Protriptyline Hydrochloride Prescribing Information
Warnings: Clinical Worsening and Suicide Risk,
PRECAUTIONS: Information for Patients, and
Precautions: Pediatric Use)
Protriptyline hydrochloride tablets are indicated for the
treatment of symptoms of mental depression in patients who are under close
medical supervision. Its activating properties make it particularly suitable for
withdrawn and anergic patients.
Dosage should be initiated at a low level and increased gradually, noting carefully the clinical response and any evidence of intolerance.
Fifteen to 40 mg a day divided into 3 or 4 doses. If necessary, dosage may be increased to 60 mg a day. Dosages above this amount are not recommended. Increases should be made in the morning dose.
In general, lower dosages are recommended for these patients. Five mg 3 times a day may be given initially, and increased gradually if necessary. In elderly patients, the cardiovascular system must be monitored closely if the daily dose exceeds 20 mg.
When satisfactory improvement has been reached, dosage should be reduced to the smallest amount that will maintain relief of symptoms.
Minor adverse reactions require reduction in dosage. Major adverse reactions or evidence of hypersensitivity require prompt discontinuation of the drug.
The safety and effectiveness of protriptyline in pediatric patients have not been established.
Protriptyline hydrochloride tablets are contraindicated in
patients who have shown prior hypersensitivity to it.
It should not be given concomitantly with a monoamine oxidase inhibiting
compound. Hyperpyretic crises, severe convulsions, and deaths have occurred in
patients receiving tricyclic antidepressant and monoamine oxidase inhibiting
drugs simultaneously. When it is desired to substitute protriptyline for a
monoamine oxidase inhibitor, a minimum of 14 days should be allowed to elapse
after the latter is discontinued. Protriptyline should then be initiated
cautiously with gradual increase in dosage until optimum response is
achieved.
Protriptyline is contraindicated in patients taking cisapride because of the
possibility of adverse cardiac interactions including prolongation of the QT
interval, cardiac arrhythmias and conduction system disturbances.
This drug should not be used during the acute recovery phase following
myocardial infarction.
Within each category the following adverse reactions are listed in order of decreasing severity. Included in the listing are a few adverse reactions which have not been reported with this specific drug. However, the pharmacological similarities among the tricyclic antidepressant drugs require that each of the reactions be considered when protriptyline is administered. Protriptyline is more likely to aggravate agitation and anxiety and produce cardiovascular reactions such as tachycardia and hypotension.
To report
www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Protriptyline HCl is N-methyl-5H dibenzo [a,d]-cycloheptene-5-propanamine hydrochloride. Its molecular formula is C
19H
21N•HCl and its structural formula is:
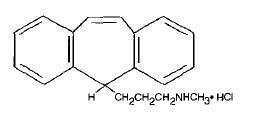
Protriptyline HCl, dibenzocycloheptene derivative, has a molecular weight of 299.84. It is a white to yellowish powder that is freely soluble in water and soluble in dilute HCl. Protriptyline HCl is supplied as 5 mg or 10 mg film-coated tablets. Inactive ingredients are anhydrous lactose, crospovidone, dibasic calcium phosphate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol, talc, titanium dioxide, FD&C Yellow#6, and the 10 mg tablets contain D & C Yellow#10.