Methylergonovine Maleate
Methylergonovine Maleate Prescribing Information
Following delivery of the placenta, for routine management of uterine atony, hemorrhage and subinvolution of the uterus. For control of uterine hemorrhage in the second stage of labor following delivery of the anterior shoulder.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration.
One tablet, 0.2 mg, 3 or 4 times daily in the puerperium for a maximum of 1 week.
Hypertension; toxemia; pregnancy; and hypersensitivity.
The most common adverse reaction is hypertension associated in several cases with seizure and/or headache. Hypotension has also been reported. Abdominal pain (caused by uterine contractions), nausea and vomiting have occurred occasionally. Rarely observed reactions have included: acute myocardial infarction, transient chest pains, vasoconstriction, vasospasm, coronary arterial spasm, bradycardia, tachycardia, dyspnea, hematuria, thrombophlebitis, water intoxication, hallucinations, leg cramps, dizziness, tinnitus, nasal congestion, diarrhea, diaphoresis, palpitation, rash, and foul taste.
There have been rare isolated reports of anaphylaxis, without a proven causal relationship to the drug product.
The following adverse drug reactions have been derived from post-marketing experience with methylergonovine maleate via spontaneous case reports. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not possible to reliably estimate their frequency which is therefore categorized as not known.
Cerebrovascular accident, paraesthesia
Ventricular fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, angina pectoris, atrioventricular block
There have been rare reports of serious adverse events in connection with the coadministration of certain ergot alkaloid drugs (e.g., dihydroergotamine and ergotamine) and potent CYP 3A4 inhibitors, resulting in vasospasm leading to cerebral ischemia and/or ischemia of the extremities. Although there have been no reports of such interactions with methylergonovine alone, potent CYP 3A4 inhibitors should not be coadministered with methylergonovine. Examples of some of the more potent CYP 3A4 inhibitors include macrolide antibiotics (e.g., erythromycin, troleandomycin, clarithromycin), HIV protease or reverse transcriptase inhibitors (e.g., ritonavir, indinavir, nelfinavir, delavirdine) or azole antifungals (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole, voriconazole). Less potent CYP 3A4 inhibitors should be administered with caution. Less potent inhibitors include saquinavir, nefazodone, fluconazole, grapefruit juice, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, zileuton, and clotrimazole. These lists are not exhaustive, and the prescriber should consider the effects on CYP 3A4 of other agents being considered for concomitant use with methylergonovine.
Drugs (e.g. nevirapine, rifampicin) that are strong inducers of CYP3A4 are likely to decrease the pharmacological action of methylergonovine maleate.
Caution should be exercised when methylergonovine maleate is used concurrently with beta-blockers. Concomitant administration with beta-blockers may enhance the vasoconstrictive action of ergot alkaloids.
Anesthetics like halothan and methoxyfluran may reduce the oxytocic potency of methylergonovine maleate.
Methylergonovine maleate produces vasoconstriction and can be expected to reduce the effect of glyceryl trinitrate and other antianginal drugs.
No pharmacokinetic interactions involving other cytochrome P450 isoenzymes are known.
Caution should be exercised when methylergonovine maleate is used concurrently with other vasoconstrictors, ergot alkaloids, or prostaglandins.
Methylergonovine maleate is a semi-synthetic ergot alkaloid used for the prevention and control of postpartum hemorrhage.
Methylergonovine maleate is available in tablets for oral ingestion containing 0.2 mg methylergonovine maleate.
Active Ingredient: methylergonovine maleate USP, 0.2 mg. Inactive Ingredients: acacia, gelatin, lactose monohydrate, methylparaben, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone, propylparaben, corn starch, stearic acid, and tartaric acid.
Chemically, methylergonovine maleate is designated as ergoline-8-carboxamide, 9,10-didehydro-
Its structural formula is
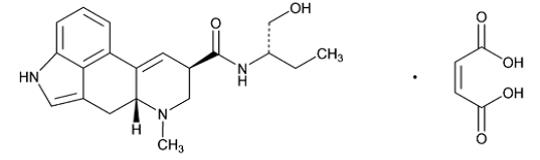
C20H25N3O2·C4H4O4 M.W. 455.50
FDA approved dissolution test specifications differ from USP.