Prudoxin - Doxepin Hydrochloride cream
(Doxepin Hydrochloride)Prudoxin - Doxepin Hydrochloride cream Prescribing Information
PRUDOXIN® Cream is indicated for the short-term (up to 8 days) management of moderate pruritus in adult patients with atopic dermatitis or lichen simplex chronicus. (See
A thin film of PRUDOXIN®Cream should be applied four times each day with at least a 3 to 4 hour interval between applications. There are no data to establish the safety and effectiveness of PRUDOXIN®Cream when used for greater than 8 days. Chronic use beyond eight days may result in higher systemic levels and should be avoided. Use of PRUDOXIN®Cream for longer than 8 days may result in an increased likelihood of contact sensitization.
The risk for sedation may increase with greater body surface area application of PRUDOXIN®Cream (See WARNINGSsection). Clinical experience has shown that drowsiness is significantly more common in patients applying PRUDOXIN®Cream to over 10% of body surface area; therefore, patients with greater than 10% of body surface area (see WARNINGSsection) affected should be particularly cautioned concerning possible drowsiness and other systemic adverse effects of doxepin. If excessive drowsiness occurs, it may be necessary to do one or more of the following: reduce the body surface area treated, reduce the number of applications per day, reduce the amount of cream applied, or discontinue the drug.
Occlusive dressings may increase the absorption of most topical drugs; therefore, occlusive dressings should not be utilized with PRUDOXIN®Cream.
A thin film of PRUDOXIN® Cream should be applied four times each day with at least a 3 to 4 hour interval between applications. There are no data to establish the safety and effectiveness of PRUDOXIN® Cream when used for greater than 8 days. Chronic use beyond eight days may result in higher systemic levels and should be avoided. Use of PRUDOXIN® Cream for longer than 8 days may result in an increased likelihood of contact sensitization.
The risk for sedation may increase with greater body surface area application of PRUDOXIN® Cream (See
Drowsiness occurs in over 20% of patients treated with PRUDOXIN®Cream, especially in patients receiving treatment to greater than 10% of their body surface area.
The sedating effects of alcoholic beverages, antihistamines, and other CNS depressants may be potentiated when PRUDOXIN®Cream is used.
If excessive drowsiness occurs it may be necessary to reduce the frequency of applications, the amount of cream applied, and/or the percentage of body surface area treated, or discontinue the drug. However, the efficacy with reduced frequency of applications has not been established.
Keep this product away from the eyes.
Drowsiness occurs in over 20% of patients treated with PRUDOXIN®Cream, especially in patients receiving treatment to greater than 10% of their body surface area.
The sedating effects of alcoholic beverages, antihistamines, and other CNS depressants may be potentiated when PRUDOXIN®Cream is used.
If excessive drowsiness occurs it may be necessary to reduce the frequency of applications, the amount of cream applied, and/or the percentage of body surface area treated, or discontinue the drug. However, the efficacy with reduced frequency of applications has not been established.
Keep this product away from the eyes.
Occlusive dressings may increase the absorption of most topical drugs; therefore, occlusive dressings should not be utilized with PRUDOXIN® Cream.
Because doxepin HCl has an anticholinergic effect and because significant plasma levels of doxepin are detectable after topical PRUDOXIN® Cream application, the use of PRUDOXIN® Cream is contraindicated in patients with untreated narrow angle glaucoma or a tendency to urinary retention.
PRUDOXIN® Cream is contraindicated in individuals who have shown previous sensitivity to any of its components.
These occurred in 76 of 330 (23%) of patients treated with PRUDOXIN® Cream compared to 54 of 334 (16%) of patients treated with vehicle cream. Most of these reactions were categorized as "mild"; however, approximately 25% of patients who reported burning and/or stinging reported the reaction as "severe". Four patients treated with PRUDOXIN® Cream withdrew from the study because of the burning and/or stinging.
The table below presents the adverse events reported at an incidence of ≥ 1 % in either PRUDOXIN® or vehicle cream treatment groups during the trials:
Adverse Event | PRUDOXIN® | Vehicle |
Burning /Stinging | 76 (23.0%) | 54 (16.2%) |
Drowsiness | 71 (21.5%) | 7 (2.1%) |
Dry Mouth1 | 32 (9.7%) | 4 (1.2%) |
Pruritus2 | 13 (3.9%) | 20 (6.0%) |
Fatigue/Tiredness | 10 (3.0%) | 5 (1.5%) |
Exacerbated Eczema | 10 (3.0%) | 8 (2.4%) |
Other Application Site Reaction3 | 10 (3.0%) | 16 (4.8%) |
Dizziness4 | 7 (2.1%) | 3 (0.9%) |
Mental/Emotional Changes | 6 (1.8%) | 1 (0.3%) |
Taste Perversion5 | 5 (1.5%) | 1 (0.3%) |
Edema | 4 (1.2%) | 1 (0.3%) |
Headache | 3 (0.9%) | 14 (4.2%) |
1Includes reports of “dry lips”, “dry throat”, and “thirst” | ||
2Includes reports of “pruritus exacerbated” | ||
3Includes report of “increased irritation at application site” | ||
4Includes reports of “lightheadedness” and “dizziness/vertigo” | ||
5Includes reports of “bitter taste” and “metallic taste in mouth” | ||
Adverse events occurring in 0.5% to < 1.0% of PRUDOXIN® Cream treated patients in the controlled clinical trials included: nervousness/anxiety, tongue numbness, fever, and nausea.
Studies have not been performed examining drug interactions with PRUDOXIN® Cream. However, since plasma levels of doxepin following topical application of PRUDOXIN® Cream can reach levels obtained with oral doxepin HCl therapy, the following drug interactions are possible following topical PRUDOXIN® Cream application:
Poor metabolizers have higher than expected plasma concentrations of tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) when given usual doses. Depending on the fraction of drug metabolized by P450 2D6, the increase in plasma concentration may be small, or quite large (8-fold increase in plasma AUC of the TCA).
In addition, certain drugs inhibit the activity of this isozyme and make normal metabolizers resemble poor metabolizers. An individual who is stable on a given dosage regimen of a TCA may become abruptly toxic when given one of these inhibiting drugs as concomitant therapy. The drugs that inhibit cytochrome P450 2D6 include some that are not metabolized by the enzyme (quinidine; cimetidine) and many that are substrates for P450 2D6 (many other antidepressants, phenothiazines, and the Type 1C antiarrhythmics propafenone and flecainide). While all the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), e.g., fluoxetine, sertraline, and paroxetine, inhibit P450 2D6, they may vary in the extent of inhibition. The extent to which SSRI-TCA interactions may pose clinical problems will depend on the degree of inhibition and the pharmacokinetics of the SSRI involved. Nevertheless, caution is indicated in the co-administration of TCAs with any of the SSRIs. Of particular importance, sufficient time must elapse before initiating TCA treatment in a patient being withdrawn from fluoxetine, given the long half- life of the parent and active metabolite (at least 5 weeks may be necessary).
Concomitant use of tricyclic antidepressants with drugs that can inhibit cytochrome P450 2D6 may require lower doses than usually prescribed for either the tricyclic antidepressant or the other drug. It is desirable to monitor TCA plasma levels whenever a TCA is going to be co-administered with another drug known to be an inhibitor of P450 2D6.
PRUDOXIN® (doxepin hydrochloride) Cream, 5% is a topical cream. Each gram contains: 50 mg of doxepin hydrochloride (equivalent to 44.3 mg of doxepin).
Doxepin hydrochloride, USP is one of a class of agents known as dibenzoxepin tricyclic antidepressant compounds. It is an isomeric mixture of N,N-dimethyldibenz[
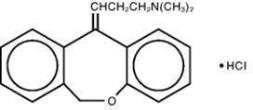
PRUDOXIN® Cream also contains sorbitol, cetyl alcohol, isopropyl myristate, glyceryl stearate, PEG- 100 stearate, petrolatum, benzyl alcohol, titanium dioxide and purified water.