Pregabalin
Pregabalin Prescribing Information
Warnings and Precautions (5.3, 5.4) 06/2025
Pregabalin capsules are indicated for:
- Neuropathic pain associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) (1)
- Postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) (1)
- Adjunctive therapy for the treatment of partial-onset seizures in patients 1 month of age and older (1)
- Fibromyalgia (1)
- Neuropathic pain associated with spinal cord injury (1)
• For adult indications, begin dosing at 150 mg/day. For partial onset seizure dosing in pediatric patients 1 month of age and older, refer to
The recommended dosages for adults and pediatric patients 1 month of age and older are included in Table 1. Administer the total daily dosage orally in two or three divided doses as indicated in Table 1. In pediatric patients, the recommended dosing regimen is dependent upon body weight. Based on clinical response and tolerability, dosage may be increased, approximately weekly.
Age and Body Weight | Recommended Initial Dosage | Recommended Maximum Dosage | Frequency of Administration |
| Adults (17 years and older) | 150 mg/day | 600 mg/day | 2 or 3 divided doses |
| Pediatric patients weighing 30 kg or more | 2.5 mg/kg/day | 10 mg/kg/day (not to exceed 600 mg/day) | 2 or 3 divided doses |
| Pediatric patients weighing less than 30 kg | 3.5 mg/kg/day | 14 mg/kg/day | 1 month to less than 4 years of age: 3 divided doses 4 years of age and older: 2 or 3 divided doses |
Both the efficacy and adverse event profiles of pregabalin capsules have been shown to be dose-related. The effect of dose escalation rate on the tolerability of pregabalin capsules has not been formally studied.
The efficacy of adjunctive pregabalin capsules in patients taking gabapentin has not been evaluated in controlled trials. Consequently, dosing recommendations for the use of pregabalin capsules with gabapentin cannot be offered.
The maximum recommended dose of pregabalin capsules are 100 mg three times a day (300 mg/day) in patients with creatinine clearance of at least 60 mL/min. Begin dosing at 50 mg three times a day (150 mg/day). The dose may be increased to 300 mg/day within 1 week based on efficacy and tolerability.
Although pregabalin capsules were also studied at 600 mg/day, there is no evidence that this dose confers additional significant benefit and this dose was less well tolerated. In view of the dose-dependent adverse reactions, treatment with doses above 300 mg/day is not recommended
The recommended dose of pregabalin capsules is 75 to 150 mg two times a day, or 50 to 100 mg three times a day (150 to 300 mg/day) in patients with creatinine clearance of at least 60 mL/min. Begin dosing at 75 mg two times a day, or 50 mg three times a day (150 mg/day). The dose may be increased to 300 mg/day within 1 week based on efficacy and tolerability.
Patients who do not experience sufficient pain relief following 2 to 4 weeks of treatment with 300 mg/day, and who are able to tolerate pregabalin capsules, may be treated with up to 300 mg two times a day, or 200 mg three times a day (600 mg/day). In view of the dose-dependent adverse reactions and the higher rate of treatment discontinuation due to adverse reactions, reserve dosing above 300 mg/day for those patients who have on-going pain and are tolerating 300 mg daily
The recommended dosages for adults and pediatric patients 1 month of age and older are included in Table 1. Administer the total daily dosage orally in two or three divided doses as indicated in Table 1. In pediatric patients, the recommended dosing regimen is dependent upon body weight. Based on clinical response and tolerability, dosage may be increased, approximately weekly.
Age and Body Weight | Recommended Initial Dosage | Recommended Maximum Dosage | Frequency of Administration |
| Adults (17 years and older) | 150 mg/day | 600 mg/day | 2 or 3 divided doses |
| Pediatric patients weighing 30 kg or more | 2.5 mg/kg/day | 10 mg/kg/day (not to exceed 600 mg/day) | 2 or 3 divided doses |
| Pediatric patients weighing less than 30 kg | 3.5 mg/kg/day | 14 mg/kg/day | 1 month to less than 4 years of age: 3 divided doses 4 years of age and older: 2 or 3 divided doses |
Both the efficacy and adverse event profiles of pregabalin capsules have been shown to be dose-related. The effect of dose escalation rate on the tolerability of pregabalin capsules has not been formally studied.
The efficacy of adjunctive pregabalin capsules in patients taking gabapentin has not been evaluated in controlled trials. Consequently, dosing recommendations for the use of pregabalin capsules with gabapentin cannot be offered.
The recommended dose of pregabalin capsules for fibromyalgia is 300 to 450 mg/day. Begin dosing at 75 mg two times a day (150 mg/day). The dose may be increased to 150 mg two times a day (300 mg/day) within 1 week based on efficacy and tolerability. Patients who do not experience sufficient benefit with 300 mg/day may be further increased to 225 mg two times a day (450 mg/day). Although pregabalin capsules were also studied at 600 mg/day, there is no evidence that this dose confers additional benefit and this dose was less well tolerated. In view of the dose-dependent adverse reactions, treatment with doses above 450 mg/day is not recommended
The recommended dose range of pregabalin capsules for the treatment of neuropathic pain associated with spinal cord injury is 150 to 600 mg/day. The recommended starting dose is 75 mg two times a day (150 mg/day). The dose may be increased to 150 mg two times a day (300 mg/day) within 1 week based on efficacy and tolerability. Patients who do not experience sufficient pain relief after 2 to 3 weeks of treatment with 150 mg two times a day and who tolerate pregabalin capsules may be treated with up to 300 mg two times a day
• Dosing recommendations:
| INDICATION | Dosing Regimen | Maximum Dose | ||||||||||||||||
DPN Pain The maximum recommended dose of pregabalin capsules are 100 mg three times a day (300 mg/day) in patients with creatinine clearance of at least 60 mL/min. Begin dosing at 50 mg three times a day (150 mg/day). The dose may be increased to 300 mg/day within 1 week based on efficacy and tolerability. Although pregabalin capsules were also studied at 600 mg/day, there is no evidence that this dose confers additional significant benefit and this dose was less well tolerated. In view of the dose-dependent adverse reactions, treatment with doses above 300 mg/day is not recommended [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. | 3 divided doses per day | 300 mg/day within 1 week | ||||||||||||||||
PHN The recommended dose of pregabalin capsules is 75 to 150 mg two times a day, or 50 to 100 mg three times a day (150 to 300 mg/day) in patients with creatinine clearance of at least 60 mL/min. Begin dosing at 75 mg two times a day, or 50 mg three times a day (150 mg/day). The dose may be increased to 300 mg/day within 1 week based on efficacy and tolerability. [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. | 2 or 3 divided doses per day | 300 mg/day within 1 week. Maximum dose of 600 mg/day. | ||||||||||||||||
Adjunctive Therapy for Partial-Onset Seizures in Pediatric and Adult Patients Weighing 30 kg or More The recommended dosages for adults and pediatric patients 1 month of age and older are included in Table 1. Administer the total daily dosage orally in two or three divided doses as indicated in Table 1. In pediatric patients, the recommended dosing regimen is dependent upon body weight. Based on clinical response and tolerability, dosage may be increased, approximately weekly. Table 1. Recommended Dosage for Adults and Pediatric Patients 1 Month and Older
Both the efficacy and adverse event profiles of pregabalin capsules have been shown to be dose-related. The effect of dose escalation rate on the tolerability of pregabalin capsules has not been formally studied. The efficacy of adjunctive pregabalin capsules in patients taking gabapentin has not been evaluated in controlled trials. Consequently, dosing recommendations for the use of pregabalin capsules with gabapentin cannot be offered. | 2 or 3 divided doses per day | Maximum dose of 600 mg/day. | ||||||||||||||||
Adjunctive Therapy for Partial-Onset Seizures in Pediatric Patients Weighing Less than 30 kg The recommended dosages for adults and pediatric patients 1 month of age and older are included in Table 1. Administer the total daily dosage orally in two or three divided doses as indicated in Table 1. In pediatric patients, the recommended dosing regimen is dependent upon body weight. Based on clinical response and tolerability, dosage may be increased, approximately weekly. Table 1. Recommended Dosage for Adults and Pediatric Patients 1 Month and Older
Both the efficacy and adverse event profiles of pregabalin capsules have been shown to be dose-related. The effect of dose escalation rate on the tolerability of pregabalin capsules has not been formally studied. The efficacy of adjunctive pregabalin capsules in patients taking gabapentin has not been evaluated in controlled trials. Consequently, dosing recommendations for the use of pregabalin capsules with gabapentin cannot be offered. | 1 month to less than 4 years: 3 divided doses per day 4 years and older: 2 or 3 divided doses per day | 14 mg/kg/day. | ||||||||||||||||
Fibromyalgia The recommended dose of pregabalin capsules for fibromyalgia is 300 to 450 mg/day. Begin dosing at 75 mg two times a day (150 mg/day). The dose may be increased to 150 mg two times a day (300 mg/day) within 1 week based on efficacy and tolerability. Patients who do not experience sufficient benefit with 300 mg/day may be further increased to 225 mg two times a day (450 mg/day). Although pregabalin capsules were also studied at 600 mg/day, there is no evidence that this dose confers additional benefit and this dose was less well tolerated. In view of the dose-dependent adverse reactions, treatment with doses above 450 mg/day is not recommended [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. | 2 divided doses per day | 300 mg/day within 1 week. Maximum dose of 450 mg/day. | ||||||||||||||||
Neuropathic Pain Associated with Spinal Cord InjuryThe recommended dose range of pregabalin capsules for the treatment of neuropathic pain associated with spinal cord injury is 150 to 600 mg/day. The recommended starting dose is 75 mg two times a day (150 mg/day). The dose may be increased to 150 mg two times a day (300 mg/day) within 1 week based on efficacy and tolerability. Patients who do not experience sufficient pain relief after 2 to 3 weeks of treatment with 150 mg two times a day and who tolerate pregabalin capsules may be treated with up to 300 mg two times a day [see Clinical Studies (14.5)]. | 2 divided doses per day | 300 mg/day within 1 week. Maximum dose of 600 mg/day. |
• Dose should be adjusted in adult patients with reduced renal function.
In view of dose-dependent adverse reactions and since pregabalin capsules are eliminated primarily by renal excretion, adjust the dose in adult patients with reduced renal function. The use of pregabalin capsules in pediatric patients with compromised renal function has not been studied.
Base the dose adjustment in patients with renal impairment on creatinine clearance (CLcr), as indicated in Table 2. To use this dosing table, an estimate of the patient's CLcr in mL/min is needed. CLcr in mL/min may be estimated from serum creatinine (mg/dL) determination using the Cockcroft and Gault equation:
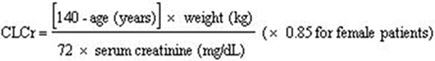
Next, refer to the Dosage and Administration section to determine the recommended total daily dose based on indication, for a patient with normal renal function (CLcr greater than or equal to 60 mL/min). Then refer to Table 2 to determine the corresponding renal adjusted dose.
(For example: A patient initiating pregabalin capsule therapy for postherpetic neuralgia with normal renal function (CLcr greater than or equal to 60 mL/min), receives a total daily dose of 150 mg/day pregabalin. Therefore, a renal impaired patient with a CLcr of 50 mL/min would receive a total daily dose of 75 mg/day pregabalin administered in two or three divided doses.)
For patients undergoing hemodialysis, adjust the pregabalin daily dose based on renal function. In addition to the daily dose adjustment, administer a supplemental dose immediately following every 4-hour hemodialysis treatment (see Table 2).
Creatinine Clearance (CLcr) (mL/min) | Total Pregabalin Daily Dose (mg/day)* | Dose Regimen | |||
| Greater than or equal to 60 | 150 | 300 | 450 | 600 | BID or TID |
| 30 - 60 | 75 | 150 | 225 | 300 | BID or TID |
| 15 - 30 | 25 - 50 | 75 | 100 - 150 | 150 | QD or BID |
| Less than 15 | 25 | 25 - 50 | 50 - 75 | 75 | QD |
| Supplementary dosage following hemodialysis (mg)† | |||||
| Patients on the 25 mg QD regimen: take one supplemental dose of 25 mg or 50 mg Patients on the 25 - 50 mg QD regimen: take one supplemental dose of 50 mg or 75 mg Patients on the 50 - 75 mg QD regimen: take one supplemental dose of 75 mg or 100 mg Patients on the 75 mg QD regimen: take one supplemental dose of 100 mg or 150 mg | |||||
TID= Three divided doses; BID = Two divided doses; QD = Single daily dose.
* Total daily dose (mg/day) should be divided as indicated by dose regimen to provide mg/dose.
† Supplementary dose is a single additional dose.
Capsules: 25 mg, 50 mg, 75 mg, 100 mg, 150 mg, 200 mg, 225 mg, and 300 mg
Pregabalin, USP is described chemically as (
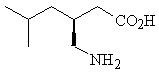
Pregabalin, USP is a white to off-white, crystalline solid with a pKa1of 4.2 and a pKa2of 10.6. It is freely soluble in water and both basic and acidic aqueous solutions. The log of the partition coefficient (n-octanol/0.05M phosphate buffer) at pH 7.4 is – 1.35.
Pregabalin capsules are administered orally and are supplied as imprinted hard-shell capsules containing 25, 50, 75, 100, 150, 200, 225, and 300 mg of pregabalin USP, along with pregelatinized starch, and talc as inactive ingredients. The capsule shells contain gelatin and titanium dioxide. In addition, the orange capsule shells contain iron oxide red and titanium dioxide and the white capsule shells contain titanium dioxide. Sodium Lauryl Sulfate (SLS) is a manufacturing aid that may or may not be present in the capsule shells. The imprinting ink contains shellac, black iron oxide and potassium hydroxide.

Pregabalin capsules are available as follows:
25 mg capsules:
White to off white opaque hard gelatin capsule imprinted “4E 25” on the cap and “4E 25” on the body with black ink, containing white to off white powder; available in:
Bottles of 90: NDC: 25000-179-07
50 mg capsules:
White to off white opaque hard gelatin capsule imprinted “4F 50” with 360-degree band on the cap and “4F 50” with 360 degree band on the body with black ink, containing white to off white powder, available in:
Bottles of 90: NDC: 25000-180-07
75 mg capsules:
Orange opaque / White to off white opaque hard gelatin capsule imprinted “4G 75” on the cap and “4G 75” on the body with black ink, containing white to off white powder, available in:
Bottles of 90: NDC: 25000-181-07
100 mg capsules:
Orange opaque hard gelatin capsule imprinted “4H 100” on the cap and “4H 100” on the body with black ink, containing white to off white powder, available in:
Bottles of 90: NDC: 25000-182-07
150 mg capsules:
White to off white opaque hard gelatin capsule imprinted “4I 150” on the cap and “4I 150” on the body with black ink, containing white to off white powder, available in:
Bottles of 90: NDC: 25000-183-07
200 mg capsules:
Light orange opaque hard gelatin capsule imprinted “4J 200” on the cap and “4J 200” on the body with black ink, containing white to off white powder, available in:
Bottles of 90: NDC: 25000-184-07
225 mg capsules:
Light orange opaque/ white to off white opaque hard gelatin capsule imprinted “4K 225” on the cap and “4K 225” on the body with black ink, containing white to off white powder, available in:
Bottles of 90: NDC: 25000-185-07
300 mg capsules:
Orange opaque / White to off white opaque hard gelatin capsule imprinted “4L 300” on the cap and “4L 300” on the body with black ink, containing white to off white powder, available in:
Bottles of 90: NDC: 25000-186-07
Storage and Handling
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) (see USP Controlled Room Temperature).
Dispense in a tight (USP), child-resistant containers.
Lactation: Breastfeeding is not recommended.
Small amounts of pregabalin have been detected in the milk of lactating women. A pharmacokinetic study in lactating women detected pregabalin in breast milk at average steady state concentrations approximately 76% of those in maternal plasma. The estimated average daily infant dose of pregabalin from breast milk (assuming mean milk consumption of
150 mL/kg/day) was 0.31 mg/kg/day, which on a mg/kg basis would be approximately 7% of the maternal dose (
Based on animal studies, there is a potential risk of tumorigenicity with pregabalin exposure via breast milk to the breastfed infant
A pharmacokinetic study in ten lactating women, who were at least 12 weeks postpartum, evaluated the concentrations of pregabalin in plasma and breast milk. Pregabalin 150 mg oral capsule was given every 12 hours (300 mg daily dose) for a total of four doses. Pregabalin was detected in breast milk at average steady-state concentrations approximately 76% of those in maternal plasma. The estimated average daily infant dose of pregabalin from breast milk (assuming mean milk consumption of 150 mL/kg/day) was 0.31 mg/kg/day, which on a mg/kg basis would be approximately 7% of the maternal dose. The study did not evaluate the effects of pregabalin on milk production. Infants did not receive breast milk obtained during the dosing period, therefore, the effects of pregabalin on the breast fed infant were not evaluated.
Pregabalin capsules are contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to pregabalin or any of its components. Angioedema and hypersensitivity reactions have occurred in patients receiving pregabalin therapy
There have been postmarketing reports of hypersensitivity in patients shortly after initiation of treatment with pregabalin. Adverse reactions included skin redness, blisters, hives, rash, dyspnea, and wheezing. Discontinue pregabalin immediately in patients with these symptoms.