidine tablets in patients with severe coronary insufficiency, recent myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular disease, chronic renal failure, and in patients with marked bradycardia.
Avoid using Lofexidine tablets in combination with medications that decrease pulse or blood pressure to avoid the risk of excessive bradycardia and hypotension.
- QT Prolongation [see]
5.2 Risk of QT ProlongationLofexidine tablets prolong the QT interval.
Avoid using Lofexidine tablets in patients with congenital long QT syndrome.
Monitor ECG in patients with congestive heart failure, bradyarrhythmias, hepatic impairment, renal impairment, or patients taking other medicinal products that lead to QT prolongation (e.g., methadone). In patients with electrolyte abnormalities (e.g., hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia), correct these abnormalities first, and monitor ECG upon initiation of Lofexidine tablets
[see Dosing and Administration (2.1), Adverse Reactions (6.1), Special Populations (8.6, 8.7), Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. - Central Nervous System Depression [see]
5.3 Increased Risk of Central Nervous System Depression with Concomitant use of CNS Depressant DrugsLofexidine tablets potentiate the CNS depressive effects of benzodiazepines and can also be expected to potentiate the CNS depressive effects of alcohol, barbiturates, and other sedating drugs. Advise patients to inform their healthcare provider of other medications they are taking, including alcohol.
Advise patients using Lofexidine tablets in an outpatient setting that, until they learn how they respond to Lofexidine tablets, they should be careful or avoid doing activities such as driving or operating heavy machinery.
- Opioid Overdose [see]
5.4 Increased Risk of Opioid Overdose after Opioid DiscontinuationLofexidine tablets are not a treatment for opioid use disorder. Patients who complete opioid discontinuation are likely to have a reduced tolerance to opioids and are at increased risk of fatal overdose should they resume opioid use. Use Lofexidine tablets in patients with opioid use disorder only in conjunction with a comprehensive management program for the treatment of opioid use disorder and inform patients and caregivers of this increased risk of overdose.
- Discontinuation Symptoms [see]
5.5 Risk of Discontinuation SymptomsStopping Lofexidine tablets abruptly can cause a marked rise in blood pressure. Symptoms including diarrhea, insomnia, anxiety, chills, hyperhidrosis, and extremity pain have also been observed with Lofexidine tablets discontinuation. Instruct patients not to discontinue therapy without consulting their healthcare provider. When discontinuing therapy with Lofexidine tablets, gradually reduce the dose
[see Dosing and Administration (2.1)].Symptoms related to discontinuation can be managed by administration of the previous Lofexidine tablet dose and subsequent taper.
Lofexidine tablets contain lofexidine, a central alpha-2 adrenergic agonist, as the hydrochloride salt. Lofexidine hydrochloride is chemically designated as 2-[1-(2,6-dichlorophenoxy)ethyl]-4,5 dihydro-1
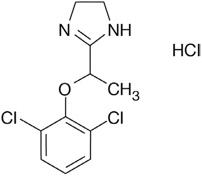
Lofexidine hydrochloride is a white to off-white crystalline powder freely soluble in water, methanol, and ethanol. It is slightly soluble in chloroform and practically insoluble in n-hexane and benzene.
Lofexidine tablets are available as round, convex-shaped, peach-colored, film-coated tablets for oral administration. Each tablet contains 0.18 lofexidine, equivalent to 0.2 mg of lofexidine hydrochloride, and the following inactive ingredients: 92.6 mg lactose, 12.3 mg citric acid, 1.1 mg povidone, 5.7 mg microcrystalline cellulose, 1.4 mg calcium stearate, 0.7 mg sodium lauryl sulphate, and Opadry OY S 9480 (contains indigo carmine and sunset yellow).
Two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials supported the efficacy of lofexidine.