Neomycin Polymyxin B Sulfates And Dexamethasone
(Neomycin Sulfate, Polymyxin B Sulfate And Dexamethasone)Neomycin Polymyxin B Sulfates And Dexamethasone Prescribing Information
For steroid-responsive inflammatory ocular conditions for which a corticosteroid is indicated and where bacterial infection or a risk of bacterial infection exists.
Ocular corticosteroids are indicated in inflammatory conditions of the palpebral and bulbar conjunctiva, cornea, and anterior segment of the globe where the inherent risk of corticosteroids use in certain infective conjunctivitides is accepted to obtain a diminution in edema and inflammation. They are also indicated in chronic anterior uveitis and corneal injury from chemical, radiation or thermal burns; or penetration of foreign bodies.
The use of a combination drug with an anti-infective component is indicated where the risk of infection is high or where there is an expectation that potentially dangerous numbers of bacteria will be present in the eye.
The particular anti-infective drug in this product is active against the following common bacterial eye pathogens:
This product does not provide adequate coverage against:
One to two drops in the conjunctival sac(s). In severe disease, drops may be used hourly, being tapered to discontinuation as the inflammation subsides. In mild disease, drops may be used up to four to six times daily. Not more than 20 mL should be prescribed initially, and the prescription should not be refilled without further evaluation as outlined in
PRECAUTIONSabove.
Neomycin and polymyxin B sulfates and dexamethasone ophthalmic suspension is contraindicated in most viral diseases of the cornea and conjunctiva, including epithelial herpes simplex keratitis (dendritic keratitis), vaccinia, varicella, and also in mycobacterial infection of the eye and fungal diseases of ocular structures. Neomycin and polymyxin B sulfates and dexamethasone ophthalmic suspension is also contraindicated in individuals with known or suspected hypersensitivity to any of the ingredients of this preparation and to other corticosteroids.
Adverse reactions have occurred with corticosteroid/anti-infective combination drugs which can be attributed to the corticosteroid component, the anti-infective component, or the combination. Exact incidence figures are not available since no denominator of treated patients is available.
Reactions occurring most often from the presence of the anti-infective ingredient are allergic sensitizations. The reactions due to the corticosteroid component are: elevation of IOP with possible development of glaucoma, and infrequent optic nerve damage; posterior subcapsular cataract formation; and delayed wound healing. Corticosteroid-containing preparations have also been reported to cause perforation of the globe. Keratitis, conjunctivitis, corneal ulcers, and conjunctival hyperemia have occasionally been reported following use of steroids.
Additional adverse reactions identified from post marketing use include ulcerative keratitis, headache, and Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
The following additional adverse reactions have been reported with dexamethasone use:
Cushing’s syndrome and adrenal suppression may occur after use of dexamethasone in excess of the listed dosing instructions in predisposed patients, including children and patients treated with CYP3A4 inhibitors.
Neomycin and polymyxin B sulfates and dexamethasone ophthalmic suspension, USP is a multiple dose anti-infective steroid combination in sterile suspension form for topical application. The chemical structure for the active ingredient, dexamethasone, is:
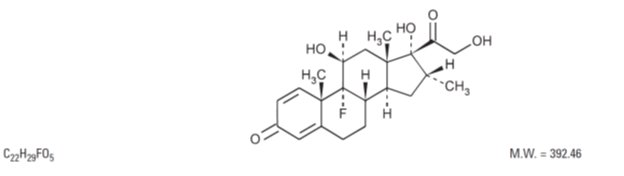
The other active ingredients are neomycin sulfate and polymyxin B sulfate. The structural formula for neomycin sulfate is:
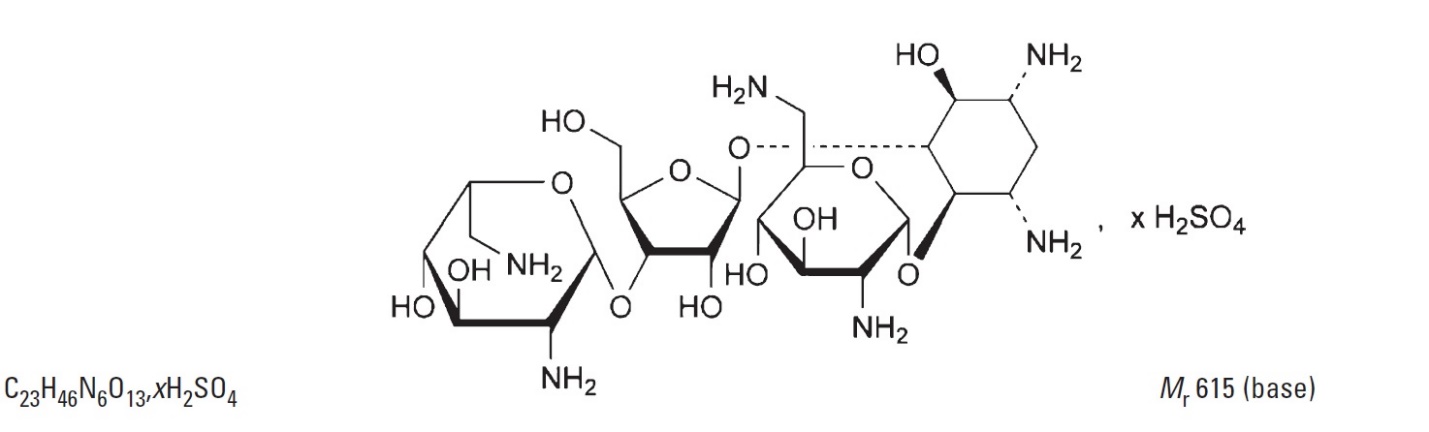
The structural formula for polymyxin B sulfate is:
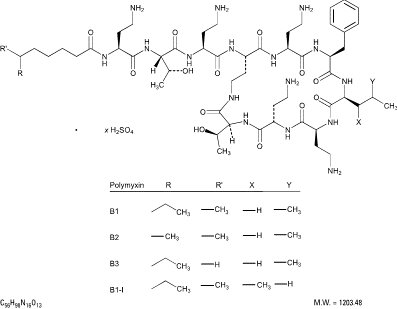
Corticosteroids suppress the inflammatory response to a variety of agents and they probably delay or slow healing. Since corticosteroids may inhibit the body’s defense mechanism against infection, a concomitant antimicrobial drug may be used when this inhibition is considered to be clinically significant in a particular case.
When a decision to administer both a corticosteroid and an antimicrobial is made, the administration of such drugs in combination has the advantage of greater patient compliance and convenience, with the added assurance that the appropriate dosage of both drugs is administered, plus assured compatibility of ingredients when both types of drugs are in the same formulation and, particularly, that the correct volume of drug is delivered and retained.
The relative potency of corticosteroids depends on the molecular structure, concentration and release from the vehicle.