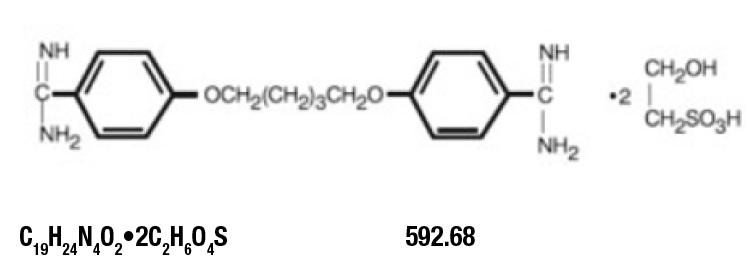
Pentamidine Isethionate
Pentamidine Isethionate Prescribing Information
Pentamidine isethionate for injection is indicated for the treatment of pneumonia due to
Contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to pentamidine isethionate.
The most frequently reported spontaneous adverse events (1 to 30%) reported in clinical trials, regardless of their relation to pentamidine isethionate therapy were as follows (n=424):
| Cardiovascular: | |
| -Hypotension | 5.0% |
| Gastrointestinal: | |
| -Anorexia/Nausea | 5.9% |
| Hematologic: | |
| -Anemia | 1.2% |
| -Leukopenia | 10.4% |
| -Thrombocytopenia | 2.6% |
| Hepatic: | |
| -Elevated liver function tests | 8.7% |
| Metabolic: | |
| -Hypoglycemia | 5.9% |
| Neurologic: | |
| -Confusion/hallucinations | 1.7% |
| Skin: | |
| -Sterile abscess and/or necrosis, pain, or induration at the site of IM injection | 11.1% |
| -Rash | 3.3% |
| Special Senses: | |
| -Bad taste | 1.7% |
| Urogenital: | |
| -Azotemia | 8.5% |
| -Elevated serum creatinine | 23.6% |
| -Elevated blood urea nitrogen | 6.6% |
| -Impaired renal function | 28.8% |
Adverse events with a frequency of less than 1% incidence were as follows (No causal relationship to treatment has been established for these adverse events):
Body as a whole: | Allergic reaction (i.e. urticaria, itching, rash), anaphylaxis, arthralgia, chills, extrapulmonary pneumocystosis, headache, night sweats, and Stevens-Johnson syndrome. |
Cardiovascular: | Abnormal ST segment of electrocardiogram, cardiac arrhythmias, cerebrovascular accident, hypertension, palpitations, phlebitis, syncope, tachycardia, vasodilatation, vasculitis and ventricular tachycardia. |
Gastrointestinal: | Abdominal pain, diarrhea, dry mouth, dyspepsia, hematochezia, hypersalivation, melena, pancreatitis, splenomegaly, and vomiting. |
Hematological: | Defibrination, eosinophilia, neutropenia, pancytopenia, and prolonged clotting time. |
Hepatic: | Hepatic dysfunction, hepatitis and hepatomegaly |
Metabolic: | Hyperglycemia, hyperkalemia, hypocalcemia, and hypomagnesemia. |
Neurological: | Anxiety, confusion, depression, dizziness, drowsiness, emotional lability, hypesthesia, insomnia, memory loss, neuropathy, nervousness, neuralgia, paranoia, paresthesia, peripheral neuropathy, seizure, tremors, unsteady gait, and vertigo. |
Respiratory system: | Asthma, bronchitis, bronchospasm, chest congestion, chest tightness, coryza, cyanosis, eosinophilic or interstitial pneumonitis, gagging, hemoptysis, hyperventilation, laryngitis, laryngospasm, non-specific lung disorder, nasal congestion, pleuritis, pneumothorax, rales, rhinitis, shortness of breath, and tachypnea. |
Skin: | Desquamation, dry and breaking hair, dry skin, erythema, dermatitis, pruritus, rash, and urticaria. |
Special senses: | Blepharitis, blurred vision, conjunctivitis, contact lens discomfort, eye pain or discomfort, loss of hearing, loss of taste, and loss of smell. |
Urogenital: | Flank pain, hematuria, incontinence, nephritis, renal dysfunction and renal failure. |
From post-marketing clinical experience with pentamidine isethionate, the following adverse events have been reported: cough, diabetes mellitus/ketoacidosis, dyspnea, infiltration (extravasation–see
Fatalities due to severe hypotension, hypoglycemia, acute pancreatitis and cardiac arrhythmias have been reported in patients treated with pentamidine isethionate, both by the IM and IV routes. Severe hypotension may result after a single IM or IV dose and is more likely with rapid IV administration (see
No drug interaction studies with pentamidine isethionate for injection have been conducted.
Because the nephrotoxic effects may be additive, the concomitant or sequential use of pentamidine isethionate and other nephrotoxic drugs such as aminoglycosides, amphotericin B, cisplatin, foscarnet, or vancomycin should be closely monitored and avoided, if possible.
Pentamidine isethionate for injection, an anti-protozoal agent, is a sterile, nonpyrogenic, lyophilized product. After reconstitution, it should be administered by intramuscular (IM) or intravenous (IV) routes (see
The contents of one vial (300 mg) should be dissolved in 3 mL of Sterile Water for Injection, USP at 22° to 30°C (72° to 86°F). The calculated daily dose should then be withdrawn and administered by deep IM injection.
The contents of one vial (300 mg) should first be dissolved in 3 to 5 mL of Sterile Water for Injection, USP, or 5% Dextrose Injection, USP at 22°to 30°C (72° to 86°F). The calculated dose of pentamidine isethionate should then be withdrawn and diluted further in 50 to 250 mL of 5% Dextrose Injection, USP.
Aseptic technique should be employed in preparation of all solutions. Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration whenever solution and container permit.
After reconstitution with sterile water, the pentamidine isethionate solution is stable for 48 hours in the original vial at room temperature if protected from light. To avoid crystallization,store at 22° to 30°C (72° to 86°F). Intravenous infusion solutions of pentamidine isethionate at 1 mg/mL and 2.5 mg/mL prepared in 5% Dextrose Injection, USP are stable at room temperature for up to 24 hours.
Intravenous (IV) solutions of pentamidine isethionate have been shown to be incompatible with fluconazole and foscarnet sodium. IV solutions of pentamidine isethionate have been shown to be compatible with IV solutions of zidovudine (AZT) and diltiazem hydrochloride.