Midazolam
(Midazolam Hydrochloride)Midazolam Prescribing Information
Midazolam injection is indicated:
• intramuscularly or intravenously for preoperative sedation/anxiolysis/amnesia;• intravenously as an agent for sedation/anxiolysis/amnesia prior to or during diagnostic, therapeutic or endoscopic procedures, such as bronchoscopy, gastroscopy, cystoscopy, coronary angiography, cardiac catheterization, oncology procedures, radiologic procedures, suture of lacerations and other procedures either alone or in combination with other CNS depressants;• intravenously for induction of general anesthesia, before administration of other anesthetic agents. With the use of narcotic premedication, induction of anesthesia can be attained within a relatively narrow dose range and in a short period of time. Intravenous midazolam can also be used as a component of intravenous supplementation of nitrous oxide and oxygen (balanced anesthesia);• continuous intravenous infusion for sedation of intubated and mechanically ventilated patients as a component of anesthesia or during treatment in a critical care setting.
Prior to the intravenous administration of midazolam in any dose, the immediate availability of oxygen, resuscitative drugs, age- and size-appropriate equipment for bag/valve/mask ventilation and intubation, and skilled personnel for the maintenance of a patent airway and support of ventilation should be ensured. Patients should be continuously monitored for early signs of hypoventilation, airway obstruction, or apnea, with means readily available (e.g., pulse oximetry). Hypoventilation, airway obstruction, and apnea can lead to hypoxia and/or cardiac arrest unless effective countermeasures are taken immediately. The immediate availability of specific reversal agents (flumazenil) is highly recommended. Vital signs should continue to be monitored during the recovery period. Because intravenous midazolam can depress respiration (see
Concomitant use of benzodiazepines, including midazolam, and opioids may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death. If a decision is made to use midazolam concomitantly with opioids, monitor patients closely for respiratory depression and sedation (see
Serious cardiorespiratory adverse events have occurred after administration of midazolam. These have included respiratory depression, airway obstruction, oxygen desaturation, apnea, respiratory arrest and/or cardiac arrest, sometimes resulting in death or permanent neurologic injury. There have also been rare reports of hypotensive episodes requiring treatment during or after diagnostic or surgical manipulations particularly in adult or pediatric patients with hemodynamic instability. Hypotension occurred more frequently in the sedation studies in patients premedicated with a narcotic.
Midazolam must never be used without individualization of dosage particularly when used with other medications capable of producing central nervous system depression.
See
Reactions such as agitation, involuntary movements (including tonic/clonic movements and muscle tremor), hyperactivity and combativeness have been reported in both adult and pediatric patients. These reactions may be due to inadequate or excessive dosing or improper administration of midazolam; however, consideration should be given to the possibility of cerebral hypoxia or true paradoxical reactions. Should such reactions occur, the response to each dose of midazolam and all other drugs, including local anesthetics, should be evaluated before proceeding. Reversal of such responses with flumazenil has been reported in pediatric patients.
Concomitant use of barbiturates, alcohol or other central nervous system depressants may increase the risk of hypoventilation, airway obstruction, desaturation, or apnea and may contribute to profound and/or prolonged drug effect. Narcotic premedication also depresses the ventilatory response to carbon dioxide stimulation.
Higher risk adult and pediatric surgical patients, elderly patients and debilitated adult and pediatric patients require lower dosages, whether or not concomitant sedating medications have been administered. Adult or pediatric patients with COPD are unusually sensitive to the respiratory depressant effect of midazolam. Pediatric and adult patients undergoing procedures involving the upper airway such as upper endoscopy or dental care, are particularly vulnerable to episodes of desaturation and hypoventilation due to partial airway obstruction. Adult and pediatric patients with chronic renal failure and patients with congestive heart failure eliminate midazolam more slowly (see
Injectable midazolam should not be administered to adult or pediatric patients in shock or coma, or in acute alcohol intoxication with depression of vital signs. Particular care should be exercised in the use of intravenous midazolam in adult or pediatric patients with uncompensated acute illnesses, such as severe fluid or electrolyte disturbances.
There have been limited reports of intra-arterial injection of midazolam. Adverse events have included local reactions, as well as isolated reports of seizure activity in which no clear causal relationship was established. Precautions against unintended intra-arterial injection should be taken. Extravasation should also be avoided.
The safety and efficacy of midazolam following nonintravenous and nonintramuscular routes of administration have not been established. Midazolam should only be administered intramuscularly or intravenously.
Midazolam is associated with a high incidence of partial or complete impairment of recall for the next several hours. The decision as to when patients who have received injectable midazolam, particularly on an outpatient basis, may again engage in activities requiring complete mental alertness, operate hazardous machinery or drive a motor vehicle must be individualized. Gross tests of recovery from the effects of midazolam (see
Use of midazolam late in pregnancy can result in sedation (respiratory depression, lethargy, hypotonia) and/or withdrawal symptoms (hyperreflexia, irritability, restlessness, tremors, inconsolable crying, and feeding difficulties) in the neonate (see
Exposure to excessive amounts of benzyl alcohol has been associated with toxicity (hypotension, metabolic acidosis), particularly in neonates, and an increased incidence of kernicterus, particularly in small preterm infants. There have been rare reports of deaths, primarily in preterm infants, associated with exposure to excessive amounts of benzyl alcohol. The amount of benzyl alcohol from medications is usually considered negligible compared to that received in flush solutions containing benzyl alcohol. Administration of high dosages of medications (including midazolam) containing this preservative must take into account the total amount of benzyl alcohol administered. The recommended dosage range of midazolam for preterm and term infants includes amounts of benzyl alcohol well below that associated with toxicity; however, the amount of benzyl alcohol at which toxicity may occur is not known. If the patient requires more than the recommended dosages or other medications containing this preservative, the practitioner must consider the daily metabolic load of benzyl alcohol from these combined sources (see
Some published studies in children suggest that similar deficits may occur after repeated or prolonged exposures to anesthetic agents early in life and may result in adverse cognitive or behavioral effects. These studies have substantial limitations, and it is not clear if the observed effects are due to the anesthetic/sedation drug administration or other factors such as the surgery or underlying illness.
Anesthetic and sedation drugs are a necessary part of the care of children needing surgery, other procedures, or tests that cannot be delayed, and no specific medications have been shown to be safer than any other. Decisions regarding the timing of any elective procedures requiring anesthesia should take into consideration the benefits of the procedure weighed against the potential risks.
Concomitant use of benzodiazepines and opioids may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death. Monitor patients for respiratory depression and sedation (see
Midazolam must never be used without individualization of dosage. The initial intravenous dose for sedation in adult patients may be as little as 1 mg, but should not exceed 2.5 mg in a normal healthy adult. Lower doses are necessary for older (over 60 years) or debilitated patients and in patients receiving concomitant narcotics or other central nervous system (CNS) depressants. The initial dose and all subsequent doses should always be titrated slowly; administer over at least 2 minutes and allow an additional 2 or more minutes to fully evaluate the sedative effect. The use of the 1 mg/mL formulation or dilution of the 1 mg/mL or 5 mg/mL formulation is recommended to facilitate slower injection. Doses of sedative medications in pediatric patients must be calculated on a mg/kg basis, and initial doses and all subsequent doses should always be titrated slowly. The initial pediatric dose of midazolam for sedation/anxiolysis/amnesia is age, procedure, and route dependent (see
Prior to the intravenous administration of midazolam in any dose, the immediate availability of oxygen, resuscitative drugs, age- and size-appropriate equipment for bag/valve/mask ventilation and intubation, and skilled personnel for the maintenance of a patent airway and support of ventilation should be ensured. Patients should be continuously monitored for early signs of hypoventilation, airway obstruction, or apnea, with means readily available (e.g., pulse oximetry). Hypoventilation, airway obstruction, and apnea can lead to hypoxia and/or cardiac arrest unless effective countermeasures are taken immediately. The immediate availability of specific reversal agents (flumazenil) is highly recommended. Vital signs should continue to be monitored during the recovery period. Because intravenous midazolam can depress respiration (see
Concomitant use of benzodiazepines, including midazolam, and opioids may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death. If a decision is made to use midazolam concomitantly with opioids, monitor patients closely for respiratory depression and sedation (see
Serious cardiorespiratory adverse events have occurred after administration of midazolam. These have included respiratory depression, airway obstruction, oxygen desaturation, apnea, respiratory arrest and/or cardiac arrest, sometimes resulting in death or permanent neurologic injury. There have also been rare reports of hypotensive episodes requiring treatment during or after diagnostic or surgical manipulations particularly in adult or pediatric patients with hemodynamic instability. Hypotension occurred more frequently in the sedation studies in patients premedicated with a narcotic.
Midazolam must never be used without individualization of dosage particularly when used with other medications capable of producing central nervous system depression.
See
Reactions such as agitation, involuntary movements (including tonic/clonic movements and muscle tremor), hyperactivity and combativeness have been reported in both adult and pediatric patients. These reactions may be due to inadequate or excessive dosing or improper administration of midazolam; however, consideration should be given to the possibility of cerebral hypoxia or true paradoxical reactions. Should such reactions occur, the response to each dose of midazolam and all other drugs, including local anesthetics, should be evaluated before proceeding. Reversal of such responses with flumazenil has been reported in pediatric patients.
Concomitant use of barbiturates, alcohol or other central nervous system depressants may increase the risk of hypoventilation, airway obstruction, desaturation, or apnea and may contribute to profound and/or prolonged drug effect. Narcotic premedication also depresses the ventilatory response to carbon dioxide stimulation.
Higher risk adult and pediatric surgical patients, elderly patients and debilitated adult and pediatric patients require lower dosages, whether or not concomitant sedating medications have been administered. Adult or pediatric patients with COPD are unusually sensitive to the respiratory depressant effect of midazolam. Pediatric and adult patients undergoing procedures involving the upper airway such as upper endoscopy or dental care, are particularly vulnerable to episodes of desaturation and hypoventilation due to partial airway obstruction. Adult and pediatric patients with chronic renal failure and patients with congestive heart failure eliminate midazolam more slowly (see
Injectable midazolam should not be administered to adult or pediatric patients in shock or coma, or in acute alcohol intoxication with depression of vital signs. Particular care should be exercised in the use of intravenous midazolam in adult or pediatric patients with uncompensated acute illnesses, such as severe fluid or electrolyte disturbances.
There have been limited reports of intra-arterial injection of midazolam. Adverse events have included local reactions, as well as isolated reports of seizure activity in which no clear causal relationship was established. Precautions against unintended intra-arterial injection should be taken. Extravasation should also be avoided.
The safety and efficacy of midazolam following nonintravenous and nonintramuscular routes of administration have not been established. Midazolam should only be administered intramuscularly or intravenously.
Midazolam is associated with a high incidence of partial or complete impairment of recall for the next several hours. The decision as to when patients who have received injectable midazolam, particularly on an outpatient basis, may again engage in activities requiring complete mental alertness, operate hazardous machinery or drive a motor vehicle must be individualized. Gross tests of recovery from the effects of midazolam (see
Use of midazolam late in pregnancy can result in sedation (respiratory depression, lethargy, hypotonia) and/or withdrawal symptoms (hyperreflexia, irritability, restlessness, tremors, inconsolable crying, and feeding difficulties) in the neonate (see
Exposure to excessive amounts of benzyl alcohol has been associated with toxicity (hypotension, metabolic acidosis), particularly in neonates, and an increased incidence of kernicterus, particularly in small preterm infants. There have been rare reports of deaths, primarily in preterm infants, associated with exposure to excessive amounts of benzyl alcohol. The amount of benzyl alcohol from medications is usually considered negligible compared to that received in flush solutions containing benzyl alcohol. Administration of high dosages of medications (including midazolam) containing this preservative must take into account the total amount of benzyl alcohol administered. The recommended dosage range of midazolam for preterm and term infants includes amounts of benzyl alcohol well below that associated with toxicity; however, the amount of benzyl alcohol at which toxicity may occur is not known. If the patient requires more than the recommended dosages or other medications containing this preservative, the practitioner must consider the daily metabolic load of benzyl alcohol from these combined sources (see
Some published studies in children suggest that similar deficits may occur after repeated or prolonged exposures to anesthetic agents early in life and may result in adverse cognitive or behavioral effects. These studies have substantial limitations, and it is not clear if the observed effects are due to the anesthetic/sedation drug administration or other factors such as the surgery or underlying illness.
Anesthetic and sedation drugs are a necessary part of the care of children needing surgery, other procedures, or tests that cannot be delayed, and no specific medications have been shown to be safer than any other. Decisions regarding the timing of any elective procedures requiring anesthesia should take into consideration the benefits of the procedure weighed against the potential risks.
Reactions such as agitation, involuntary movements, hyperactivity and combativeness have been reported in adult and pediatric patients. Should such reactions occur, caution should be exercised before continuing administration of midazolam (see
Prior to the intravenous administration of midazolam in any dose, the immediate availability of oxygen, resuscitative drugs, age- and size-appropriate equipment for bag/valve/mask ventilation and intubation, and skilled personnel for the maintenance of a patent airway and support of ventilation should be ensured. Patients should be continuously monitored for early signs of hypoventilation, airway obstruction, or apnea, with means readily available (e.g., pulse oximetry). Hypoventilation, airway obstruction, and apnea can lead to hypoxia and/or cardiac arrest unless effective countermeasures are taken immediately. The immediate availability of specific reversal agents (flumazenil) is highly recommended. Vital signs should continue to be monitored during the recovery period. Because intravenous midazolam can depress respiration (see
Concomitant use of benzodiazepines, including midazolam, and opioids may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death. If a decision is made to use midazolam concomitantly with opioids, monitor patients closely for respiratory depression and sedation (see
Serious cardiorespiratory adverse events have occurred after administration of midazolam. These have included respiratory depression, airway obstruction, oxygen desaturation, apnea, respiratory arrest and/or cardiac arrest, sometimes resulting in death or permanent neurologic injury. There have also been rare reports of hypotensive episodes requiring treatment during or after diagnostic or surgical manipulations particularly in adult or pediatric patients with hemodynamic instability. Hypotension occurred more frequently in the sedation studies in patients premedicated with a narcotic.
Midazolam must never be used without individualization of dosage particularly when used with other medications capable of producing central nervous system depression.
See
Reactions such as agitation, involuntary movements (including tonic/clonic movements and muscle tremor), hyperactivity and combativeness have been reported in both adult and pediatric patients. These reactions may be due to inadequate or excessive dosing or improper administration of midazolam; however, consideration should be given to the possibility of cerebral hypoxia or true paradoxical reactions. Should such reactions occur, the response to each dose of midazolam and all other drugs, including local anesthetics, should be evaluated before proceeding. Reversal of such responses with flumazenil has been reported in pediatric patients.
Concomitant use of barbiturates, alcohol or other central nervous system depressants may increase the risk of hypoventilation, airway obstruction, desaturation, or apnea and may contribute to profound and/or prolonged drug effect. Narcotic premedication also depresses the ventilatory response to carbon dioxide stimulation.
Higher risk adult and pediatric surgical patients, elderly patients and debilitated adult and pediatric patients require lower dosages, whether or not concomitant sedating medications have been administered. Adult or pediatric patients with COPD are unusually sensitive to the respiratory depressant effect of midazolam. Pediatric and adult patients undergoing procedures involving the upper airway such as upper endoscopy or dental care, are particularly vulnerable to episodes of desaturation and hypoventilation due to partial airway obstruction. Adult and pediatric patients with chronic renal failure and patients with congestive heart failure eliminate midazolam more slowly (see
Injectable midazolam should not be administered to adult or pediatric patients in shock or coma, or in acute alcohol intoxication with depression of vital signs. Particular care should be exercised in the use of intravenous midazolam in adult or pediatric patients with uncompensated acute illnesses, such as severe fluid or electrolyte disturbances.
There have been limited reports of intra-arterial injection of midazolam. Adverse events have included local reactions, as well as isolated reports of seizure activity in which no clear causal relationship was established. Precautions against unintended intra-arterial injection should be taken. Extravasation should also be avoided.
The safety and efficacy of midazolam following nonintravenous and nonintramuscular routes of administration have not been established. Midazolam should only be administered intramuscularly or intravenously.
Midazolam is associated with a high incidence of partial or complete impairment of recall for the next several hours. The decision as to when patients who have received injectable midazolam, particularly on an outpatient basis, may again engage in activities requiring complete mental alertness, operate hazardous machinery or drive a motor vehicle must be individualized. Gross tests of recovery from the effects of midazolam (see
Use of midazolam late in pregnancy can result in sedation (respiratory depression, lethargy, hypotonia) and/or withdrawal symptoms (hyperreflexia, irritability, restlessness, tremors, inconsolable crying, and feeding difficulties) in the neonate (see
Exposure to excessive amounts of benzyl alcohol has been associated with toxicity (hypotension, metabolic acidosis), particularly in neonates, and an increased incidence of kernicterus, particularly in small preterm infants. There have been rare reports of deaths, primarily in preterm infants, associated with exposure to excessive amounts of benzyl alcohol. The amount of benzyl alcohol from medications is usually considered negligible compared to that received in flush solutions containing benzyl alcohol. Administration of high dosages of medications (including midazolam) containing this preservative must take into account the total amount of benzyl alcohol administered. The recommended dosage range of midazolam for preterm and term infants includes amounts of benzyl alcohol well below that associated with toxicity; however, the amount of benzyl alcohol at which toxicity may occur is not known. If the patient requires more than the recommended dosages or other medications containing this preservative, the practitioner must consider the daily metabolic load of benzyl alcohol from these combined sources (see
Some published studies in children suggest that similar deficits may occur after repeated or prolonged exposures to anesthetic agents early in life and may result in adverse cognitive or behavioral effects. These studies have substantial limitations, and it is not clear if the observed effects are due to the anesthetic/sedation drug administration or other factors such as the surgery or underlying illness.
Anesthetic and sedation drugs are a necessary part of the care of children needing surgery, other procedures, or tests that cannot be delayed, and no specific medications have been shown to be safer than any other. Decisions regarding the timing of any elective procedures requiring anesthesia should take into consideration the benefits of the procedure weighed against the potential risks.
Midazolam injection should only be administered intramuscularly or intravenously (see
Prior to the intravenous administration of midazolam in any dose, the immediate availability of oxygen, resuscitative drugs, age- and size-appropriate equipment for bag/valve/mask ventilation and intubation, and skilled personnel for the maintenance of a patent airway and support of ventilation should be ensured. Patients should be continuously monitored for early signs of hypoventilation, airway obstruction, or apnea, with means readily available (e.g., pulse oximetry). Hypoventilation, airway obstruction, and apnea can lead to hypoxia and/or cardiac arrest unless effective countermeasures are taken immediately. The immediate availability of specific reversal agents (flumazenil) is highly recommended. Vital signs should continue to be monitored during the recovery period. Because intravenous midazolam can depress respiration (see
Concomitant use of benzodiazepines, including midazolam, and opioids may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death. If a decision is made to use midazolam concomitantly with opioids, monitor patients closely for respiratory depression and sedation (see
Serious cardiorespiratory adverse events have occurred after administration of midazolam. These have included respiratory depression, airway obstruction, oxygen desaturation, apnea, respiratory arrest and/or cardiac arrest, sometimes resulting in death or permanent neurologic injury. There have also been rare reports of hypotensive episodes requiring treatment during or after diagnostic or surgical manipulations particularly in adult or pediatric patients with hemodynamic instability. Hypotension occurred more frequently in the sedation studies in patients premedicated with a narcotic.
Midazolam must never be used without individualization of dosage particularly when used with other medications capable of producing central nervous system depression.
See
Reactions such as agitation, involuntary movements (including tonic/clonic movements and muscle tremor), hyperactivity and combativeness have been reported in both adult and pediatric patients. These reactions may be due to inadequate or excessive dosing or improper administration of midazolam; however, consideration should be given to the possibility of cerebral hypoxia or true paradoxical reactions. Should such reactions occur, the response to each dose of midazolam and all other drugs, including local anesthetics, should be evaluated before proceeding. Reversal of such responses with flumazenil has been reported in pediatric patients.
Concomitant use of barbiturates, alcohol or other central nervous system depressants may increase the risk of hypoventilation, airway obstruction, desaturation, or apnea and may contribute to profound and/or prolonged drug effect. Narcotic premedication also depresses the ventilatory response to carbon dioxide stimulation.
Higher risk adult and pediatric surgical patients, elderly patients and debilitated adult and pediatric patients require lower dosages, whether or not concomitant sedating medications have been administered. Adult or pediatric patients with COPD are unusually sensitive to the respiratory depressant effect of midazolam. Pediatric and adult patients undergoing procedures involving the upper airway such as upper endoscopy or dental care, are particularly vulnerable to episodes of desaturation and hypoventilation due to partial airway obstruction. Adult and pediatric patients with chronic renal failure and patients with congestive heart failure eliminate midazolam more slowly (see
Injectable midazolam should not be administered to adult or pediatric patients in shock or coma, or in acute alcohol intoxication with depression of vital signs. Particular care should be exercised in the use of intravenous midazolam in adult or pediatric patients with uncompensated acute illnesses, such as severe fluid or electrolyte disturbances.
There have been limited reports of intra-arterial injection of midazolam. Adverse events have included local reactions, as well as isolated reports of seizure activity in which no clear causal relationship was established. Precautions against unintended intra-arterial injection should be taken. Extravasation should also be avoided.
The safety and efficacy of midazolam following nonintravenous and nonintramuscular routes of administration have not been established. Midazolam should only be administered intramuscularly or intravenously.
Midazolam is associated with a high incidence of partial or complete impairment of recall for the next several hours. The decision as to when patients who have received injectable midazolam, particularly on an outpatient basis, may again engage in activities requiring complete mental alertness, operate hazardous machinery or drive a motor vehicle must be individualized. Gross tests of recovery from the effects of midazolam (see
Use of midazolam late in pregnancy can result in sedation (respiratory depression, lethargy, hypotonia) and/or withdrawal symptoms (hyperreflexia, irritability, restlessness, tremors, inconsolable crying, and feeding difficulties) in the neonate (see
Exposure to excessive amounts of benzyl alcohol has been associated with toxicity (hypotension, metabolic acidosis), particularly in neonates, and an increased incidence of kernicterus, particularly in small preterm infants. There have been rare reports of deaths, primarily in preterm infants, associated with exposure to excessive amounts of benzyl alcohol. The amount of benzyl alcohol from medications is usually considered negligible compared to that received in flush solutions containing benzyl alcohol. Administration of high dosages of medications (including midazolam) containing this preservative must take into account the total amount of benzyl alcohol administered. The recommended dosage range of midazolam for preterm and term infants includes amounts of benzyl alcohol well below that associated with toxicity; however, the amount of benzyl alcohol at which toxicity may occur is not known. If the patient requires more than the recommended dosages or other medications containing this preservative, the practitioner must consider the daily metabolic load of benzyl alcohol from these combined sources (see
Some published studies in children suggest that similar deficits may occur after repeated or prolonged exposures to anesthetic agents early in life and may result in adverse cognitive or behavioral effects. These studies have substantial limitations, and it is not clear if the observed effects are due to the anesthetic/sedation drug administration or other factors such as the surgery or underlying illness.
Anesthetic and sedation drugs are a necessary part of the care of children needing surgery, other procedures, or tests that cannot be delayed, and no specific medications have been shown to be safer than any other. Decisions regarding the timing of any elective procedures requiring anesthesia should take into consideration the benefits of the procedure weighed against the potential risks.
Care should be taken to avoid intra-arterial injection or extravasation (see
Prior to the intravenous administration of midazolam in any dose, the immediate availability of oxygen, resuscitative drugs, age- and size-appropriate equipment for bag/valve/mask ventilation and intubation, and skilled personnel for the maintenance of a patent airway and support of ventilation should be ensured. Patients should be continuously monitored for early signs of hypoventilation, airway obstruction, or apnea, with means readily available (e.g., pulse oximetry). Hypoventilation, airway obstruction, and apnea can lead to hypoxia and/or cardiac arrest unless effective countermeasures are taken immediately. The immediate availability of specific reversal agents (flumazenil) is highly recommended. Vital signs should continue to be monitored during the recovery period. Because intravenous midazolam can depress respiration (see
Concomitant use of benzodiazepines, including midazolam, and opioids may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death. If a decision is made to use midazolam concomitantly with opioids, monitor patients closely for respiratory depression and sedation (see
Serious cardiorespiratory adverse events have occurred after administration of midazolam. These have included respiratory depression, airway obstruction, oxygen desaturation, apnea, respiratory arrest and/or cardiac arrest, sometimes resulting in death or permanent neurologic injury. There have also been rare reports of hypotensive episodes requiring treatment during or after diagnostic or surgical manipulations particularly in adult or pediatric patients with hemodynamic instability. Hypotension occurred more frequently in the sedation studies in patients premedicated with a narcotic.
Midazolam must never be used without individualization of dosage particularly when used with other medications capable of producing central nervous system depression.
See
Reactions such as agitation, involuntary movements (including tonic/clonic movements and muscle tremor), hyperactivity and combativeness have been reported in both adult and pediatric patients. These reactions may be due to inadequate or excessive dosing or improper administration of midazolam; however, consideration should be given to the possibility of cerebral hypoxia or true paradoxical reactions. Should such reactions occur, the response to each dose of midazolam and all other drugs, including local anesthetics, should be evaluated before proceeding. Reversal of such responses with flumazenil has been reported in pediatric patients.
Concomitant use of barbiturates, alcohol or other central nervous system depressants may increase the risk of hypoventilation, airway obstruction, desaturation, or apnea and may contribute to profound and/or prolonged drug effect. Narcotic premedication also depresses the ventilatory response to carbon dioxide stimulation.
Higher risk adult and pediatric surgical patients, elderly patients and debilitated adult and pediatric patients require lower dosages, whether or not concomitant sedating medications have been administered. Adult or pediatric patients with COPD are unusually sensitive to the respiratory depressant effect of midazolam. Pediatric and adult patients undergoing procedures involving the upper airway such as upper endoscopy or dental care, are particularly vulnerable to episodes of desaturation and hypoventilation due to partial airway obstruction. Adult and pediatric patients with chronic renal failure and patients with congestive heart failure eliminate midazolam more slowly (see
Injectable midazolam should not be administered to adult or pediatric patients in shock or coma, or in acute alcohol intoxication with depression of vital signs. Particular care should be exercised in the use of intravenous midazolam in adult or pediatric patients with uncompensated acute illnesses, such as severe fluid or electrolyte disturbances.
There have been limited reports of intra-arterial injection of midazolam. Adverse events have included local reactions, as well as isolated reports of seizure activity in which no clear causal relationship was established. Precautions against unintended intra-arterial injection should be taken. Extravasation should also be avoided.
The safety and efficacy of midazolam following nonintravenous and nonintramuscular routes of administration have not been established. Midazolam should only be administered intramuscularly or intravenously.
Midazolam is associated with a high incidence of partial or complete impairment of recall for the next several hours. The decision as to when patients who have received injectable midazolam, particularly on an outpatient basis, may again engage in activities requiring complete mental alertness, operate hazardous machinery or drive a motor vehicle must be individualized. Gross tests of recovery from the effects of midazolam (see
Use of midazolam late in pregnancy can result in sedation (respiratory depression, lethargy, hypotonia) and/or withdrawal symptoms (hyperreflexia, irritability, restlessness, tremors, inconsolable crying, and feeding difficulties) in the neonate (see
Exposure to excessive amounts of benzyl alcohol has been associated with toxicity (hypotension, metabolic acidosis), particularly in neonates, and an increased incidence of kernicterus, particularly in small preterm infants. There have been rare reports of deaths, primarily in preterm infants, associated with exposure to excessive amounts of benzyl alcohol. The amount of benzyl alcohol from medications is usually considered negligible compared to that received in flush solutions containing benzyl alcohol. Administration of high dosages of medications (including midazolam) containing this preservative must take into account the total amount of benzyl alcohol administered. The recommended dosage range of midazolam for preterm and term infants includes amounts of benzyl alcohol well below that associated with toxicity; however, the amount of benzyl alcohol at which toxicity may occur is not known. If the patient requires more than the recommended dosages or other medications containing this preservative, the practitioner must consider the daily metabolic load of benzyl alcohol from these combined sources (see
Some published studies in children suggest that similar deficits may occur after repeated or prolonged exposures to anesthetic agents early in life and may result in adverse cognitive or behavioral effects. These studies have substantial limitations, and it is not clear if the observed effects are due to the anesthetic/sedation drug administration or other factors such as the surgery or underlying illness.
Anesthetic and sedation drugs are a necessary part of the care of children needing surgery, other procedures, or tests that cannot be delayed, and no specific medications have been shown to be safer than any other. Decisions regarding the timing of any elective procedures requiring anesthesia should take into consideration the benefits of the procedure weighed against the potential risks.
Midazolam Injection may be mixed in the same syringe with the following frequently used premedications: morphine sulfate, meperidine, atropine sulfate or scopolamine. Midazolam, at a concentration of 0.5 mg/mL, is compatible with 5% dextrose in water and 0.9% sodium chloride for up to 24 hours and with lactated Ringer's solution for up to 4 hours. Both the 1 mg/mL and 5 mg/mL formulations of midazolam may be diluted with 0.9% sodium chloride or 5% dextrose in water.
Injectable midazolam is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to the drug. Benzodiazepines are contraindicated in patients with acute narrow-angle glaucoma. Benzodiazepines may be used in patients with open-angle glaucoma only if they are receiving appropriate therapy. Measurements of intraocular pressure in patients without eye disease show a moderate lowering following induction with midazolam; patients with glaucoma have not been studied.
Midazolam is not intended for intrathecal or epidural administration due to the presence of the preservative benzyl alcohol in the dosage form. Midazolam injection is contraindicated for use in premature infants because the formulation contains benzyl alcohol (see
Prior to the intravenous administration of midazolam in any dose, the immediate availability of oxygen, resuscitative drugs, age- and size-appropriate equipment for bag/valve/mask ventilation and intubation, and skilled personnel for the maintenance of a patent airway and support of ventilation should be ensured. Patients should be continuously monitored for early signs of hypoventilation, airway obstruction, or apnea, with means readily available (e.g., pulse oximetry). Hypoventilation, airway obstruction, and apnea can lead to hypoxia and/or cardiac arrest unless effective countermeasures are taken immediately. The immediate availability of specific reversal agents (flumazenil) is highly recommended. Vital signs should continue to be monitored during the recovery period. Because intravenous midazolam can depress respiration (see
Concomitant use of benzodiazepines, including midazolam, and opioids may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death. If a decision is made to use midazolam concomitantly with opioids, monitor patients closely for respiratory depression and sedation (see
Serious cardiorespiratory adverse events have occurred after administration of midazolam. These have included respiratory depression, airway obstruction, oxygen desaturation, apnea, respiratory arrest and/or cardiac arrest, sometimes resulting in death or permanent neurologic injury. There have also been rare reports of hypotensive episodes requiring treatment during or after diagnostic or surgical manipulations particularly in adult or pediatric patients with hemodynamic instability. Hypotension occurred more frequently in the sedation studies in patients premedicated with a narcotic.
Midazolam must never be used without individualization of dosage particularly when used with other medications capable of producing central nervous system depression.
See
Reactions such as agitation, involuntary movements (including tonic/clonic movements and muscle tremor), hyperactivity and combativeness have been reported in both adult and pediatric patients. These reactions may be due to inadequate or excessive dosing or improper administration of midazolam; however, consideration should be given to the possibility of cerebral hypoxia or true paradoxical reactions. Should such reactions occur, the response to each dose of midazolam and all other drugs, including local anesthetics, should be evaluated before proceeding. Reversal of such responses with flumazenil has been reported in pediatric patients.
Concomitant use of barbiturates, alcohol or other central nervous system depressants may increase the risk of hypoventilation, airway obstruction, desaturation, or apnea and may contribute to profound and/or prolonged drug effect. Narcotic premedication also depresses the ventilatory response to carbon dioxide stimulation.
Higher risk adult and pediatric surgical patients, elderly patients and debilitated adult and pediatric patients require lower dosages, whether or not concomitant sedating medications have been administered. Adult or pediatric patients with COPD are unusually sensitive to the respiratory depressant effect of midazolam. Pediatric and adult patients undergoing procedures involving the upper airway such as upper endoscopy or dental care, are particularly vulnerable to episodes of desaturation and hypoventilation due to partial airway obstruction. Adult and pediatric patients with chronic renal failure and patients with congestive heart failure eliminate midazolam more slowly (see
Injectable midazolam should not be administered to adult or pediatric patients in shock or coma, or in acute alcohol intoxication with depression of vital signs. Particular care should be exercised in the use of intravenous midazolam in adult or pediatric patients with uncompensated acute illnesses, such as severe fluid or electrolyte disturbances.
There have been limited reports of intra-arterial injection of midazolam. Adverse events have included local reactions, as well as isolated reports of seizure activity in which no clear causal relationship was established. Precautions against unintended intra-arterial injection should be taken. Extravasation should also be avoided.
The safety and efficacy of midazolam following nonintravenous and nonintramuscular routes of administration have not been established. Midazolam should only be administered intramuscularly or intravenously.
Midazolam is associated with a high incidence of partial or complete impairment of recall for the next several hours. The decision as to when patients who have received injectable midazolam, particularly on an outpatient basis, may again engage in activities requiring complete mental alertness, operate hazardous machinery or drive a motor vehicle must be individualized. Gross tests of recovery from the effects of midazolam (see
Use of midazolam late in pregnancy can result in sedation (respiratory depression, lethargy, hypotonia) and/or withdrawal symptoms (hyperreflexia, irritability, restlessness, tremors, inconsolable crying, and feeding difficulties) in the neonate (see
Exposure to excessive amounts of benzyl alcohol has been associated with toxicity (hypotension, metabolic acidosis), particularly in neonates, and an increased incidence of kernicterus, particularly in small preterm infants. There have been rare reports of deaths, primarily in preterm infants, associated with exposure to excessive amounts of benzyl alcohol. The amount of benzyl alcohol from medications is usually considered negligible compared to that received in flush solutions containing benzyl alcohol. Administration of high dosages of medications (including midazolam) containing this preservative must take into account the total amount of benzyl alcohol administered. The recommended dosage range of midazolam for preterm and term infants includes amounts of benzyl alcohol well below that associated with toxicity; however, the amount of benzyl alcohol at which toxicity may occur is not known. If the patient requires more than the recommended dosages or other medications containing this preservative, the practitioner must consider the daily metabolic load of benzyl alcohol from these combined sources (see
Some published studies in children suggest that similar deficits may occur after repeated or prolonged exposures to anesthetic agents early in life and may result in adverse cognitive or behavioral effects. These studies have substantial limitations, and it is not clear if the observed effects are due to the anesthetic/sedation drug administration or other factors such as the surgery or underlying illness.
Anesthetic and sedation drugs are a necessary part of the care of children needing surgery, other procedures, or tests that cannot be delayed, and no specific medications have been shown to be safer than any other. Decisions regarding the timing of any elective procedures requiring anesthesia should take into consideration the benefits of the procedure weighed against the potential risks.
Midazolam should not be administered by rapid injection in the neonatal population. Severe hypotension and seizures have been reported following rapid intravenous administration, particularly, with concomitant use of fentanyl.
Midazolam injection contains benzyl alcohol as a preservative. Benzyl alcohol, a component of this product, has been associated with serious adverse events and death, particularly in pediatric patients. The "gasping syndrome", (characterized by central nervous system depression, metabolic acidosis, gasping respirations, and high levels of benzyl alcohol and its metabolites found in the blood and urine) has been associated with benzyl alcohol dosages greater than 99 mg/kg/day in neonates and low-birth-weight neonates. Additional symptoms may include gradual neurological deterioration, seizures, intracranial hemorrhage, hematologic abnormalities, skin breakdown, hepatic and renal failure, hypotension, bradycardia, and cardiovascular collapse. Although normal therapeutic doses of this product deliver amounts of benzyl alcohol that are substantially lower than those reported in association with the "gasping syndrome", the minimum amount of benzyl alcohol at which toxicity may occur is not known. Premature and low-birth-weight infants, as well as patients receiving high dosages, may be more likely to develop toxicity. Practitioners administering this and other medications containing benzyl alcohol should consider the combined daily metabolic load of benzyl alcohol from all sources.
Prior to the intravenous administration of midazolam in any dose, the immediate availability of oxygen, resuscitative drugs, age- and size-appropriate equipment for bag/valve/mask ventilation and intubation, and skilled personnel for the maintenance of a patent airway and support of ventilation should be ensured. Patients should be continuously monitored for early signs of hypoventilation, airway obstruction, or apnea, with means readily available (e.g., pulse oximetry). Hypoventilation, airway obstruction, and apnea can lead to hypoxia and/or cardiac arrest unless effective countermeasures are taken immediately. The immediate availability of specific reversal agents (flumazenil) is highly recommended. Vital signs should continue to be monitored during the recovery period. Because intravenous midazolam can depress respiration (see
Concomitant use of benzodiazepines, including midazolam, and opioids may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death. If a decision is made to use midazolam concomitantly with opioids, monitor patients closely for respiratory depression and sedation (see
Serious cardiorespiratory adverse events have occurred after administration of midazolam. These have included respiratory depression, airway obstruction, oxygen desaturation, apnea, respiratory arrest and/or cardiac arrest, sometimes resulting in death or permanent neurologic injury. There have also been rare reports of hypotensive episodes requiring treatment during or after diagnostic or surgical manipulations particularly in adult or pediatric patients with hemodynamic instability. Hypotension occurred more frequently in the sedation studies in patients premedicated with a narcotic.
Midazolam must never be used without individualization of dosage particularly when used with other medications capable of producing central nervous system depression.
See
Reactions such as agitation, involuntary movements (including tonic/clonic movements and muscle tremor), hyperactivity and combativeness have been reported in both adult and pediatric patients. These reactions may be due to inadequate or excessive dosing or improper administration of midazolam; however, consideration should be given to the possibility of cerebral hypoxia or true paradoxical reactions. Should such reactions occur, the response to each dose of midazolam and all other drugs, including local anesthetics, should be evaluated before proceeding. Reversal of such responses with flumazenil has been reported in pediatric patients.
Concomitant use of barbiturates, alcohol or other central nervous system depressants may increase the risk of hypoventilation, airway obstruction, desaturation, or apnea and may contribute to profound and/or prolonged drug effect. Narcotic premedication also depresses the ventilatory response to carbon dioxide stimulation.
Higher risk adult and pediatric surgical patients, elderly patients and debilitated adult and pediatric patients require lower dosages, whether or not concomitant sedating medications have been administered. Adult or pediatric patients with COPD are unusually sensitive to the respiratory depressant effect of midazolam. Pediatric and adult patients undergoing procedures involving the upper airway such as upper endoscopy or dental care, are particularly vulnerable to episodes of desaturation and hypoventilation due to partial airway obstruction. Adult and pediatric patients with chronic renal failure and patients with congestive heart failure eliminate midazolam more slowly (see
Injectable midazolam should not be administered to adult or pediatric patients in shock or coma, or in acute alcohol intoxication with depression of vital signs. Particular care should be exercised in the use of intravenous midazolam in adult or pediatric patients with uncompensated acute illnesses, such as severe fluid or electrolyte disturbances.
There have been limited reports of intra-arterial injection of midazolam. Adverse events have included local reactions, as well as isolated reports of seizure activity in which no clear causal relationship was established. Precautions against unintended intra-arterial injection should be taken. Extravasation should also be avoided.
The safety and efficacy of midazolam following nonintravenous and nonintramuscular routes of administration have not been established. Midazolam should only be administered intramuscularly or intravenously.
Midazolam is associated with a high incidence of partial or complete impairment of recall for the next several hours. The decision as to when patients who have received injectable midazolam, particularly on an outpatient basis, may again engage in activities requiring complete mental alertness, operate hazardous machinery or drive a motor vehicle must be individualized. Gross tests of recovery from the effects of midazolam (see
Use of midazolam late in pregnancy can result in sedation (respiratory depression, lethargy, hypotonia) and/or withdrawal symptoms (hyperreflexia, irritability, restlessness, tremors, inconsolable crying, and feeding difficulties) in the neonate (see
Exposure to excessive amounts of benzyl alcohol has been associated with toxicity (hypotension, metabolic acidosis), particularly in neonates, and an increased incidence of kernicterus, particularly in small preterm infants. There have been rare reports of deaths, primarily in preterm infants, associated with exposure to excessive amounts of benzyl alcohol. The amount of benzyl alcohol from medications is usually considered negligible compared to that received in flush solutions containing benzyl alcohol. Administration of high dosages of medications (including midazolam) containing this preservative must take into account the total amount of benzyl alcohol administered. The recommended dosage range of midazolam for preterm and term infants includes amounts of benzyl alcohol well below that associated with toxicity; however, the amount of benzyl alcohol at which toxicity may occur is not known. If the patient requires more than the recommended dosages or other medications containing this preservative, the practitioner must consider the daily metabolic load of benzyl alcohol from these combined sources (see
Some published studies in children suggest that similar deficits may occur after repeated or prolonged exposures to anesthetic agents early in life and may result in adverse cognitive or behavioral effects. These studies have substantial limitations, and it is not clear if the observed effects are due to the anesthetic/sedation drug administration or other factors such as the surgery or underlying illness.
Anesthetic and sedation drugs are a necessary part of the care of children needing surgery, other procedures, or tests that cannot be delayed, and no specific medications have been shown to be safer than any other. Decisions regarding the timing of any elective procedures requiring anesthesia should take into consideration the benefits of the procedure weighed against the potential risks.
The concomitant use of benzodiazepines and opioids increases the risk of respiratory depression because of actions at different receptor sites in the CNS that control respiration. Benzodiazepines interact at GABAA sites and opioids interact primarily at mu receptors. When benzodiazepines and opioids are combined, the potential for benzodiazepines to significantly worsen opioid-related respiratory depression exists. Limit dosage and duration of concomitant use of benzodiazepines and opioids, and monitor patients closely for respiratory depression and sedation. Monitor patients closely for respiratory depression and sedation.
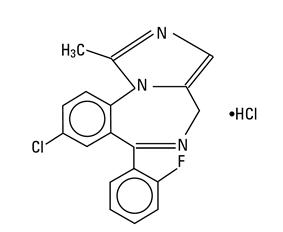
Midazolam hydrochloride injection is a water-soluble benzodiazepine available as a sterile, nonpyrogenic parenteral dosage form for intravenous or intramuscular injection. Each mL contains midazolam hydrochloride equivalent to 1 mg or 5 mg midazolam compounded with 0.8% sodium chloride and 0.01% disodium edetate, with 1% benzyl alcohol as preservative; the pH is adjusted to approximately 3 with hydrochloric acid and, if necessary, sodium hydroxide.
Midazolam is a white to light yellow crystalline compound, insoluble in water. The hydrochloride salt of midazolam, which is formed