Nafcillin
(Nafcillin Sodium)Nafcillin Prescribing Information
Nafcillin is indicated in the treatment of infections caused by penicillinase-producing staphylococci which have demonstrated susceptibility to the drug. Culture and susceptibility tests should be performed initially to determine the causative organism and its susceptibility to the drug (see
For specific information regarding susceptibility test interpretive criteria and associated test methods and quality control standards recognized by FDA for nafcillin for injection, please see:
Nafcillin should not be used in infections caused by organisms susceptible to penicillin G. If the susceptibility tests indicate that the infection is due to a methicillin-resistant
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Nafcillin for Injection and other antibacterial drugs, Nafcillin for Injection should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
Nafcillin for Injection, in the Pharmacy Bulk Package Bottle is for intravenous injection only.
The usual intravenous dosage for adults is 500 mg every 4 hours. For severe infections, 1 gram every 4 hours is recommended. Administer slowly over at least 30 to 60 minutes to minimize the risk of vein irritation and extravasation. Bacteriologic studies to determine the causative organisms and their susceptibility to nafcillin should always be performed. Duration of therapy varies with the type and severity of infection as well as the overall condition of the patient; therefore, it should be determined by the clinical and bacteriological response of the patient. In severe staphylococcal infections, therapy with nafcillin should be continued for at least 14 days. Therapy should be continued for at least 48 hours after the patient has become afebrile, asymptomatic, and cultures are negative. The treatment of endocarditis and osteomyelitis may require a longer duration of therapy.
Nafcillin-probenecid therapy is generally limited to those infections where very high serum levels of nafcillin are necessary.
No dosage alterations are necessary for patients with renal dysfunction, including those on hemodialysis. Hemodialysis does not accelerate nafcillin clearance from the blood.
For patients with hepatic insufficiency and renal failure, measurement of nafcillin serum levels should be performed and dosage adjusted accordingly.
With intravenous administration, particularly in elderly patients, care should be taken because of the possibility of thrombophlebitis.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration whenever solution and container permit.
Do not add supplementary medication to Nafcillin for Injection, USP.
A history of a hypersensitivity (anaphylactic) reaction to any penicillin is a contraindication.
The reported incidence of allergic reactions to penicillin ranges from 0.7 to 10 percent (see
SERIOUS AND OCCASIONALLY FATAL HYPERSENSITIVITY (ANAPHYLACTIC) REACTIONS HAVE BEEN REPORTED IN PATIENTS ON PENICILLIN THERAPY. THESE REACTIONS ARE MORE LIKELY TO OCCUR IN INDIVIDUALS WITH A HISTORY OF PENICILLIN HYPERSENSITIVITY AND/OR A HISTORY OF SENSITIVITY TO MULTIPLE ALLERGENS. THERE HAVE BEEN REPORTS OF INDIVIDUALS WITH A HISTORY OF PENICILLIN HYPERSENSITIVITY WHO HAVE EXPERIENCED SEVERE REACTIONS WHEN TREATED WITH CEPHALOSPORINS. BEFORE INITIATING THERAPY WITH NAFCILLIN, CAREFUL INQUIRY SHOULD BE MADE CONCERNING PREVIOUS HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS TO PENICILLINS, CEPHALOSPORINS, OR OTHER ALLERGENS. IF AN ALLERGIC REACTION OCCURS, NAFCILLIN SHOULD BE DISCONTINUED AND APPROPRIATE THERAPY INSTITUTED.
If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing antibiotic use not directed against
Two types of allergic reactions to penicillins are noted clinically, immediate and delayed.
Immediate reactions usually occur within 20 minutes of administration and range in severity from urticaria and pruritus to angioneurotic edema, laryngospasm, bronchospasm, hypotension, vascular collapse, and death. Such immediate anaphylactic reactions are very rare (see
SERIOUS AND OCCASIONALLY FATAL HYPERSENSITIVITY (ANAPHYLACTIC) REACTIONS HAVE BEEN REPORTED IN PATIENTS ON PENICILLIN THERAPY. THESE REACTIONS ARE MORE LIKELY TO OCCUR IN INDIVIDUALS WITH A HISTORY OF PENICILLIN HYPERSENSITIVITY AND/OR A HISTORY OF SENSITIVITY TO MULTIPLE ALLERGENS. THERE HAVE BEEN REPORTS OF INDIVIDUALS WITH A HISTORY OF PENICILLIN HYPERSENSITIVITY WHO HAVE EXPERIENCED SEVERE REACTIONS WHEN TREATED WITH CEPHALOSPORINS. BEFORE INITIATING THERAPY WITH NAFCILLIN, CAREFUL INQUIRY SHOULD BE MADE CONCERNING PREVIOUS HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS TO PENICILLINS, CEPHALOSPORINS, OR OTHER ALLERGENS. IF AN ALLERGIC REACTION OCCURS, NAFCILLIN SHOULD BE DISCONTINUED AND APPROPRIATE THERAPY INSTITUTED.
If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing antibiotic use not directed against
Delayed allergic reactions to penicillin therapy usually occur after 48 hours and sometimes as late as 2 to 4 weeks after initiation of therapy. Manifestations of this type of reaction include serum sickness-like symptoms (i.e., fever, malaise, urticaria, myalgia, arthralgia, abdominal pain) and various skin rashes. Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, stomatitis, black or hairy tongue, and other symptoms of gastrointestinal irritation may occur, especially during oral penicillin therapy.
Tetracycline, a bacteriostatic antibiotic, may antagonize the bactericidal effect of penicillin, and concurrent use of these drugs should be avoided.
Nafcillin in high dosage regimens, i.e., 2 grams every 4 hours, has been reported to decrease the effects of warfarin. When nafcillin and warfarin are used concomitantly, the prothrombin time should be closely monitored and the dose of warfarin adjusted as necessary. This effect may persist for up to 30 days after nafcillin has been discontinued.
Nafcillin when administered concomitantly with cyclosporine has been reported to result in subtherapeutic cyclosporine levels. The nafcillin-cyclosporine interaction was documented in a patient during two separate courses of therapy. When cyclosporine and nafcillin are used concomitantly in organ transplant patients, the cyclosporine levels should be monitored.
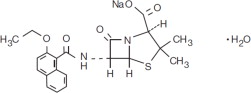
Nafcillin for Injection, USP is a semisynthetic antibiotic penicillin derived from the penicillin nucleus 6-aminopenicillanic acid. It is the sodium salt in a parenteral dosage form. The chemical name is 4-Thia-1-azabicyclo [3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid, 6-[[(2-ethoxy-1-naphthalenyl)carbonyl]amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-monosodium salt, monohydrate [2S(2α,5α,6β)]. It is resistant to inactivation by the enzyme penicillinase (beta-lactamase). The structural formula of nafcillin sodium is as follows:
 | |
| C21H21N2NaO5S•H2O | M.W. 454.48 |
Each Nafcillin for Injection, USP Pharmacy Bulk Package is supplied as a dry powder in bottles containing nafcillin sodium and is intended for intravenous use only. It is soluble in water. The pH of the aqueous solution is 6.0 to 8.5. Each Pharmacy Bulk Package bottle contains nafcillin sodium, as the monohydrate equivalent to 10 grams of nafcillin. The sodium content is 65.8 mg [2.9 mEq] per gram of nafcillin. The product is buffered with 40 mg sodium citrate per gram.
A Pharmacy Bulk Package is a container of sterile dosage form which contains many single doses. The contents are intended for use in a pharmacy admixture program and are restricted to the preparation of admixtures for intravenous infusion. FURTHER DILUTION IS REQUIRED AFTER RECONSTITUTION, (see
Nafcillin for Injection, in the Pharmacy Bulk Package Bottle is for intravenous injection only.
The usual intravenous dosage for adults is 500 mg every 4 hours. For severe infections, 1 gram every 4 hours is recommended. Administer slowly over at least 30 to 60 minutes to minimize the risk of vein irritation and extravasation. Bacteriologic studies to determine the causative organisms and their susceptibility to nafcillin should always be performed. Duration of therapy varies with the type and severity of infection as well as the overall condition of the patient; therefore, it should be determined by the clinical and bacteriological response of the patient. In severe staphylococcal infections, therapy with nafcillin should be continued for at least 14 days. Therapy should be continued for at least 48 hours after the patient has become afebrile, asymptomatic, and cultures are negative. The treatment of endocarditis and osteomyelitis may require a longer duration of therapy.
Nafcillin-probenecid therapy is generally limited to those infections where very high serum levels of nafcillin are necessary.
No dosage alterations are necessary for patients with renal dysfunction, including those on hemodialysis. Hemodialysis does not accelerate nafcillin clearance from the blood.
For patients with hepatic insufficiency and renal failure, measurement of nafcillin serum levels should be performed and dosage adjusted accordingly.
With intravenous administration, particularly in elderly patients, care should be taken because of the possibility of thrombophlebitis.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration whenever solution and container permit.
Do not add supplementary medication to Nafcillin for Injection, USP.
The container closure may be penetrated only one time after reconstitution using a suitable sterile transfer device or dispensing set which allows measured dispensing of the contents. Use of a syringe and needle is not recommended as it may cause leakage. Use of this product is restricted to a suitable work area, such as a laminar flow hood.
The withdrawal of container contents should be accomplished without delay. However, should this not be possible, a maximum of
Each Nafcillin for Injection, USP Pharmacy Bulk Package bottle contains nafcillin sodium as the monohydrate equivalent to 10 grams nafcillin and is designed for use in the pharmacy in preparing IV additives. Add 93 mL Sterile Water for Injection, USP or 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP. The resulting solution will contain 100 mg nafcillin per mL and will require further dilution.