Mesalamine Rectal
(Mesalamine)Mesalamine Rectal Prescribing Information
| • Warnings and Precautions | |
Renal Impairment (Renal impairment, including minimal change disease, acute and chronic interstitial nephritis, and renal failure, has been reported in patients given products such as Mesalamine Rectal Suppositories that contain mesalamine or are converted to mesalamine. In animal studies, the kidney was the principal organ of mesalamine toxicity [see Adverse Reactions (6.2), Nonclinical Toxicology (13.2)] .Evaluate renal function prior to initiation of Mesalamine Rectal Suppositories and periodically while on therapy. Evaluate the risks and benefits of using Mesalamine Rectal Suppositories in patients with known renal impairment or a history of renal disease or taking concomitant nephrotoxic drugs. Discontinue Mesalamine if renal function deteriorates while on therapy. [see Drug Interactions (7.1), Use in Specific Populations (8.6)] . | 11/2022 |
Mesalamine Rectal Suppositories are indicated in adults for the treatment of mildly to moderately active ulcerative proctitis.
The recommended dosage of Mesalamine Rectal Suppositories in adults is 1000 mg administered rectally once daily at bedtime for 3 to 6 weeks depending on symptoms and sigmoidoscopic findings. Safety and effectiveness of Mesalamine Rectal Suppositories beyond 6 weeks have not been established.
- Evaluate renal function prior to initiation of Mesalamine Rectal Suppository therapy [see.]
5.1 Renal ImpairmentRenal impairment, including minimal change disease, acute and chronic interstitial nephritis, and renal failure, has been reported in patients given products such as Mesalamine Rectal Suppositories that contain mesalamine or are converted to mesalamine. In animal studies, the kidney was the principal organ of mesalamine toxicity
[see Adverse Reactions (6.2), Nonclinical Toxicology (13.2)].Evaluate renal function prior to initiation of Mesalamine Rectal Suppositories and periodically while on therapy.
Evaluate the risks and benefits of using Mesalamine Rectal Suppositories in patients with known renal impairment or a history of renal disease or taking concomitant nephrotoxic drugs. Discontinue Mesalamine if renal function deteriorates while on therapy.[see Drug Interactions (7.1), Use in Specific Populations (8.6)]. - Do not cut or break the suppository.
- Retain the suppository for one to three hours or longer, if possible.
- Drink an adequate amount of fluids [see]
5.7 NephrolithiasisCases of nephrolithiasis have been reported with the use of mesalamine, including stones of 100% mesalamine content. Mesalamine-containing stones are radiotransparent and undetectable by standard radiography or computed tomography (CT). Ensure adequate hydration during treatment with Mesalamine Rectal Suppositories.
- If a dose of Mesalamine Rectal Suppositories is missed, administer as soon as possible, unless it is almost time for next dose. Do not use two Mesalamine Rectal Suppositories at the same time to make up for a missed dose.
- Mesalamine Rectal Suppositories will cause staining of direct contact surfaces, including but not limited to fabrics, flooring, painted surfaces, marble, granite, vinyl, and enamel. Keep Mesalamine Rectal Suppositories away from these surfaces to prevent staining.
Mesalamine Rectal Suppository: 1000 mg mesalamine in a torpedo shaped, white to beige suppository.
Clinical trials of Mesalamine Rectal Suppositories did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 years and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients. Reports from uncontrolled clinical studies and postmarketing reporting systems suggested a higher incidence of blood dyscrasias (i.e., agranulocytosis, neutropenia and pancytopenia) in patients receiving mesalamine-containing products such as Mesalamine Rectal Suppositories who were 65 years or older compared to younger patients. Monitor complete blood cell counts and platelet counts in elderly patients during treatment with Mesalamine Rectal Suppositories. In general, consider the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concurrent disease or other drug therapy in elderly patients when prescribing Mesalamine Rectal Suppositories
Mesalamine Rectal Suppositories are contraindicated in patients with known or suspected hypersensitivity to salicylates or aminosalicylates or to any ingredients in the suppository vehicle
Hypersensitivity reactions have been reported in patients taking sulfasalazine. Some patients may have a similar reaction to Mesalamine Rectal Suppositories or to other compounds that contain or are converted to mesalamine.
As with sulfasalazine, mesalamine-induced hypersensitivity reactions may present as internal organ involvement, including myocarditis, pericarditis, nephritis, hepatitis, pneumonitis and hematologic abnormalities. Evaluate patients immediately if signs or symptoms of a hypersensitivity reaction are present. Discontinue Mesalamine Rectal Suppositories if an alternative etiology for the signs and symptoms cannot be established.
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of Mesalamine Rectal Suppositories or other mesalamine-containing products. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Body as a Whole:drug fever, fatigue, lupus-like syndrome, medication residue
- Cardiac Disorders:myocarditis, pericarditis, pericardial effusion[see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Endocrine:Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus
- Eye disorders:eye swelling
- Gastrointestinal Disorders:abdominal cramps, abdominal distension, anal pruritus, anorectal discomfort, constipation, feces discolored, flatulence, frequent bowel movements, gastrointestinal bleeding, mucus stools, nausea, painful defecation, pancreatitis, proctalgia, rectal discharge, rectal tenesmus, stomach discomfort, vomiting
- Hepatic Disorders:cholestatic jaundice, hepatitis, jaundice, Kawasaki-like syndrome including changes in liver enzymes, liver necrosis, liver failure
- Hematologic Disorders:agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, thrombocytopenia
- Neurological/Psychiatric Disorders:Guillain-Barre syndrome, peripheral neuropathy, transverse myelitis, intracranial hypertension
- Renal Disorders:interstitial nephritis, renal failure, minimal change disease, nephrolithiasis[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.7)]
- Urine discoloration occurring ex-vivo caused by contact of mesalamine, including inactive metabolite, with surfaces or water treated with hypochlorite containing bleach
- Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders:hypersensitivity pneumonitis (including allergic alveolitis, eosinophilic pneumonitis, interstitial pneumonitis), pleuritis/pleurisy
- Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorder:alopecia, erythema, erythema nodosum, pruritus, psoriasis, pyoderma gangrenosum, urticaria, SJS/TEN, DRESS and AGEP[see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Urogenital:reversible oligospermia
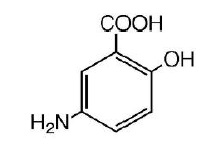
The active ingredient in Mesalamine Rectal Suppository 1000 mg suppositories for rectal use is mesalamine, also known as mesalazine or 5- aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA). Chemically, mesalamine is 5-amino-2-hydroxybenzoic acid, and is classified as an aminosalicylate. Each Mesalamine Rectal Suppository contains 1000 mg of mesalamine (USP) in a base of Hard Fat, NF.
The empirical formula is C7H7NO3, representing a molecular weight of 153.14. The structural formula is:
 |
