Oxacillin
(Oxacillin Sodium)Oxacillin Prescribing Information
Oxacillin is indicated in the treatment of infections caused by penicillinase producing staphylococci which have demonstrated susceptibility to the drug. Cultures and susceptibility tests should be performed initially to determine the causative organism and its susceptibility to the drug (see
Oxacillin may be used to initiate therapy in suspected cases of resistant staphylococcal infections prior to the availability of susceptibility test results. Oxacillin should not be used in infections caused by organisms susceptible to penicillin G. If the susceptibility tests indicate that the infection is due to an organism other than a resistant
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Oxacillin for Injection, USP and other antibacterial drugs, Oxacillin for Injection, USP should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
Reconstitute as directed below (Pharmacy Bulk Package) prior to further dilution.
Concentration mg/mL | Sterile Water for Injection, USP | 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP | M/6 Molar Sodium Lactate Solution | 5% Dextrose in Water | 5% Dextrose in 0.45% Sodium Chloride | 10% Invert Sugar Injection, USP | Lactated Ringers Solution |
ROOM TEMPERATURE (25°C) | |||||||
10 to 100 | 4 Days | 4 Days | |||||
10 to 30 | 24 Hrs | 24 Hrs | |||||
0.5 to 2 | 6 Hrs | 6 Hrs | 6 Hrs | ||||
REFRIGERATION (4°C) | |||||||
10 to 100 | 7 Days | 7 Days | |||||
10 to 30 | 4 Days | 4 Days | 4 Days | 4 Days | 4 Days | ||
FROZEN (-15°C) | |||||||
50 to 100 | 30 Days | ||||||
250/1.5 mL | 30 Days | ||||||
100 | 30 Days | ||||||
10 to 100 | 30 Days | 30 Days | 30 Days | 30 Days | 30 Days | ||
Stability studies on Oxacillin Sodium at concentrations of 0.5 mg/mL and 2 mg/mL in various intravenous solutions listed below indicate the drug will lose less than 10% activity at room temperature (70°F) during a 6-hour period.
5% Dextrose in Normal Saline
10% D-Fructose in Water
10% Invert Sugar in Normal Saline
10% Invert Sugar Plus 0.3% Potassium Chloride in Water
Only those solutions listed above should be used for the intravenous infusion of Oxacillin Sodium. The concentration of the antibiotic should fall within the range specified. The drug concentration and the rate and volume of the infusion should be adjusted so that the total dose of oxacillin is administered before the drug loses its stability in the solution in use.
If another agent is used in conjunction with oxacillin therapy,
This glass Pharmacy Bulk Package bottle contains 10 grams Oxacillin Sodium and is designed for use in the pharmacy in preparing IV
a. The container closure may be penetrated only one time after reconstitution, utilizing a suitable sterile dispensing set which allows measured distribution of the contents.
b. Use of this product is restricted to a suitable work area, such as a laminar flow hood.
c. Once this container closure has been punctured, withdrawal of the contents should be completed without delay. If prompt fluid transfer cannot be accomplished, discard the contents no
later than 4 HOURS
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
Do not add supplementary medication to Oxacillin for Injection, USP.
A history of a hypersensitivity (anaphylactic) reaction to any penicillin is a contraindication.
Agranulocytosis, neutropenia, and bone marrow depression have been associated with the use of oxacillin. Hepatotoxicity, characterized by fever, nausea, and vomiting associated with abnormal liver function tests, mainly elevated SGOT levels, has been associated with the use of oxacillin.
Tetracycline, a bacteriostatic antibiotic, may antagonize the bactericidal effect of penicillin and concurrent use of these drugs should be avoided.
Oxacillin blood levels may be increased and prolonged by concurrent administration of probenecid which blocks the renal tubular secretion of penicillins. Probenecid decreases the apparent volume of distribution and slows the rate of excretion by competitively inhibiting renal tubular secretion of penicillins.
Oxacillin-probenecid therapy should be limited to those infections where very high serum levels of oxacillin are necessary.
Oxacillin for Injection, USP is a semisynthetic penicillin antibiotic derived from the penicillin nucleus, 6-amino-penicillanic acid. It is the sodium salt in parenteral dosage form. Each Pharmacy Bulk Package bottle of Oxacillin for Injection, USP contains oxacillin sodium monohydrate equivalent to 10 grams of oxacillin. The sodium content is 64 mg [2.8 mEq] per gram oxacillin. The product is buffered with 21 mg dibasic sodium phosphate per gram oxacillin. Oxacillin for Injection, USP is a white to off-white powder filled in clear glass bottles. Dilute solutions are essentially clear and colorless to yellow.
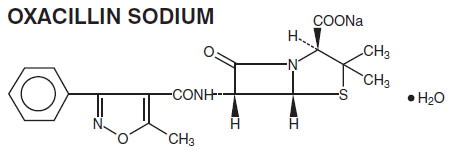
The chemical name of oxacillin sodium is 4-Thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid, 3,3-dimethyl-6-[[(5-methyl-3-phenyl-4-isoxazolyl)carbonyl]-amino]-7-oxo-, monosodium salt, monohydrate, [2
A pharmacy bulk package is a container of a sterile preparation for parenteral use that contains many single doses. The contents of this pharmacy bulk package are intended for use by a pharmacy admixture service for addition to suitable parenteral fluids in the preparation of admixtures for intravenous infusion (see