Oxybutynin Chloride
Oxybutynin Chloride Prescribing Information
Oxybutynin chloride tablets, USP are indicated for the relief of symptoms of bladder instability associated with voiding in patients with uninhibited neurogenic or reflex neurogenic bladder (i.e., urgency, frequency, urinary leakage, urge incontinence, dysuria).
The usual dose is one 5-mg tablet two to three times a day. The maximum recommended dose is one 5-mg tablet four times a day. A lower starting dose of 2.5 mg two or three times a day is recommended for the frail elderly.
The usual dose is one 5-mg tablet two times a day. The maximum recommended dose is one 5-mg tablet three times a day.
Oxybutynin chloride tablets are contraindicated in patients with urinary retention, gastric retention and other severe decreased gastrointestinal motility conditions, uncontrolled narrow-angle glaucoma and in patients who are at risk for these conditions.
Oxybutynin chloride tablets are also contraindicated in patients who have demonstrated hypersensitivity to the drug substance or other components of the product.
The safety and efficacy of oxybutynin chloride was evaluated in a total of 199 patients in three clinical trials. These participants were treated with oxybutynin chloride 5 to 20 mg/day for up to 6 weeks. Table 3 shows the incidence of adverse events judged by investigators to be at least possibly related to treatment and reported by at least 5% of patients.
| Body System | Adverse Event | Oxybutynin Chloride (5 to 20 mg/day) (n=199) |
| Infections and Infestations | Urinary tract infection | 6.5% |
| Psychiatric Disorders | Insomnia | 5.5% |
| | Nervousness | 6.5% |
| Nervous System Disorders | Dizziness | 16.6% |
| | Somnolence | 14.0% |
| | Headache | 7.5% |
| Eye Disorders | Blurred vision | 9.6% |
| Gastrointestinal Disorders | Dry mouth | 71.4% |
| | Constipation | 15.1% |
| | Nausea | 11.6% |
| | Dyspepsia | 6.0% |
| Renal and Urinary Disorders | Urinary Hesitation | 8.5% |
| | Urinary Retention | 6.0% |
The most common adverse events reported by patients receiving oxybutynin chloride 5 to 20 mg/day were the expected side effects of anticholinergic agents. The incidence of dry mouth was dose-related.
In addition, the following adverse events were reported by 1 to <5% of patients using oxybutynin chloride (5 to 20 mg/day) in all studies.
The concomitant use of oxybutynin with other anticholinergic drugs or with other agents which produce dry mouth, constipation, somnolence (drowsiness), and/or other anticholinergic-like effects may increase the frequency and/or severity of such effects.
Anticholinergic agents may potentially alter the absorption of some concomitantly administered drugs due to anticholinergic effects on gastrointestinal motility. This may be of concern for drugs with a narrow therapeutic index. Anticholinergic agents may also antagonize the effects of prokinetic agents, such as metoclopramide.
Mean oxybutynin chloride plasma concentrations were approximately 3 to 4 fold higher when oxybutynin was administered with ketoconazole, a potent CYP3A4 inhibitor.
Other inhibitors of the cytochrome P450 3A4 enzyme system, such as antimycotic agents (e.g., itraconazole and miconazole) or macrolide antibiotics (e.g., erythromycin and clarithromycin), may alter oxybutynin mean pharmacokinetic parameters (i.e., Cmax and AUC). The clinical relevance of such potential interactions is not known. Caution should be used when such drugs are co-administered.
Each scored oxybutynin chloride tablet, USP contains 5 mg of oxybutynin chloride. Chemically, oxybutynin chloride is d, l (racemic) 4-diethylamino-2-butynyl phenylcyclohexylglycolate hydrochloride. The molecular formula of oxybutynin chloride is C22H31NO3•HCl. The structural formula appears below:
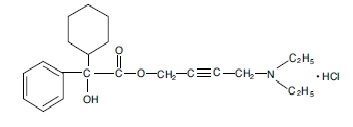
Oxybutynin chloride, USP is a white crystalline solid with a molecular weight of 393.95. It is readily soluble in water and acids, but relatively insoluble in alkalis.
Oxybutynin chloride Tablets, USP also contains anhydrous lactose, croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose.
Oxybutynin chloride tablets, USP are for oral administration.
Therapeutic Category: Antispasmodic, anticholinergic.
Meets USP Dissolution Test 2.