Md Gastroview
(Diatrizoate Meglumine And Diatrizoate Sodium)Md Gastroview Prescribing Information
MD-Gastroview (Diatrizoate Meglumine and Diatrizoate Sodium Solution) is indicated for radiographic examination of segments of the gastrointestinal tract (esophagus, stomach, proximal small intestine, and colon). The preparation is particularly indicated when a more viscous agent such as barium sulfate, which is not water-soluble, is not feasible or is potentially dangerous.
MD-Gastroview may also be used as an adjunct to contrast enhancement in computed tomography of the torso (body imaging); the preparation is indicated, in conjunction with intravenous administration of a radiopaque contrast agent, when unenhanced imaging may not provide sufficient definition in distinguishing normal loops of bowel from adjacent organs or areas of suspected pathology.
The routine preparatory measures employed for barium studies are also appropriate for this agent.
For pediatric and severely cachectic patients, the maintenance of an intravenous fluid line may be advisable.
Do not administer to patients with a known hypersensitivity to MD-Gastroview or any of its components.
Most adverse reactions to enteral diagnostic radiopaque agents are mild and transitory. Nausea, vomiting and/or diarrhea, urticaria with erythema, hypoxia, acute dyspnea, tachyarrhythmia, and anaphylaxis have occurred following ingestion of the contrast medium, particularly when high concentrations or large volumes of solution are administered. Severe changes in serum osmolarity and electrolyte concentrations may produce shock-like states (
MD-Gastroview (Diatrizoate Meglumine and Diatrizoate Sodium Solution) is a palatable lemon-vanilla flavored water-soluble iodinated radiopaque contrast medium for oral or rectal administration only. Each mL contains 660 mg diatrizoate meglumine and 100 mg diatrizoate sodium; pH has been adjusted to 6.0 to 7.6 with sodium hydroxide. Each mL contains approximately 4.8 mg (0.21 mEq) sodium and 367 mg organically bound iodine. MD-Gastroview does not contain the wetting agent polysorbate 80.
The inactive ingredients are: Edetate Disodium Dihydrate, Lemon-Vanilla Flavor, Sodium Citrate, Sodium Hydroxide, Sodium Saccharin, Water for Injection. Air in the container is displaced with nitrogen.
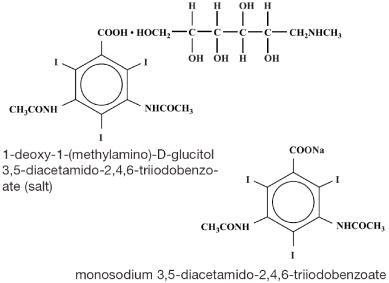
Diatrizoate meglumine is designated chemically as 1-deoxy-1-(methylamino)-D-glucitol 3,5-diacetamido-2,4,6-triiodobenzoate (salt); diatrizoate sodium is monosodium 3,5-diacetamido-2,4,6-triiodobenzoate. The two salts have the following structural formulae:
The most important characteristic of contrast media is the iodine content. The relatively high atomic weight of iodine contributes sufficient radiodensity for radiographic contrast with surrounding tissues.
Diagnostic enteral radiopaque agents have few known pharmacological effects. Diatrizoate meglumine and diatrizoate sodium exert a mild laxative effect attributable to their high osmolarity.
Diatrizoate meglumine and diatrizoate sodium are sparingly absorbed from the intact gastrointestinal tract, and therefore permit gastrointestinal opacification and delineation after oral or rectal administration. Oral administration is used for radiographic evaluation of the esophagus, stomach and proximal small intestine. Rectal administration is used for examination of the colon; however, visualization of the distal small bowel is generally unsatisfactory, since the hypertonicity of the medium causes intraluminal diffusion of water with subsequent dilution of the medium. Enough absorption from the gastrointestinal tract to permit incidental visualization of the urinary tract has been reported; this should also be considered when thyroid testing is being contemplated, since iodine-mediated thyrotropic effects may occur (
Diagnostic procedures which involve the use of radiopaque contrast agents should be carried out under the direction of personnel with the prerequisite training and with a thorough knowledge of the particular procedure to be performed. Appropriate facilities should be available for coping with any complication of administration, as well as for treatment of reaction to the contrast medium (
Rectal administration of undiluted MD-Gastroview in any patient, particularly with large doses and/or in those with overdistention, has been reported to be associated with mucosal irritation.
Cases of hyperthyroidism have been reported with the use of oral contrast media. Some of these patients reportedly had multinodular goiters which may have been responsible for the increased hormone synthesis in response to excess iodine. Administration of an intravascular iodinated radiopaque diagnostic agent to a hyperthyroid patient precipitated thyroid storm; a similar situation could follow administration of oral preparations of iodides. Therefore, caution should be exercised when administering enteral gastrointestinal radiopaque agents to hyperthyroid and euthyroid goiterous patients.
Consideration should be given to the potential for precipitation of water-soluble contrast agents under conditions that may promote hyperacidity (i.e., fasting, emotional upset, or stress). Harmful effects directly attributable to precipitate formation have not been reported. However, the possibility of interpreting the precipitate radiologically as an anatomical abnormality (i.e., ulceration of the stomach or small intestine) or injury, should be kept in mind.
Patients should receive the following information and instructions:
- This drug has been prescribed to perform an X-ray of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Inform the physician if pregnant or if allergic to iodine, any foods, or X-ray materials.
- The iodine in diatrizoate salts may interfere with some thyroid tests if these are needed in the future. Inform the attending physician at that time about this gastrointestinal study.
- This drug may cause abdominal cramping, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, skin rashes, itching, heartburn, dizziness, or headache in some patients, but most reactions are mild and pass quickly.
The results of protein bound iodine (PBI) and radioactive iodine uptake studies, which depend on iodine estimations, will not accurately reflect thyroid function for six months, and possibly as long as one year, following the administration of diagnostic enteral radiopaque media.
Thyroid function tests, if indicated, generally should be performed prior to the administration of any iodinated agent. However, thyroid function can be evaluated after use of these agents by using T3resin uptake and total or free thyroxine (T4) assays, which are not dependent on iodine estimations.
Small quantities of contrast medium in the intestinal tract may cause false low trypsin values when determined spectrophotometrically. Therefore, duodenal instillation should not precede pancreatic function tests involving spectrophotometric trypsin assays.
Any test which might be affected by contrast media should be performed prior to administration of the contrast medium.
Long-term studies in animals have not been performed to evaluate carcinogenic or mutagenic potential, or possible impairment of fertility in males or females.
When administered intravenously, diatrizoate salts cross the placenta and are evenly distributed in fetal tissues.
No teratogenic effects attributable to diatrizoate meglumine or diatrizoate sodium have been observed in teratology studies performed in animals. There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because small amounts of these agents may be absorbed, and animal teratology studies are not always predictive of human response, these agents should be used during pregnancy only when clearly needed.
Procedures including radiation involve a certain risk related to the exposure of the fetus.
Diatrizoate meglumine is excreted in breast milk following intravascular administration.
Because small amounts of enteral gastrointestinal radiopaque agents may be absorbed following oral or rectal administration, caution should be exercised when they are administered to a nursing woman.
See WARNINGS, and PRECAUTIONS, General.
Local injury to the colonic mucosa, particularly in the presence of underlying disease which interferes with intestinal viability, has been reported in cases where recommended doses and dilutions (