Prednisolone Sodium Phosphate Oral Solution
(Prednisolone Sodium Phosphate)Prednisolone Sodium Phosphate Oral Solution Prescribing Information
Prednisolone sodium phosphate oral solution (25 mg prednisolone per 5 mL) is indicated in the following conditions:
Control of severe or incapacitating allergic conditions intractable to adequate trials of conventional treatment in adult and pediatric populations with: seasonal or perennial allergic rhinitis; asthma; contact dermatitis; atopic dermatitis; serum sickness; drug hypersensitivity reactions.
Pemphigus; bullous dermatitis herpetiformis; severe erythema multiforme (Stevens-Johnson syndrome); exfoliative erythroderma; mycosis fungoides.
To induce diuresis or remission of proteinuria in nephrotic syndrome in adults with lupus erythematosus and in adults and pediatric populations, with idiopathic nephritic syndrome, without uremia.
Primary or secondary adrenocortical insufficiency (hydrocortisone or cortisone is the first choice; synthetic analogs may be used in conjunction with mineralocorticoids where applicable; in infancy mineralocorticoid supplementation is of particular importance); congenital adrenal hyperplasia; hypercalcemia associated with cancer; nonsuppurative thyroiditis.
To tide the patient over a critical period of the disease in: ulcerative colitis; regional enteritis.
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura in adults; selected cases of secondary thrombocytopenia; acquired (autoimmune) hemolytic anemia; pure red cell aplasia; Diamond-Blackfan anemia.
For the treatment of acute leukemia and aggressive lymphomas in adults and children.
Acute exacerbations of multiple sclerosis.
Uveitis and ocular inflammatory conditions unresponsive to topical corticosteroids; temporal arteritis; sympathetic ophthalmia.
Symptomatic sarcoidosis; idiopathic eosinophilic pneumonias; fulminating or disseminated pulmonary tuberculosis when used concurrently with appropriate antituberculous chemotherapy; asthma (as distinct from allergic asthma listed above under “Allergic States”), hypersensitivity pneumonitis, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia (PCP) associated with hypoxemia occurring in an HIV (+) individual who is also under treatment with appropriate anti-PCP antibiotics. Studies support the efficacy of systemic corticosteroids for the
treatment of these conditions: allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, idiopathic bronchiolitis obliterans with organizing pneumonia.
As adjunctive therapy for short term administration (to tide the patient over an acute episode or exacerbation) in: psoriatic arthritis; rheumatoid arthritis, including juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (selected cases may require low dose maintenance therapy); ankylosing spondylitis; acute and subacute bursitis; acute nonspecific tenosynovitis; acute gouty arthritis; epicondylitis. For the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis (polymyositis), polymyalgia rheumatica, Sjogren’s syndrome, relapsing polychondritis, and certain cases of vasculitis.
Tuberculous meningitis with subarachnoid block or impending block, tuberculosis with enlarged mediastinal lymph nodes causing respiratory difficulty, and tuberculosis with pleural or pericardial effusion (appropriate antituberculous chemotherapy must be used concurrently when treating any tuberculosis complications); trichinosis with neurologic or myocardial involvement; acute or
chronic solid organ rejection (with or without other agents).
The initial dosage of prednisolone sodium phosphate oral solution (25 mg prednisolone per 5 mL) may vary from 1 mL to 12 mL (5 to 60 mg prednisolone base) per day depending on the specific disease entity being treated. In situations of less severity, lower doses will generally suffice while in selected patients higher initial doses may be required. The initial dosage should be maintained or adjusted until a satisfactory response is noted. If after a reasonable period of time, there is a lack of satisfactory clinical response, prednisolone sodium phosphate oral solution (25 mg prednisolone per 5 mL) should be discontinued and the patient placed on other appropriate therapy.
In the treatment of acute exacerbations of multiple sclerosis, daily doses of 200 mg of prednisolone for a week followed by 80 mg every other day or 4 to 8 mg dexamethasone every other day for one month have been shown to be effective.
In pediatric patients, the initial dose of prednisolone sodium phosphate oral solution (25 mg prednisolone per 5 mL) may vary depending on the specific disease entity being treated. The range of initial doses is 0.14 to 2 mg/kg/day in three or four divided doses (4 to 60 mg/m
2bsa/day).
The standard regimen used to treat nephrotic syndrome in pediatric patients is 60 mg/m2/day given in three divided doses for 4 weeks, followed by 4 weeks of single dose alternate-day therapy at 40 mg/m
2/day.
The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) recommended dosing for systemic prednisone, prednisolone or methylprednisolone in children whose asthma is uncontrolled by inhaled corticosteroids and long-acting bronchodilators is 1-2 mg/kg/day in single or divided doses. It is further recommended that short course, or “burst” therapy, be continued until a child achieves a peak expiratory flow rate of 80% of his or her personal best or symptoms resolve. This usually requires 3 to 10 days of treatment, although it can take longer. There is no evidence that tapering the dose after improvement will prevent a relapse.

Systemic fungal infections.
Hypersensitivity to the drug or any of its components.
Cardiovascular: Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in premature infants.
Inc. at 1-866-762-2365 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or
www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Prednisolone sodium phosphate oral solution is a dye free, pale to light yellow solution. Each 5 mL (teaspoonful) of prednisolone sodium phosphate oral solution contains 33.6 mg prednisolone sodium phosphate (25 mg prednisolone base) in a palatable, aqueous vehicle. Prednisolone sodium phosphate oral solution also contains antibitter mask, corn syrup, edetate disodium, glycerin, grape flavor, hydroxyethylcellulose, methylparaben, potassium phosphate dibasic, potassium phosphate monobasic, purified water, and sodium saccharin.
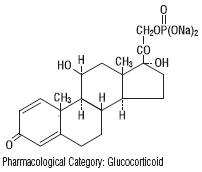
Prednisolone sodium phosphate occurs as white or slightly yellow, friable granules or powder. It is freely soluble in water; soluble in methanol; slightly soluble in alcohol and in chloroform; and very slightly soluble in acetone and in dioxane. The chemical name of prednisolone sodium phosphate is pregna-1,4-diene-3,20- dione,11,17-dihydroxy- 21-(phosphonooxy)- disodium salt, (11ß)-. The empirical formula is C
21H
27Na
2O
8P; the molecular weight is 484.39. Its chemical structure is:
Naturally occurring glucocorticoids (hydrocortisone), which also have salt-retaining properties, are used as replacement therapy in adrenocortical deficiency states. Their synthetic analogs are primarily used for their potent anti-inflammatory effects in disorders of many organ systems.
Prednisolone is a synthetic adrenocortical steroid drug with predominantly glucocorticoid properties. Some of these properties reproduce the physiological actions of endogenous glucocorticosteroids, but others do not necessarily reflect any of the adrenal hormones’ normal functions; they are seen only after administration of large therapeutic doses of the drug. The pharmacological effects of prednisolone which are due to its glucocorticoid properties include: promotion of gluconeogenesis; increased deposition of glycogen in the liver; inhibition of the utilization of glucose; anti-insulin activity; increased catabolism of protein; increased lipolysis; stimulation of fat synthesis and storage; increased glomerular filtration rate and resulting increase in urinary excretion of urate (creatinine excretion remains unchanged); and increased calcium excretion.
Depressed production of eosinophils and lymphocytes occurs, but erythropoiesis and production of polymorphonuclear leukocytes are stimulated. Inflammatory processes (edema, fibrin deposition, capillary dilatation, migration of leukocytes and phagocytosis) and the later stages of wound healing (capillary proliferation, deposition of collagen, cicatrization) are inhibited.
Prednisolone can stimulate secretion of various components of gastric juice. Suppression of the production of corticotropin may lead to suppression of endogenous corticosteroids. Prednisolone has slight mineralocorticoid activity, whereby entry of sodium into cells and loss of intracellular potassium is stimulated. This is particularly evident in the kidney, where rapid ion exchange leads to sodium retention and hypertension.
Prednisolone is rapidly and well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract following oral administration.
Prednisolone sodium phosphate oral solution produces a 14% higher peak plasma level of prednisolone which occurs 20% faster than that seen with tablets. Prednisolone is 70-90% protein-bound in the plasma, and it is eliminated from the plasma with a half-life of 2 to 4 hours. It is metabolized mainly in the liver and excreted in the urine as sulfate and glucuronide conjugates.
The systemic availability, metabolism and elimination of prednisolone after administration of single weight-based doses (0.8 mg/kg) of intravenous (IV) prednisolone and oral prednisone were reported in a small study of 19 young (23 to 34 years) and 12 elderly (65 to 89 years) subjects. Results showed that the systemic availability of total and unbound prednisolone, as well as interconversion between prednisolone and prednisone were independent of age. The mean unbound fraction of prednisolone was higher, and steady-state volume of distribution (Vss) of unbound prednisolone was reduced in elderly patients. Plasma prednisolone concentrations were higher in elderly subjects, and the higher AUCs of total and unbound prednisolone were most likely reflective of an impaired metabolic clearance, evidenced by reduced fractional urinary clearance of 6ß -hydroxyprednisolone. Despite these findings of higher total and unbound prednisolone concentrations, elderly subjects had higher AUCs of cortisol, suggesting that the elderly population is less sensitive to suppression of endogenous cortisol or their capacity for hepatic inactivation of cortisol is diminished.