Risedronate Sodium
Risedronate Sodium Prescribing Information
35 mg film-coated, round, orange biconvex tablet, engraved 'APO' on one side, 'RIS' over '35' on the other side.
75 mg film-coated, round, dark pink biconvex tablet, engraved 'APO' on one side, 'RIS' over '75' on the other side.
150 mg film-coated, round, blue biconvex tablet, engraved 'APO' on one side, 'RIS' over '150' on the other side.
Risedronate sodium tablets are contraindicated in patients with the following conditions:
- Abnormalities of the esophagus which delay esophageal emptying such as stricture or achalasia [see Warnings and Precautions ()]
5.2 Upper Gastrointestinal Adverse ReactionsRisedronate sodium tablets, like other bisphosphonates administered orally, may cause local irritation of the upper gastrointestinal mucosa. Because of these possible irritant effects and a potential for worsening of the underlying disease, caution should be used when risedronate sodium is given to patients with active upper gastrointestinal problems (such as known Barrett’s esophagus, dysphagia, other esophageal diseases, gastritis, duodenitis or ulcers) [
see Contraindications , Adverse Reactions , Information for Patients].Esophageal adverse experiences, such as esophagitis, esophageal ulcers and esophageal erosions, occasionally with bleeding and rarely followed by esophageal stricture or perforation, have been reported in patients receiving treatment with oral bisphosphonates. In some cases, these have been severe and required hospitalization. Physicians should therefore be alert to any signs or symptoms signaling a possible esophageal reaction and patients should be instructed to discontinue risedronate sodium tablets and seek medical attention if they develop dysphagia, odynophagia, retrosternal pain or new or worsening heartburn.
The risk of severe esophageal adverse experiences appears to be greater in patients who lie down after taking oral bisphosphonates and/or who fail to swallow it with the recommended full glass (6 to 8 ounces) of water, and/or who continue to take oral bisphosphonates after developing symptoms suggestive of esophageal irritation. Therefore, it is very important that the full dosing instructions are provided to, and understood by, the patient [
see Dosage and Administration]. In patients who cannot comply with dosing instructions due to mental disability, therapy with risedronate sodium tablets should be used under appropriate supervision.There have been post-marketing reports of gastric and duodenal ulcers with oral bisphosphonate use, some severe and with complications, although no increased risk was observed in controlled clinical trials.
- Inability to stand or sit upright for at least 30 minutes [see Dosage and Administration (), Warnings and Precautions (
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATIONTreatment of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis: 5 mg daily, 35 mg once-a-week, 75 mg two consecutive days each month, 150 mg once-a-month
Prevention of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis: 5 mg daily, 35 mg once-a-week
Men with Osteoporosis: 35 mg once-a-week
Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis: 5 mg daily
Paget's Disease: 30 mg daily for 2 months
Instruct patients to:
- Swallow tablet whole with 6 to 8 ounces of plain water, at least 30 minutes before the first food, beverage, or medication of the day.
- Avoid lying down for 30 minutes
- Take supplemental calcium and vitamin D if dietary intake is inadequate
2.1 Treatment of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis [see Indications and Usage (1.1)]The recommended regimen is:
- one 5 mg tablet orally, taken daily
or
- one 35 mg tablet orally, taken once-a-week
or
- one 75 mg tablet orally, taken on two consecutive days for a total of two tablets each month
or
- one 150 mg tablet orally, taken once-a-month
2.2 Prevention of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis [see Indications and Usage (1.1)]The recommended regimen is:
• one 5 mg tablet orally, taken daily
or
• one 35 mg tablet orally, taken once-a-week
or
• alternatively, one 75 mg tablet orally, taken on two consecutive days for a total of two tablets each month may be considered
or
• alternatively, one 150 mg tablet orally, taken once-a-month may be considered
2.3 Treatment to Increase Bone Mass in Men with Osteoporosis [see Indications and Usage (1.2)]The recommended regimen is:
• one 35 mg tablet orally, taken once-a-week2.4 Treatment and Prevention of Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis [see Indications and Usage (1.3)]The recommended regimen is:
• one 5 mg tablet orally, taken daily
2.5 Treatment of Paget's Disease [see Indications and Usage (1.4)]The recommended treatment regimen is 30 mg orally once daily for 2 months. Retreatment may be considered (following post-treatment observation of at least 2 months) if relapse occurs, or if treatment fails to normalize serum alkaline phosphatase. For retreatment, the dose and duration of therapy are the same as for initial treatment. No data are available on more than 1 course of retreatment.
2.6 Important Administration InstructionsInstruct patients to do the following:
- Take risedronate sodium tablets at least 30 minutes before the first food or drink of the day other than water, and before taking any oral medication or supplementation, including calcium, antacids, or vitamins to maximize absorption and clinical benefit, [see Drug Interactions]. Avoid the use of water with supplements, including mineral water, because they may have a higher concentration of calcium.
- Swallow risedronate sodium tablets whole with a full glass of plain water (6 to 8 ounces). Avoid lying down for 30 minutes after taking the medication [see Warnings and Precautions]. Do not chew or suck the tablet because of a potential for oropharyngeal ulceration.
- Do not eat or drink anything except plain water, or take other medications for at least 30 minutes after taking risedronate sodium tablets.
2.7 Recommendations for Calcium and Vitamin D SupplementationInstruct patients to take supplemental calcium and vitamin D if their dietary intake is inadequate; and to take calcium supplements, antacids, magnesium-based supplements or laxatives, and iron preparations at a different time of the day as they interfere with the absorption of risedronate sodium tablets.
2.8 Administration Instructions for Missed DosesInstruct patients about missing risedronate sodium tablet doses as follows:
- If a dose of risedronate sodium tablet 35 mg once-a-week is missed:
- Take 1 tablet on the morning after they remember and return to taking 1 tablet once-a-week, as originally scheduled on their chosen day.
- Do not take 2 tablets on the same day.
- If one or both tablets of risedronate sodium tablets 75 mg on two consecutive days per month are missed, and the next month’s scheduled doses are more than 7 days away:
- If both tablets are missed, take one risedronate sodium 75 mg tablet in the morning after the day it is remembered and then the other tablet on the next consecutive morning.
- If only one risedronate sodium 75 mg tablet is missed, take the missed tablet in the morning after the day it is remembered
- Return to taking their risedronate sodium 75 mg tablets on two consecutive days per month as originally scheduled.
- Do not take more than two 75 mg tablets within 7 days.
- If one or both tablets of risedronate sodium 75 mg tablets on two consecutive days per month are missed, and the next month's scheduled doses are within 7 days:
- Wait until their next month’s scheduled doses and then continue taking risedronate sodium 75 mg tablets on two consecutive days per month as originally scheduled.
- If the dose of risedronate sodium tablets 150 mg once-a-month is missed, and the next month’s scheduled dose is more than 7 days away:
- Take the missed tablet in the morning after the day it is remembered and then return to taking their risedronate sodium tablet 150 mg once-a-month as originally scheduled.
- Do not take more than one 150 mg tablet within 7 days.
- If the dose of risedronate sodium 150 mg tablet once-a-month is missed, and the next month's scheduled dose is within 7 days:
- Wait until their next month’s scheduled dose and then continue taking risedronate sodium 150 mg tablets once-a-month as originally scheduled.
)]5.2 Upper Gastrointestinal Adverse ReactionsRisedronate sodium tablets, like other bisphosphonates administered orally, may cause local irritation of the upper gastrointestinal mucosa. Because of these possible irritant effects and a potential for worsening of the underlying disease, caution should be used when risedronate sodium is given to patients with active upper gastrointestinal problems (such as known Barrett’s esophagus, dysphagia, other esophageal diseases, gastritis, duodenitis or ulcers) [
see Contraindications , Adverse Reactions , Information for Patients].Esophageal adverse experiences, such as esophagitis, esophageal ulcers and esophageal erosions, occasionally with bleeding and rarely followed by esophageal stricture or perforation, have been reported in patients receiving treatment with oral bisphosphonates. In some cases, these have been severe and required hospitalization. Physicians should therefore be alert to any signs or symptoms signaling a possible esophageal reaction and patients should be instructed to discontinue risedronate sodium tablets and seek medical attention if they develop dysphagia, odynophagia, retrosternal pain or new or worsening heartburn.
The risk of severe esophageal adverse experiences appears to be greater in patients who lie down after taking oral bisphosphonates and/or who fail to swallow it with the recommended full glass (6 to 8 ounces) of water, and/or who continue to take oral bisphosphonates after developing symptoms suggestive of esophageal irritation. Therefore, it is very important that the full dosing instructions are provided to, and understood by, the patient [
see Dosage and Administration]. In patients who cannot comply with dosing instructions due to mental disability, therapy with risedronate sodium tablets should be used under appropriate supervision.There have been post-marketing reports of gastric and duodenal ulcers with oral bisphosphonate use, some severe and with complications, although no increased risk was observed in controlled clinical trials.
- Hypocalcemia [see Warnings and Precautions ()]
5.3 Mineral MetabolismHypocalcemia has been reported in patients taking risedronate sodium tablets. Treat hypocalcemia and other disturbances of bone and mineral metabolism before starting risedronate sodium tablets therapy. Instruct patients to take supplemental calcium and vitamin D if their dietary intake is inadequate. Adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D is important in all patients, especially in patients with Paget’s disease in whom bone turnover is significantly elevated [
see Contraindications , Adverse Reactions , Information for Patients]. - Known hypersensitivity to risedronate sodium tablets or any of its excipients. Angioedema, generalized rash, bullous skin reactions, Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis have been reported [see Adverse Reactions ()]
6.2 Postmarketing ExperienceBecause these adverse reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Hypersensitivity ReactionsHypersensitivity and skin reactions have been reported, including angioedema, generalized rash, bullous skin reactions, Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis.
Gastrointestinal Adverse EventsEvents involving upper gastrointestinal irritation, such as esophagitis and esophageal or gastric ulcers, have been reported
[see Warnings and Precautions ].Musculoskeletal PainBone, joint, or muscle pain, described as severe or incapacitating, have been reported rarely
[see Warnings and Precautions ].Eye InflammationReactions of eye inflammation including iritis and uveitis have been reported rarely.
Jaw OsteonecrosisOsteonecrosis of the jaw has been reported rarely
[see Warnings and Precautions ].PulmonaryAsthma exacerbations
No specific drug-drug interaction studies were performed. Risedronate is not metabolized and does not induce or inhibit hepatic microsomal drug-metabolizing enzymes (for example, Cytochrome P450).
No specific drug-drug interaction studies were performed. Risedronate is not metabolized and does not induce or inhibit hepatic microsomal drug-metabolizing enzymes (for example, Cytochrome P450).
Calcium, antacids, or oral medications containing divalent cations interfere with the absorption of risedronate sodium
Co-administration of risedronate sodium tablets and calcium, antacids, or oral medications containing divalent cations will interfere with the absorption of risedronate sodium tablets.
One study of about 500 early postmenopausal women has been conducted to date in which treatment with risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily plus estrogen replacement therapy was compared to estrogen replacement therapy alone. Exposure to study drugs was approximately 12 to 18 months and the primary endpoint was change in BMD. If considered appropriate, risedronate sodium tablets may be used concomitantly with hormone replacement therapy.
Of over 5700 patients enrolled in the risedronate sodium tablets Phase 3 osteoporosis studies, aspirin use was reported by 31% of patients, 24% of whom were regular users (3 or more days per week). Forty-eight percent of patients reported NSAID use, 21% of whom were regular users. Among regular aspirin or NSAID users, the incidence of upper gastrointestinal adverse experiences in placebo-treated patients (24.8%) was similar to that in risedronate sodium-treated patients (24.5%).
Of over 5700 patients enrolled in the risedronate sodium tablets Phase 3 osteoporosis studies, 21% used H2blockers and/or PPIs. Among these patients, the incidence of upper gastrointestinal adverse experiences in the placebo-treated patients was similar to that in risedronate sodium-treated patients.
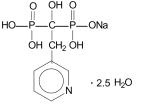
Risedronate sodium tablets, USP are pyridinyl bisphosphonates that inhibit osteoclast-mediated bone resorption and modulate bone metabolism. Each risedronate sodium tablet, USP for oral administration contains the equivalent of 35, 75, or 150 mg of anhydrous risedronate sodium in the form of the hemi-pentahydrate. The empirical formula for risedronate sodium hemi-pentahydrate is C7H10NO7P2Na •2.5 H2O. The chemical name of risedronate sodium is [1-hydroxy-2-(3-pyridinyl)ethylidene]bis[phosphonic acid] monosodium salt. The chemical structure of risedronate sodium hemi-pentahydrate is the following:
Molecular Weight:
Anhydrous: 305.10
Hemi-pentahydrate: 350.13
Risedronate sodium, USP is a white powder. It is soluble in water and essentially insoluble in common organic solvents.
Risedronate sodium tablets, USP are pyridinyl bisphosphonates that inhibit osteoclast-mediated bone resorption and modulate bone metabolism. Each risedronate sodium tablet, USP for oral administration contains the equivalent of 35, 75, or 150 mg of anhydrous risedronate sodium in the form of the hemi-pentahydrate. The empirical formula for risedronate sodium hemi-pentahydrate is C7H10NO7P2Na •2.5 H2O. The chemical name of risedronate sodium is [1-hydroxy-2-(3-pyridinyl)ethylidene]bis[phosphonic acid] monosodium salt. The chemical structure of risedronate sodium hemi-pentahydrate is the following:

Molecular Weight:
Anhydrous: 305.10
Hemi-pentahydrate: 350.13
Risedronate sodium, USP is a white powder. It is soluble in water and essentially insoluble in common organic solvents.
All dose strengths contain: anhydrous lactose, crospovidone, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, polyethylene glycol, silicon dioxide, and titanium dioxide.
Dose strength-specific ingredients include: 35 mg—ferric oxide red, ferric oxide yellow; 75 mg—ferric oxide red; 150 mg -FD&C blue #2, sodium phosphate monobasic monohydrate, sodium phosphate dibasic.
All dose strengths contain: anhydrous lactose, crospovidone, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, polyethylene glycol, silicon dioxide, and titanium dioxide.
Dose strength-specific ingredients include: 35 mg—ferric oxide red, ferric oxide yellow; 75 mg—ferric oxide red; 150 mg -FD&C blue #2, sodium phosphate monobasic monohydrate, sodium phosphate dibasic.
The fracture efficacy of risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis was demonstrated in 2 large, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind studies that enrolled a total of almost 4000 postmenopausal women under similar protocols. The Multinational study (VERT MN) ( risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg, N = 408) was conducted primarily in Europe and Australia; a second study was conducted in North America (VERT NA) ( risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg, N = 821). Patients were selected on the basis of radiographic evidence of previous vertebral fracture, and therefore, had established disease. The average number of prevalent vertebral fractures per patient at study entry was 4 in VERT MN, and 2.5 in VERT NA, with a broad range of baseline BMD levels. All patients in these studies received supplemental calcium 1000 mg/day. Patients with low 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 levels (approximately 40 nmol/L or less) also received supplemental vitamin D 500 international units/day.
Fractures of previously undeformed vertebrae (new fractures) and worsening of pre-existing vertebral fractures were diagnosed radiographically; some of these fractures were also associated with symptoms (that is, clinical fractures). Spinal radiographs were scheduled annually and prospectively planned analyses were based on the time to a patient’s first diagnosed fracture. The primary endpoint for these studies was the incidence of new and worsening vertebral fractures across the period of 0 to 3 years. Risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily significantly reduced the incidence of new and worsening vertebral fractures and of new vertebral fractures in both VERT NA and VERT MN at all time points (Table 3). The reduction in risk seen in the subgroup of patients who had 2 or more vertebral fractures at study entry was similar to that seen in the overall study population.
Proportion of Patients with Fracture (%)Calculated by Kaplan-Meier methodology. | ||||
VERT MN | Placebo N = 678 | Risedronate Sodium Tablets 5 mg N = 696 | Absolute Risk Reduction (%) | Relative Risk Reduction (%) |
| New and Worsening | ||||
| 0 - 1 Year | 7.2 | 3.9 | 3.3 | 49 |
| 0 - 2 Years | 12.8 | 8.0 | 4.8 | 42 |
| 0 - 3 Years | 18.5 | 13.9 | 4.6 | 33 |
| New | ||||
| 0 - 1 Year | 6.4 | 2.4 | 4.0 | 65 |
| 0 - 2 Years | 11.7 | 5.8 | 5.9 | 55 |
| 0 - 3 Years | 16.3 | 11.3 | 5.0 | 41 |
VERT MN | Placebo N = 346 | Risedronate Sodium Tablets 5 mg N = 344 | Absolute Risk Reduction (%) | Relative Risk Reduction (%) |
| New and Worsening | ||||
| 0 - 1 Year | 15.3 | 8.2 | 7.1 | 50 |
| 0 - 2 Years | 28.3 | 13.9 | 14.4 | 56 |
| 0 - 3 Years | 34.0 | 21.8 | 12.2 | 46 |
| New | ||||
| 0 - 1 Year | 13.3 | 5.6 | 7.7 | 61 |
| 0 - 2 Years | 24.7 | 11.6 | 13.1 | 59 |
| 0 - 3 Years | 29.0 | 18.1 | 10.9 | 49 |
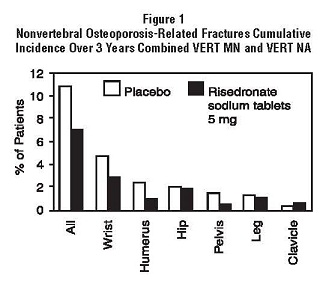
In VERT MN and VERT NA, a prospectively planned efficacy endpoint was defined consisting of all radiographically confirmed fractures of skeletal sites accepted as associated with osteoporosis. Fractures at these sites were collectively referred to as osteoporosis-related nonvertebral fractures. Risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily significantly reduced the incidence of nonvertebral osteoporosis-related fractures over 3 years in VERT NA (8% versus 5%; relative risk reduction 39%) and reduced the fracture incidence in VERT MN from 16% to 11%. There was a significant reduction from 11% to 7% when the studies were combined, with a corresponding 36% reduction in relative risk. Figure 1 shows the overall results as well as the results at the individual skeletal sites for the combined studies.
| VERT MNb | VERT NAb | BMD MNc | BMD NAc | |||||
| Placebo N = 323 | 5 mg N = 323 | Placebo N = 599 | 5 mg N = 606 | Placebo N = 161 | 5 mg N = 148 | Placebo N = 191 | 5 mg N = 193 | |
| Lumbar Spine | 1.0 | 6.6 | 0.8 | 5.0 | 0.0 | 4.0 | 0.2 | 4.8 |
| Femoral Neck | -1.4 | 1.6 | -1.0 | 1.4 | -1.1 | 1.3 | 0.1 | 2.4 |
| Femoral Trochanter | -1.9 | 3.9 | -0.5 | 3.0 | -0.6 | 2.5 | 1.3 | 4.0 |
| Midshaft Radius | -1.5* | 0.2* | -1.2* | 0.1* | ND | ND | ||
a The endpoint value is the value at the study's last time point for all patients who had BMD measured at that time; otherwise the last post-baseline BMD value prior to the study's last time point is used.
b The duration of the studies was 3 years.
c The duration of the studies was 1.5 to 2 years.
* BMD of the midshaft radius was measured in a subset of centers in VERT MN (placebo, N = 222; 5 mg, N = 214) and VERT NA (placebo, N = 310; 5 mg, N = 306).
ND = analysis not done
Risedronate sodium tablets 35 mg once-a-week (N = 485) was shown to be non-inferior to risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily (N = 480) in a 1-year, double-blind, multicenter study of postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. In the primary efficacy analysis of completers, the mean increases from baseline in lumbar spine BMD at 1 year were 4.0% (3.7, 4.3; 95% confidence interval [CI]) in the 5 mg daily group (N = 391) and 3.9% (3.6, 4.3; 95% CI) in the 35 mg once-a-week group (N = 387) and the mean difference between 5 mg daily and 35 mg once-a-week was 0.1% (-0.4, 0.6; 95% CI). The results of the intent-to-treat analysis with the last observation carried forward were consistent with the primary efficacy analysis of completers. The 2 treatment groups were also similar with regard to BMD increases at other skeletal sites.
In a double-blind, multicenter study of postmenopausal women with osteoporosis, treatment with risedronate sodium tablets 75 mg two consecutive days per month (N = 616) was shown to be non-inferior to risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily (N = 613). In the primary efficacy analysis of completers, the mean increases from baseline in lumbar spine BMD at 1 year were 3.6% (3.3, 3.9; 95% CI) in the 5 mg daily group (N = 527) and 3.4% (3.1, 3.7; 95% CI) in the 75 mg two days per month group (N = 524) with a mean difference between groups being 0.2% (-0.2, 0.6; 95% CI). The results of the intent-to-treat analysis with the last observation carried forward were consistent with the primary efficacy analysis of completers. The 2 treatment groups were also similar with regard to BMD increases at other skeletal sites.
Risedronate sodium tablets 150 mg once-a-month (N = 650) was shown to be non-inferior to risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily (N = 642) in a 1-year, double-blind, multicenter study of postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. The primary efficacy analysis was conducted in all randomized patients with baseline and post-baseline lumbar spine BMD values (modified intent-to-treat population) using last observation carried forward. The mean increases from baseline in lumbar spine BMD at 1 year were 3.4% (3.0, 3.8; 95% CI) in the 5 mg daily group (N = 561), and 3.5% (3.1, 3.9; 95% CI) in the 150 mg once-a-month group (N = 578) with a mean difference between groups being -0.1% (-0.5, 0.3; 95% CI). The results of the completers analysis were consistent with the primary efficacy analysis. The 2 treatment groups were also similar with regard to BMD increases at other skeletal sites.
Bone biopsies from 110 postmenopausal women were obtained at endpoint. Patients had received placebo or daily risedronate sodium tablets (2.5 mg or 5 mg) for 2 to 3 years. Histologic evaluation (N = 103) showed no osteomalacia, impaired bone mineralization, or other adverse effects on bone in risedronate sodium-treated women. These findings demonstrate that bone formed during risedronate sodium tablets administration is of normal quality. The histomorphometric parameter mineralizing surface, an index of bone turnover, was assessed based upon baseline and post-treatment biopsy samples from 21 treated with placebo and 23 patients treated with risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg. Mineralizing surface decreased moderately in risedronate sodium-treated patients (median percent change: placebo, -21%; risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg, -74%), consistent with the known effects of treatment on bone turnover.
In the two 3-year osteoporosis treatment studies, standing height was measured yearly by stadiometer. Both risedronate sodium and placebo-treated groups lost height during the studies. Patients who received risedronate sodium tablets had a statistically significantly smaller loss of height than those who received placebo. In VERT MN, the median annual height change was -2.4 mm/yr in the placebo group compared to -1.3 mm/yr in the risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily group. In VERT NA, the median annual height change was -1.1 mm/yr in the placebo group compared to -0.7 mm/yr in the risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily group.
Risedronate Sodium Tablets, USP are available as follows:
35 mg film-coated, round, orange biconvex tablet, engraved ‘APO’ on one side, ‘RIS’ over ‘35’ on the other side
NDC 60505-3165-0 dose pack of 4
NDC 60505-3165-2 dose pack of 12
75 mg film-coated, round, dark pink biconvex tablet, engraved ‘APO’ on one side, ‘RIS’ over ‘75’ on the other side
NDC 60505-3096-2 dose pack of 2
150 mg film-coated, round, blue biconvex tablet, engraved ‘APO’ on one side, ‘RIS’ over ‘150’ on the other side
NDC 60505-3097-2 dose pack of 1
NDC 60505-3097-4 dose pack of 3
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].